|
oxadiargyl
Herbicide
HRAC E WSSA 14; oxadiazole
NOMENCLATURE
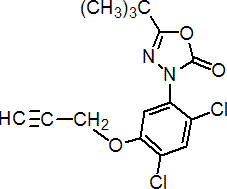
Common name oxadiargyl (pa ISO)
IUPAC name 5-tert-butyl-3-[2,4-dichloro-5-(prop-2-ynyloxy)phenyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2(3H)-one
Chemical Abstracts name 3-[2,4-dichloro-5-(2-propynyloxy)phenyl]-5-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2(3H)-one
CAS RN [39807-15-3] EEC no. 254-637-6 Development codes RP 020630 (Rhône-Poulenc)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 341.2 M.f. C15H14Cl2N2O3 Form White to beige powder, with no characteristic odour. M.p. 131 °C V.p. 2.5 ´ 10-3 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 3.95 Henry 9.1 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.484 (20 °C) Solubility In water 0.37 mg/l (20 °C). Stability Stable to heat (15 d, 54 °C), to light and in water. Stable to aqueous hydrolysis at pH 4, 5 and 7; DT50 7.3 d (pH 9).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Introduced in Latin America in 1996. Reported by R. Dickmann et al. (Proc. 1997 Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1, 51). Manufacturers Bayer CropScience
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Protoporphyrinogen IX oxidase inhibitor. Mode of action Selective herbicide, active mainly pre-emergence; effects begin at germination. It is not absorbed by the plant. Efficacy is not dependent on soil texture and type. Uses Pre-emergence and early post-emergence herbicide active on broad-leaved weeds (Amaranthus, Bidens, Chenopodium, Malva, Monochoria, Polygonum, Portulaca, Potamogeton, Raphanus, Solanum, Sonchus, Rotala), grasses (Echinochloa, Leptochloa, Brachiaria, Cenchrus, Digitaria, Eleusine, Panicum and wild rice) and annual sedges, in rice (at 50-150 g/ha), upland crops (sunflower, potato, vegetables and sugar cane, at 300-500 g/ha) and perennial crops (fruit trees and citrus, at 500-1500 g/ha). Formulation types EC; SC; WG; WP. Selected products: 'Raft' (Bayer CropScience); 'Topstar' (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Fenax' (Bayer CropScience)
ANALYSIS
By hplc with u.v. detection.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits <2000 mg/kg. Not a skin irritant; minimal eye irritation (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.16 mg/l. Other Not genotoxic.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 (14 d) for quail >2000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for quail and mallard ducks >5200 ppm. Fish Not toxic at limit of water solubility. Daphnia Not toxic at limit of water solubility. Algae EC50 (120 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 1.2 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral and contact) >200 mg/bee. Worms Non-toxic at 1000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Studies on goats and hens demonstrated that oxadiargyl is rapidly excreted; there is no evidence of accumulation in milk, eggs or edible tissues. Plants Studies on lemons, sunflowers and rice demonstrated very low levels of residues at harvest, mainly parent compound (C. R. Leake et al., Proc. 9th IUPAC Int. Congr. Pestic. Chem., London, 1998, 2, 5A-021). Soil/Environment DT50 (lab., aerobic) 18-72 d (20-30 °C), forming two major metabolites (one of which is herbicidal) which are, in turn, steadily degraded, resulting in mineralisation to CO2 and a soil-bound residue. Oxadiargyl dissipates rapidly from water into the sediment phase and is readily degraded under anaerobic conditions. Strongly adsorbed to soil (Koc 1000-3000); oxadiargyl and its two major soil metabolites show low mobility in 4 soil types and are unlikely to leach. Field results were consistent: DT50 9-25 d, mean DT90 90 d; for oxadiargyl and its two major metabolites, DT50 was 9-31 d, DT90 65-234 d; >95% of oxadiargyl residues remained in the top 10 cm of soil, and no residues were found below 30 cm. .
|