|
phenthoate
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 1B; organophosphate
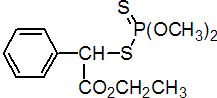
NOMENCLATURE
Common name phenthoate (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO); PAP (JMAF)
IUPAC name S-a-ethoxycarbonylbenzyl O,O-dimethyl phosphorodithioate
Chemical Abstracts name ethyl a-[(dimethoxyphosphinothioyl)thio]benzeneacetate
Other names dimephenthoate CAS RN [2597-03-7] EEC no. 219-997-0 Development codes L 561 (Agrimont); S-2940 (Sumitomo) Official codes OMS 1075; ENT 27 386
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 320.4 M.f. C12H17O4PS2 Form Colourless crystals; (tech., reddish-yellow liquid). M.p. 17-18 ºC B.p. 186-187 °C/5 mmHg V.p. 5.3 mPa (40 ºC) KOW logP = 3.69 S.g./density 1.226 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 10 mg/l (25 °C). Readily soluble in methanol, ethanol, acetone, hexane, xylene, benzene, carbon disulfide, chloroform, dichloromethane, acetonitrile, tetrahydrofuran; in n-hexane 116, kerosene 340 (both in g/l, 25 °C) Stability Decomposes 180 °C. In water, stable under neutral and acidic conditions; degrades under alkaline conditions. F.p. 165-170 ºC
COMMERCIALISATION
History Introduced by Montecatini S.p.A. (now Isagro S.p.A.). Patents GB 834814; US 2947662 Manufacturers Agrochem; Aimco; Hanwha; Nissan; Sharda
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. Uses Control of Aphididae (aphids), Coccidae & Diaspididae (scale insects), Cicadellidae (leafhoppers), Fulgoridae (lantern bugs), Pseudococcidae (mealybugs), Tingidae (lace bugs), Pyrrhocoridae (cotton stainers, red bugs) and Pentatomidae (shield bugs), Thripidae (thrips), Aleyrodidae (whitefly), Noctuidae (bollworms, stem borers), in citrus fruit, pome fruit, olives, Japanese persimmons, chestnuts, mulberries, cotton, cereals, maize, rice, coffee, tea, sunflowers, sugar cane, tobacco, vegetables, cucurbits, and ornamentals, at 40-75 g/hl, 500-1000 g/ha. Also used for mosquito control (adults and larvae). Phytotoxicity Phytotoxic to some varieties of grape, fig, and peach, and red-skinned varieties of apple. Formulation types DP; EC. Compatibility Not compatible with pesticides which are alkaline in reaction. Selected products: 'Cidial' (Isagro); 'Aimsan' (Aimco); 'Elsan' (Nissan); 'Guard' (Crop Health); 'Vifel' (Vipesco)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Tanone' (Isagro); 'Amaze' (Biostadt); 'Genocide' (Agrochem) mixtures: 'Rogodial' (+ dimethoate) (Isagro); 'Vicidi-M' (+ etofenprox) (Vipesco); 'Viphensa' (+ fenobucarb) (Vipesco) Discontinued products: 'Papthion' * (Sumitomo)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc (B. Bazzi et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1976, 8, 159). Residues determined by glc (B. Bazzi et al., loc. cit.; Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, 6, S19; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M11; A. Ambrus et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1981, 64, 733). Details available from Isagro.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 42, 43 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 270, female rats 249, mice 350, dogs >500, guinea pigs 377, rabbits 72 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000, male mice 2620 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 3.17 mg/l air. NOEL (104 w) for dogs 0.29 mg/kg daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.003 mg/kg b.w. [1984]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II EC classification Xn; R21/22
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for pheasants 218, quail 300 mg/kg. Fish TLm (48 h) for carp 2.5, goldfish 2.4 ppm. Bees Toxic to bees. LD50 0.306 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals In mammals, phenthoate is degraded with almost equal facility by hydrolysis of the carboethoxy moiety, cleavage of the P-S or C-S bond and removal of the methoxy group by either direct demethylation or hydrolytic cleavage of the P-O bond. The following metabolites were identified in either urine or faeces: demethyl phenthoate, demethyl phenthoate acid, demethyl phenthoate oxon acid, O,O-dimethyl phosphorodithioic and phosphorothioic acids. Plants In plants, there is oxidation to the phosphorothioate, followed by hydrolysis. Phosphoric acid, dimethyl and monomethyl phosphate have been identified as metabolites. Soil/Environment DT50 £1 d in both upland and submerged soil. The degradation product is phenthoate acid.
|