|
penconazole
Fungicide
FRAC 3, G1; DMI: triazole
NOMENCLATURE
Common name penconazole (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO)
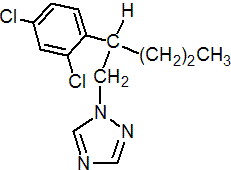
IUPAC name 1-(2,4-dichloro-b-propylphenethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole
Chemical Abstracts name 1-[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)pentyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazole
CAS RN [66246-88-6] EEC no. 266-275-6 Development codes CGA 71818 (Ciba-Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 284.2 M.f. C13H15Cl2N3 Form Fine white powder. M.p. 60.3-61.0 °C B.p. >360 °C; 99.2 °C/1.9 Pa V.p. 0.17 mPa (20 °C); 0.37 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 3.72 (pH 5.7, 25 ºC). Henry 6.6 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (20 °C, calc.). S.g./density 1.30 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 73 mg/l (25 ºC). In ethanol 730, acetone 770, toluene 610, n-hexane 24, n-octanol 400 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable to hydrolysis (pH 1-13), and to temperatures up to 350 ºC. pKa 1.51, v. weak base
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by J. Eberle et al. (Proc. Int. Congr. Plant Prot., 10th, 1983, 1, 376). Introduced by Ciba-Geigy AG (now Syngenta AG) as an agricultural fungicide, having been invented by Janssen Pharmaceutical NV and first marketed in 1983. Patents GB 1589852; BE 857570 (to Janssen Pharmaceutical) Manufacturers Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Sterol demethylation inhibitor; inhibits cell membrane ergosterol biosynthesis, stopping development of the fungi. Mode of action Systemic fungicide with protective and curative action. Absorbed by the leaves, with translocation acropetally. Uses Control of powdery mildew, pome fruit scab and other pathogenic Ascomycetes, Basidiomycetes and Deuteromycetes on vines, pome fruit, stone fruit, ornamentals, hops and vegetables, at 25-75 g/ha. Formulation types EC; EW; WP. Selected products: 'Topas' (Syngenta); 'Dallas' (Rocca)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Donna' (Syngenta); 'Ofir' (Syngenta); 'Omnex' (Syngenta); 'Relax' (Syngenta); 'Topaz' (Syngenta); 'Topaze' (Syngenta) mixtures: 'Preface' (+ dinocap) (Syngenta); 'Topas C' (+ captan) (Syngenta); 'Topas Combi' (+ sulfur) (Syngenta) Discontinued products: 'Award' * (Ciba) mixtures: 'Topas D' * (+ dithianon) (Ciba)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc. Residues determined by glc. Details available from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 65, 67 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 2125, mice 2444 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >3000 mg/kg. Not a skin irritant; irritating to eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >4000 mg/m3. NOEL (2 y) for rats 3.8, mice 0.71 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for dogs 3.3 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.03 mg/kg b.w. [1992]. Other Not mutagenic, not teratogenic, not oncogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 (8 d) for Japanese quail 2424, Pekin ducks >3000, mallard ducks >1590 mg/kg. LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 1.7-4.3, carp 3.8-4.6, bluegill sunfish 2.1-2.8 mg/l. Daphnia IC50 (48 h) 7-11 mg/l. Algae IC50 (5 d) for Scenedesmus subspicatus 3.0 mg/l; EC50 (5 d) for Selenastrum capricornutum 0.83 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to bees; LD50 (oral and topical) >5 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms >1000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals After oral administration, penconazole is rapidly eliminated practically to entirety with urine and faeces. Residues in tissues were not significant and there was no evidence for accumulation. Plants Metabolic pathways are hydroxylation of the propyl side-chain, conjugation to glucosides or metabolism to triazolylalanine and triazolylacetic acid. Soil/Environment DT50 in soil is 133-343 d, depending on soil type. DT50 for photolysis is 4 d (natural sunlight).
|