|
penoxsulam
Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; triazolopyrimidine
NOMENCLATURE
Common name penoxsulam (BSI, pa ISO)
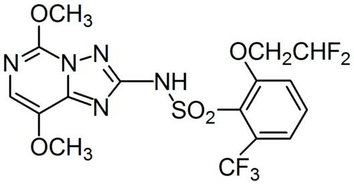
IUPAC name 3-(2,2-difluoroethoxy)-N-(5,8-dimethoxy[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidin-2-yl)-a,a,a-trifluorotoluene-2-sulfonamide; 2-(2,2-difluoroethoxy)-N-(5,8-dimethoxy[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidin-2-yl)-6-(trifluoromethyl)benzenesulfonamide
Chemical Abstracts name 2-(2,2-difluoroethoxy)-N-(5,8-dimethoxy[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidin-2-yl)-6-(trifluoromethyl)benzenesulfonamide
CAS RN [219714-96-2] Development codes DE-638; XDE-638; XR-638; X638177; DASH-001 (all Dow AgroSciences)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Purity 98% nominal. Mol. wt. 483.4 M.f. C16H14F5N5O5S Form Off white solid with a musty odour. M.p. 212 °C V.p. 9.55 ´ 10-11 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = -0.354 (unbuffered water, 19 °C) Henry 2.44 ´ 10-12 Pa m3 mol-1 (unbuffered water, calc.); 2.95 ´ 10-14 Pa m3 mol-1 (pH 7, calc.). S.g./density 1.61 (20 °C) Solubility In water 0.0049 (distilled), 0.00566 (pH 5), 0.408 (pH 7) 1.46 (pH 9) (all in g/l, 19 °C). In acetone 20.3, methanol 1.48, octanol 0.035, DMSO 78.4, NMP 40.3, 1,2-dichlorethane 1.99, acetonitrile 15.3 (all in g/l, 19 °C). Stability Stable to hydrolysis. Photolysis DT50 2 d. Storage stability >2 y. pKa 5.1 Other properties Not flammable or explosive
COMMERCIALISATION
History Under development by Dow AgroSciences LLC as a rice herbicide. Patents US 5828924 Manufacturers Dow AgroSciences
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Branched chain amino acid (leucine, isoleucine and valine) synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Selectivity is based on differential metabolism to inactive metabolites. Mode of action Absorbed via leaves, stems and roots. Symptoms include almost immediate growth inhibition, a chlorotic growing point with necrosis of the terminal bud, resulting in plant death in 2 to 4 weeks. Applied pre-emergence, post-emergence and water-applied. Uses Provides control of Echinochloa spp., as well as many broadleaf, sedge and aquatic weeds in rice. Penoxsulam provides residual weed control, depending on soil type and use rate. In tropical rice, application will be at 10-15 g/ha; in temperate rice, 20-50 g/ha. Primary use will be a post-emergence application in dry-seeded, water-seeded and transplanted rice. Formulation types SC; OD; GR.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits > 5000 mg/kg; very slight, transient irritation. Inhalation LC50 for rats >3.50 mg/l (highest attainable concentration). NOEL For rats 500 mg/kg b.w. daily (maternal), 1000 mg/kg b.w. daily (embryo-foetal). Toxicity class EPA (formulation) III (GR, SC)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Penoxsulam has low toxicity to fish, birds, terrestrial and aquatic invertebrates, with low to moderate toxicity to aquatic plants. Birds LD50 for mallard ducks >2000, bobwhite quail >2025 mg/kg b.w. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks >4310, bobwhite quail >4411 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for common carp >101, bluegill sunfish >103, rainbow trout >102, silverside >129 mg/l. NOEC (36 d) for fathead minnow 10.2 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (24 h and 48 h) >98.3 mg/l. Algae EC50 (120 h) for freshwater diatom >49.6, bluegreen algae 0.49 mg/l; EC50 (96 h) for freshwater green algae 0.086 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (14 d) for Lemna gibba 0.003 mg/l. Bees LD50 (48 h, oral) for honey bees >110 mg/bee; (48 h, contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (7 d and 14 d) >1000 mg/kg. Other beneficial spp. LR50 (glass plate test) for predatory mites 7.46 g/ha, parasitic wasp and green lacewing >40 g/ha. Extended laboratory test at 40 g/ha: predatory mite mortality 0%, effect on fecundity 8.2%; parasitic wasp mortality 0%, effect on fecundity 26%. Soil microbial NOEC >500 g/ha.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Rapidly excreted, with low potential to accumulate. Plants Following post-emergence foliar application to greenhouse plants, DT50 in indica rice 0.6 d, japonica rice 1.4 d, Echinochloa 4.4 d. Penoxsulam is first metabolised to the 5-hydroxy derivative, which is inactive. Soil/Environment Aqueous photolysis DT50 2 d; soil photolysis DT50 19 d. Under global water-seeded rice field conditions, DT50 (ave.) 6.5 d (4-10 d); under dry-seeded rice conditions DT50 (ave.) 14.6 d (13-16 d). In EU, under water-seeded field conditions DT50 (ave.) 5.9 d (5.6- 6.1 d).
|