|
paclobutrazol
Plant growth regulator
DMI: triazole
NOMENCLATURE
Common name paclobutrazol (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO, ANSI)
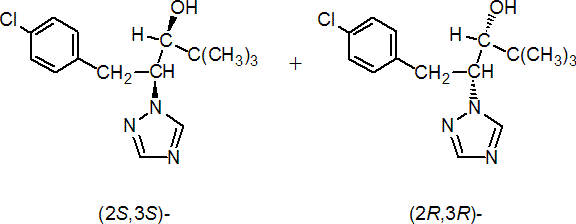
IUPAC name (2RS,3RS)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pentan-3-ol
Chemical Abstracts name (R*,R*)-(?-b-[(4-chlorophenyl)methyl]-a-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-1-ethanol
CAS RN [76738-62-0] stated stereoisomers Development codes PP333 (ICI)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. material is 90% pure. Mol. wt. 293.8 M.f. C15H20ClN3O Form White, crystalline solid. M.p. 165-166 ºC V.p. 0.001 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 3.2 Henry 1.13 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.22 g/ml Solubility In water 26 mg/l (20 ºC). In acetone 110, cyclohexanone 180, dichloromethane 100, hexane 10, xylene 60, methanol 150, propylene glycol 50 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Stable for more than 2 years at 20 ºC, and more than 6 months at 50 ºC. Stable to hydrolysis (pH 4-9), and not degraded by u.v. light (pH 7, 10 days).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Plant growth regulator reported by B. G. Lever et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1982, 1, 3), introduced by ICI Agrochemicals (now Syngenta AG) and first marketed in 1986. Patents GB 1595696; US 1595697 Manufacturers Sharda; Sundat; Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits gibberellin and sterol biosynthesis, and hence the rate of cell division. Mode of action Plant growth regulator taken up into the xylem through the leaves, stems, or roots, and translocated to growing sub-apical meristems. Produces more compact plants and enhances flowering and fruiting. Uses Used on fruit trees to inhibit vegetative growth and to improve fruit set; on pot-grown ornamentals and flower crops (e.g. chrysanthemums, begonias, freesias, poinsettias and bulbs) to inhibit growth; on rice to increase tillering, reduce lodging, and increase yield; on turf to retard growth; and on grass seed crops to reduce height and prevent lodging. To be applied as a foliar spray, as a soil drench, or by trunk injection. Has some fungicidal activity against mildew and rusts. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic, though it intensifies greening. Some spotting has been noted on periwinkle foliage at higher temperatures. Formulation types GR; SC; WP. Selected products: 'Bonzai' (ornamentals) (Syngenta); 'Cultar' (fruit trees) (Syngenta); 'Smarect' (Syngenta); 'Multeffect' (Sanonda); 'Paclo' (Vipesco); mixtures: 'Parlay C' (+ chlormequat chloride) (Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Clipper' (Syngenta); 'Profile' (Dow AgroSciences) Discontinued products: 'Bounty' * (Syngenta); 'Club' * (Zeneca); 'Drize' * (Zeneca); 'Inevitan' * (Zeneca); 'Molass' * (Zeneca); 'Oryze' * (Zeneca); 'Parlay' * (grass seeds) (Zeneca); 'Predict' * (Zeneca); 'Trimmid' * (Zeneca) mixtures: 'Holdfast D' * (+ dicamba) (Zeneca)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc or by hplc. Residues determined by tlc. Details available from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 53, 55 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 2000, female rats 1300, male mice 490, female mice 1200, guinea pigs 400-600, male rabbits 840, female rabbits 940 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats and rabbits >1000 mg/kg. Mild skin irritant; moderate eye irritant (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for male rats 4.79, female rats 3.13 mg/l air. NOEL (1 y) for dogs 75 mg/kg daily; (2 y) for rats 250 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.1 mg/kg b.w. [1988]. Other Not mutagenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) IV EC classification (Xn; R20/22| R36| N; R51, R53)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >7900 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 27.8 mg/l. NOEC 3.3 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 33.2 mg/l. Algae EC50 (cell volume) for Chlorella fusca 180 mmol/l (Pestic. Sci.,47, 337 (1996)). Bees Acute oral NOEL >0.002 mg/bee; acute percutaneous NOEL >0.040 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Soil/Environment Soil DT50 0.5-1.0 y in general; in calcareous clay loam (pH 8.8, 14% o.m.), DT50 <42 d; in coarse sandy loam (pH 6.8, 4% o.m.), DT50 >140 d.
|