|
phoxim
Insecticide
IRAC 1B; organophosphate
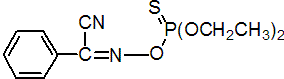
NOMENCLATURE
Common name phoxim (BSI, E-ISO, ESA); phoxime ((f) F-ISO)
IUPAC name O,O-diethyl a-cyanobenzylideneamino-oxyphosphonothioate; 2-(diethoxyphosphinothioyloxyimino)-2-phenylacetonitrile
Chemical Abstracts name 4-ethoxy-7-phenyl-3,5-dioxa-6-aza-4-phosphaoct-6-ene-8-nitrile 4-sulfide
CAS RN [14816-18-3] EEC no. 238-887-3 Development codes BAY 5621; Bayer 77 488; BAY SRA 7502 (all Bayer) Official codes OMS 1170
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 298.3 M.f. C12H15N2O3PS Form Yellow liquid; (tech., reddish-brown oil). M.p. <-23 °C B.p. Decomposes on distillation V.p. 1.80 ´ 10-1 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 4.104 (unbuffered water) Henry 1.58 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.18 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 3.4 mg/l (20 ºC). In xylene, isopropanol, polyethyleneglycol, n-octanol, ethyl acetate, dimethylsulfoxide, dichloromethane, acetonitrile and acetone >250 g/l, n-heptane 136 g/l. Stability Relatively slowly hydrolysed; DT50 (est.) 26.7 d (pH 4), 7.2 d (pH 7), 3.1 d (pH 9) (22 ºC). Gradually decomposed under u.v. irradiation.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by A. Wybou & I. Hammann (Meded. Rijksfac. Landbouwwet. Gent, 1968, 33, 817). Introduced by Bayer AG in 1970. Patents BE 678139; DE 1238902 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide with contact and stomach action. Short duration of activity. Uses Control of stored-product insects in granaries, mills, silos, ships, etc.; ants and other insects in households and in public health; caterpillars (mainly Spodoptera spp.) and soil insects in maize, vegetables, potatoes, beet and cereals, at 5 kg/ha; also migratory locusts. Phytotoxicity May exhibit some phytotoxicity to cotton. Formulation types DP; EC; GR; KN; UL; WP; Seed treatment. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Baythion' (public health) (Bayer CropScience); 'Volaton' (agricultural use) (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Valexon' (Bayer CropScience); 'Volathion' (Bayer CropScience) mixtures: 'Mieling' (+ deltamethrin) (Zhong-Xi); 'Pre Ling' (+ fenvalerate) (Zhong-Xi); 'Yuzhouxing' (+ ZXI 8901) (Zhong-Xi)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc (CIPAC Handbook, 1985, 1C, 2187); details available from Bayer CropScience. Residues determined by glc (Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, 6, S19; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M2, M12; A. Ambrus et. al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1981, 64, 733). Methods for the determination of residues are available from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews JECFA 52 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 ml/kg. Not irritating to eyes or skin (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >4.0 mg/l air (aerosol). NOEL (2 y) for rats 15, mice 1 mg/kg diet; (1 y) for male dogs 0.3, female dogs 0.1 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.004 mg/kg b.w. [1999]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R22
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LD50 for hens 40 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.53, bluegill sunfish 0.22 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.00081 mg/l (80% premix). Bees Toxic to bees by contact and respiratory action.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Rapidly metabolised in the mouse to diethylphosphoric acid and desethyl phoxim. There is also unusually rapid metabolism of the oxon, and the nitrile group is also metabolised to phoxim carboxylic acid. Elimination is very quick; almost 97% is excreted within 24 h in the urine and faeces. Plants In cotton, photochemical degradation and metabolism involve isomerisation to O,O-diethyl S-a-cyanobenzylideneaminothiophosphonoate and tetraethyl diphosphate. Soil/Environment In soil, photochemical isomerisation occurs to diethoxyphosphorylthioiminophenylacetonitrile. Tetraethyl diphosphate and tetraethyl phosphorodithioate are further metabolites. Degradation in soil is very rapid. For further details, see G. Draeger (Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. Bayer, 1977, 30, 28).
|