|
pendimethalin
Herbicide
HRAC K1 WSSA 3; dinitroaniline
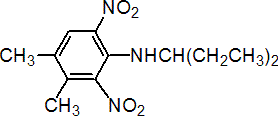
NOMENCLATURE
Common name pendimethalin (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI, WSSA); pendiméthaline ((f) F-ISO); penoxalin* (former WSSA name)
IUPAC name N-(1-ethylpropyl)-2,6-dinitro-3,4-xylidine
Chemical Abstracts name N-(1-ethylpropyl)-3,4-dimethyl-2,6-dinitrobenzenamine
CAS RN [40487-42-1] EEC no. 254-938-2 Development codes AC 92 553 (Cyanamid)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. grade is 90% pure. Mol. wt. 281.3 M.f. C13H19N3O4 Form Orange-yellow crystals. M.p. 54-58 ºC B.p. Decomposes on distillation. V.p. 1.94 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 5.2 S.g./density 1.19 at 25 ºC Solubility In water 0.33 mg/l (20 ºC). In acetone 800, xylene >800, hexane 48.98, dichloromethane >800, (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Readily soluble in benzene, toluene, and chloroform. Slightly soluble in petroleum ether and petrol. Stability Very stable in storage; store above 5 ºC and below 130 ºC. Stable to acids and alkalis. Slowly decomposed by light. DT50 in water <21 d.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by P. L. Sprankle (Proc. Br. Weed Control Conf., 12th, 1974, 2, 825). Introduced by American Cyanamid Co. (now BASF AG). Patents BE 816837; US 4199669 Manufacturers BASF; Feinchemie Schwebda; Rallis; Sundat
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Microtubule assembly inhibition. Mode of action Selective herbicide, absorbed by the roots and leaves. Affected plants die shortly after germination or following emergence from the soil. Uses Control of most annual grasses and many annual broad-leaved weeds, at 0.6-2.4 kg/ha, in cereals, onions, leeks, garlic, fennel, maize, sorghum, rice, soya beans, peanuts, brassicas, carrots, celery, black salsify, peas, field beans, lupins, evening primrose, tulips, potatoes, cotton, hops, pome fruit, stone fruit, berry fruit (including strawberries), citrus fruit, lettuce, aubergines, capsicums, established turf, and in transplanted tomatoes, sunflowers, and tobacco. Applied pre-plant incorporated, pre-emergence, pre-transplanting, or early post-emergence. Also used for control of suckers in tobacco. Phytotoxicity Injury to maize may occur if used as a pre-plant, soil-incorporated treatment. Formulation types EC; GR; SC; WG. Selected products: 'Herbadox' (BASF); 'Prowl' (BASF); 'Stomp' (BASF); 'Mopup' (Crop Health); 'Pressto' (Cequisa); 'Tremor' (Barclay)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Claymore' (BASF); 'Go-Go-San' (BASF, Kumiai); 'Pendulum' (BASF); 'Pentagon' (BASF); 'Ipimethalin-L' (Dintec); 'Pendimax' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Repose' (Cedar); 'Tata Panida' (Rallis); 'Valeran' (IQV) mixtures: 'Celtic' (+ picolinafen) (BASF); 'Chacal' (+ imazamethabenz-methyl) (BASF); 'Chekway' (+ imazaquin-ammonium) (BASF); 'Crystal' (+ flufenacet) (BASF); 'Elite' (+ imazethapyr) (BASF); 'Encore' (+ isoproturon) (BASF); 'Impuls' (+ bentazone) (BASF); 'Indiana' (+ metolachlor) (BASF); 'Jolt' (+ isoproturon) (BASF); 'Malibu Pack' (+ flufenacet) (BASF); 'Megaplus' (+ imazamethabenz-methyl) (BASF); 'Merit' (+ simazine) (BASF); 'Nirvana' (+ imazamox) (France) (BASF); 'PicoPro' (+ picolinafen) (BASF); 'Pursuit Plus' (+ imazethapyr) (BASF); 'Squadron' (+ imazaquin-ammonium) (BASF); 'Steel' (+ imazaquin+ imazethapyr) (BASF); 'Treplik Duo' (+ neburon) (BASF); 'Trump' (+ isoproturon) (BASF); 'Bullet' (+ cyanazine) (Feinchemie Schwebda); 'Comboral' (+ trifluralin) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Galaxy' (+ clomazone) (FMC); 'Pendanil' (+ propanil) (Crystal); 'Preclaim' (+ fenoxaprop-P-ethyl) (Bayer CropScience) Discontinued products: 'Sovereign' * (Novartis) mixtures: 'Activus' * (+ cyanazine) (Cyanamid); 'Monarch' * (+ prometryn) (Cyanamid); 'Oklahoma' * (+ imazamox) (BASF); 'Structure' * (+ imazaquin+ imazethapyr) (BASF); 'Totem' * (+ chlorotoluron) (Cyanamid); 'Primafit' * (+ terbuthylazine) (Novartis)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (J. C. Wyckoff, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1978, 10, 461). Residues of the 4-hydroxymethyl analogue (after formation of a derivative) and of pendimethalin determined by glc with ECD (idem, ibid.).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000, male mice 1620, female mice 1340, rabbits >5000, beagle dogs >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 for rats >320 mg/l. NOEL In 2 y feeding trials, rats receiving 100 mg/kg diet showed no ill-effects. Water GV 20 mg/l (TDI 5 mg/kg b.w.). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC classification R43| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute LD50 for mallard ducks 1421 mg/kg b.w. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail 4187 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.14, bluegill sunfish 0.2, channel catfish 0.42 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 0.28 mg/l. Bees LD50 (topical) >101.2 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, the major metabolic routes for pendimethalin involve hydroxylation of the 4-methyl and N-1-ethyl groups, oxidation of these alkyl groups to carboxylic acids, nitro-reduction, cyclisation and conjugation (J. Zulian, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1990, 38, 1743). Plants In plants, the 4-methyl group on the benzene ring is oxidised to the carboxylic acid via the alcohol. The amino nitrogen is also oxidised. At harvest time, residues in crops are below the validated sensitivity of the analytical method (0.05 ppm). Soil/Environment In soil, the 4-methyl group on the benzene ring is oxidised to the carboxylic acid via the alcohol; the amino nitrogen is also oxidised. DT50 in soil is 3-4 mo (A. Walker & W. Bond, Pestic. Sci., 1977, 8, 359). Kd ranges from 2.23 (0.01% o.m., pH 6.6) to 1638 (16.9% o.m., pH 6.8) (H. J. Pedersen et al., Pestic. Sci., 1995, 44, 131).
|