|
phorate
Insecticide, acaricide, nematicide
IRAC 1B; organophosphate
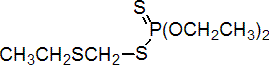
NOMENCLATURE
Common name phorate (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, ESA); timet* (former exception, USSR)
IUPAC name O,O-diethyl S-ethylthiomethyl phosphorodithioate
Chemical Abstracts name O,O-diethyl S-[(ethylthio)methyl] phosphorodithioate
CAS RN [298-02-2] EEC no. 206-052-2 Development codes EI 3911; AC 3911 (both Cyanamid) Official codes ENT 24 042
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. phorate is >90% pure. Mol. wt. 260.4 M.f. C7H17O2PS3 Form Colourless liquid (tech.). M.p. <-15 ºC (tech.) B.p. 118-120 ºC/0.8 mmHg (tech.) V.p. 85 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 3.92 Henry 5.9 ´ 10-1 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.167 (tech., 25 ºC) Solubility In water 50 mg/l (25 ºC). Miscible with alcohols, ketones, ethers, esters, aromatic, aliphatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons, dioxane, vegetable oils, and other organic solvents. Stability Stable under normal storage conditions for at least 2 years. Aqueous solutions degraded by light (DT50 1.1 d); stability to hydrolysis optimum at pH 5-7, DT50 3.2 d (pH 7), 3.9 d (pH 9). F.p. >110 °C (Setaflash closed cup)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Introduced by American Cyanamid Co. (now BASF AG) and first marketed in 1954. Patents US 2586655; US 2596076; US 2970080 (Cyanamid); US 2759010 (Bayer) Manufacturers BASF; Rallis; Sharda; United Phosphorus
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor; activity derives from metabolic conversion to phorate oxon, the phosphorothioate. Mode of action Systemic insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. Uses Control of Agromyzidae, Aleyrodidae, Aphididae, Chrysomelidae, Noctuidae, Pyralidae, Tetranychidae and certain nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.) in brassicas, beetroot, sugar beet, fodder beet, carrots, field beans, broad beans, celery, maize, sorghum, wheat, potatoes, tomatoes, hops, soya beans, sunflowers, sugar cane, alfalfa, cotton, coffee, rice, peanuts, and some ornamentals. Applied at 0.66-3.5 lb/a. Phytotoxicity Phytotoxic to apples and tobacco. Phytotoxicity is possible in beet, carrots, beans, maize, and tomatoes if granules come into direct contact with seeds in the furrow. Formulation types GR. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline compounds and with water-containing preparations. Selected products: 'Thimet' (BASF); 'Cekuforatox' (Cequisa); 'Dhan' (Dhanuka); 'Dragnet' (Crop Health); 'Kurunai' (Ramcides); 'Umet' (United Phosphorus); 'Volphor' (Ralchem)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Agrimet' (BASF); 'Geomet' (BASF); 'Granutox' (BASF, Aimco); 'Foratox' (Pesticides India); 'Phoramate' (BEC); 'Rampart' (Platte); 'Vegfru Foratox' (Pesticides India) mixtures: 'Holdem' (+ ethoprophos) (Bayer CropScience) Discontinued products: 'Terrathion' * (FCC); 'Warrant' * (Searle India)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by i.r. spectrometry (CIPAC Handbook, 1983, 1B, 1890; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 964.05). Residues of phorate and its oxidation products determined by glc (Pestic. Anal. Man., 1979, I, 201-A, 201-G, 201-H, 201-I; Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, 3, 6, S8, S13, S16, S17, S19; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M2, M5; Analyst (London), 1980,105, 515; A. Ambrus et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1981, 64, 733). Details available from BASF.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 77, 79 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 3.7, female rats 1.6, mice c. 6 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male rats 6.2, female rats 2.5, guinea pigs 20-30, male rabbits 5.6, female rabbits 2.9 mg/kg. Values for GR depend on a.i. content, carrier, test method and animal species - typical values include: male rats 98-137 mg a.i. (as GR)/kg, male rabbits 93-245 mg a.i. (as GR)/kg. Inhalation LC50 (1 h) for male rats 0.06, female rats 0.011 mg/l. NOEL In 90 d feeding trials, rats receiving 6 mg/kg diet showed no ill-effects other than depression of cholinesterase levels. ADI (JMPR) 0.0005 mg/kg b.w. [1996]. Other Not mutagenic, not teratogenic, not carcinogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ia; EPA (formulation) I EC classification T+; R27/28
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks 0.62, ring-necked pheasants 7.1 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.013, channel catfish 0.28 mg/l. Bees Toxic to bees; LD50 (topical) 10 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals In animals, phorate is metabolically oxidised to the sulfoxide and sulfone, and their phosphorothioate analogues, followed by hydrolysis to dithio-, thio-, and orthophosphoric acids. Plants Degradation is similar to that in animals. Soil/Environment In soil, metabolic oxidation gives the sulfoxide and sulfone, and their phosphorothioate analogues, and these then undergo hydrolysis, although the sulfone can persist under certain conditions (D. L. Suett, Pestic. Sci., 1975, 6, 385). Soil DT50 c. 7-10 d. Soil Koc 543.
|