|
phosalone
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 1B; organophosphate
NOMENCLATURE
Common name phosalone (BSI, E-ISO, (f) F-ISO, ANSI, ESA, JMAF); benzofos* (former exception, USSR)
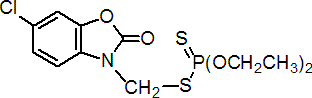
IUPAC name S-6-chloro-2,3-dihydro-2-oxobenzoxazol-3-ylmethyl O,O-diethyl phosphorodithioate
Chemical Abstracts name S-[(6-chloro-2-oxo-3(2H)-benzoxazolyl)methyl] O,O-diethyl phosphorodithioate
Other names benzphos CAS RN [2310-17-0] EEC no. 218-996-2 Development codes 11 974 RP (Rhône-Poulenc); NPH 1090 Official codes ENT 27 163
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 367.8 M.f. C12H15ClNO4PS2 Form Colourless crystals, with an odour of garlic. M.p. 42-48 °C (tech.) V.p. <0.06 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 4.01 (20 ºC) Henry 7.4 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.338 g/ml (20 ºC) Solubility In water 3.05 mg/l (25 ºC). In ethyl acetate, acetone, acetonitrile, benzene, chloroform, dichloromethane, dioxane, methyl ethyl ketone, toluene, xylene c. 1000, hexane 11 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Hydrolysed by strong alkalis and acids; DT50 9 d (pH 9).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by J. Desmoras et al. (Phytiatr. Phytopharm., 1963, 12, 199). Introduced by Rhône-Poulenc Agrochimie (now Bayer CropScience). Acquired by Cheminova in 2002. Patents GB 1005372; BE 609209; FR 1482025 Manufacturers Jiangsu Eternal
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide and acaricide showing localised penetration of plant cuticle; with contact and stomach action. Uses A non-systemic acaricide and insecticide used primarily in pome and stone fruit trees. Effective against Coleoptera, Homoptera (Aphididae), Lepidoptera (Cydia pomonella) and Thysanoptera on fruit trees. It is selective of most beneficial insects and widely used in integrated pest management programmes. Also used in grapes, oilseed rape, ornamentals, potatoes and vegetables. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic when used at the recommended application rates. At higher application rates, Golden Delicious and other yellow apple varieties have been injured. Formulation types EC; SC; WP.
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Azofene' (Cheminova, Bayer CropScience); 'Rubitox' (Cheminova, Bayer CropScience); 'Thimulone' (Cheminova, Bayer CropScience); 'Zolone' (Cheminova, Bayer CropScience); 'Fosatox' (Sepran)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc (CIPAC Handbook, 1988, D, 141). Residues determined by glc (A. Ambrus et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1981, 64, 733; Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, 5, 6, S8, S19; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M2, M5, M12).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 80, 82, 92, 94 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 120 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats 1500 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for female rats 0.7 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for rats 2.5 mg/kg b.w. ADI (JMPR) 0.02 mg/kg b.w. [1997, 2001]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II EC classification T; R25| Xn; R21| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >2150 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail 2033, mallard ducks 1659 ppm diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.63, carp 2.1 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 0.74 mg/l. Algae Low toxicity. Worms Moderately toxic.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals Rapidly eliminated, primarily via urine. Plants Rapidly degraded via oxidation, cleavage, hydrolysis and dechlorination. Soil/Environment Low mobility in soils; strongly adsorbed and rapidly degraded; DT50 c. 1-4 d.
|