|
phosmet
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 1B; organophosphate
NOMENCLATURE
Common name phosmet (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ESA); phtalofos (USSR); PMP (JMAF)
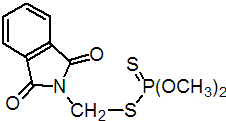
IUPAC name O,O-dimethyl S-phthalimidomethyl phosphorodithioate; N-(dimethoxyphosphinothioylthiomethyl)phthalimide
Chemical Abstracts name S-[(1,3-dihydro-1,3-dioxo-2H-isoindol-2-yl)methyl] O,O-dimethyl phosphorodithioate
CAS RN [732-11-6] EEC no. 211-987-4 Development codes R-1504 (Stauffer) Official codes OMS 232; ENT 25 705
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. material is 92% pure. Mol. wt. 317.3 M.f. C11H12NO4PS2 Form Colourless crystals; (tech., off-white or pink, waxy solid). M.p. 72.0-72.7 ºC; (tech., 66-69 ºC) V.p. 0.065 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 2.95 Henry 8.25 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) Solubility In water 25 mg/l (25 ºC). In acetone 650, benzene 600, toluene, methyl isobutyl ketone 300, xylene 250, methanol 50, kerosene 5 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Rapidly hydrolysed in alkaline media; relatively stable in acidic conditions; DT50 (20 ºC) 13 d (pH 4.5), <12 h (pH 7), <4 h (pH 8.3). Decomposes rapidly above 100 ºC. Decomposes in sunlight in aqueous solution or on glass plates. F.p. >106 ºC
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by B. A. Butt & J. C. Keller (J. Econ. Entomol., 1961, 54, 813). Introduced by Stauffer Chemical Co. (became Zeneca Agrochemicals) and now marketed by Gowan Company and others. Patents US 2767194 Manufacturers Gowan
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide and acaricide with predominantly contact action. Uses Control of lepidopterous larvae, aphids, suckers, fruit flies, and spider mites on pome fruit, stone fruit, citrus fruit, ornamentals and vines; Colorado beetles on potatoes; boll weevils on cotton; olive moths and olive thrips on olives; blossom beetles on oilseed rape; leaf beetles and weevils on alfalfa; European corn borers on maize and sorghum; sweet potato weevils on sweet potatoes in storage; etc., at 0.5-1.0 kg/ha. Also used as an animal ectoparasiticide. Formulation types DP; EC; SL; WP. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Fosdan' (General Quimica); 'Imidan' (Gowan); 'Inovitan' (Efthymiadis); 'Prolate' (Gowan)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Cekumet' (Cequisa); 'Fosmedan' (Papaeconomou) Discontinued products: 'Inovat' * (Productos OSA)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by capillary gc. Residues in crops determined by capillary gc (M. A. Luke et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1981, 64, 1187; G. H. Batchelder et al., Anal. Methods Pestic., Plant Growth Regul. Food. Addit., 1967, 5, 257; J. E. Barney et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1972, 6, 408). Details available from Gowan Co.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 83, 85 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 113, female rats 160 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for albino rabbits >5000 mg/kg; mild skin and eye irritant (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for male and female rats 1.6 mg 70% WP/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats and dogs 40 mg/kg diet. Not carcinogenic or teratogenic. ADI (JMPR) 0.01 mg/kg b.w. [1998]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II EC classification Xn; R21/22
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail 507, mallard ducks >5000 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 0.07, rainbow trout 0.23 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 8.5 mg/l. Bees LD50 0.001 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals In animals, rapid metabolism occurs to phthalamic acid, phthalic acid, and phthalic acid derivatives, which have been isolated from urine as phosmet metabolites (J. B. McBain et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1968, 16, 813-820). Plants In plants, phosmet is rapidly broken down to non-toxic metabolites. Soil/Environment Rapidly broken down in the soil.
|