|
ofurace
Fungicide
FRAC 4, A1; phenylamide: butyrolactone
NOMENCLATURE
Common name ofurace (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO, ANSI)
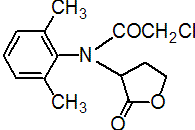
IUPAC name (?-a-(2-chloro-N-2,6-xylylacetamido)-g-butyrolactone
Chemical Abstracts name (?-2-chloro-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N-(tetrahydro-2-oxo-3-furanyl)acetamide
CAS RN [58810-48-3] unstated stereochemistry EEC no. 261-451-9 Development codes RE 20615 (Chevron); AE F057623 (AgrEvo)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. grade is ³97% pure. Mol. wt. 281.7 M.f. C14H16ClNO3 Form Colourless crystals; (tech. is an off-white to light beige, crystalline powder). M.p. 145-146 ºC V.p. 2 ´ 10-2 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 1.39 (20 °C) Henry 3.9 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.43 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 146 mg/l (20 °C). In acetone 60-75, 1,2-dichloroethane 300-600, ethyl acetate 25-30, methanol 25-30, p-xylene 8.6, heptane 0.0322 (all in g/l). Stability Hydrolysis is rapid in alkali, DT50 7 h (pH 9, 35 °C), but stable in acidic media and at elevated temperatures. Photochemical degradation in water, DT50 7 d.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Systemic fungicide introduced by Chevron Chemical Co. Rights transferred to Schering AG (now Bayer CropScience) in 1992.
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry It is assumed that it inhibits protein synthesis in fungi, by interference with the synthesis of ribosomal RNA. Mode of action Systemic fungicide with curative and protective action. Absorbed rapidly by the foliage and roots, with translocation both acropetally and basipetally. Acts by inhibiting spore germination or blocking mycelium formation. Uses In combination with other fungicides, for control of Phycomycetes, particularly downy mildew of vines, and late blights of potatoes and tomatoes. Formulation types SC; WP.
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Caltan P' (Bayer CropScience); 'Polyplus' (Bayer CropScience); 'Vamin' (Bayer CropScience) mixtures: 'Patafol' (+ mancozeb) (Bayer CropScience)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc. Residues determined by glc.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 3500, female rats 2600, mice >5000, rabbits >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >5000 mg/kg. Moderate eye irritant; mild skin irritant (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 for rats 2060 mg/m3. NOEL Long-term NOEL for rats 2.5 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.03 mg/kg b.w. Other Not mutagenic, not teratogenic, not carcinogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for red-legged partridge >5000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 29, golden orfe 57 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 46 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to bees; LD50 (oral) >58 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Ofurace is rapidly excreted, undergoing extensive phase I and phase II biotransformation. Plants Similar metabolic pathways have been detected in vines, tomatoes, and potatoes. Ofurace is relatively stable on the plant surface, but, once it has penetrated into plant material, it is metabolised by hydroxylation and conjugation. Ofurace has been defined as the residue to be monitored. Soil/Environment Degraded in soil, field DT50 c. 26 d. Only moderately adsorbed to soil and is considered to be moderately mobile. Undergoes photochemical degradation in water and is degraded in water sediment systems.
|