|
nicosulfuron
Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; sulfonylurea
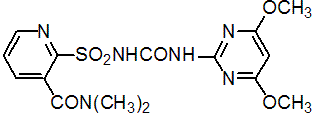
NOMENCLATURE
Common name nicosulfuron (BSI, ANSI, draft E-ISO); no name (Brazil)
IUPAC name 2-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-ylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)-N,N-dimethylnicotinamide; 1-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)-3-(3-dimethylcarbamoyl-2-pyridylsulfonyl)urea
Chemical Abstracts name 2-[[[[(4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]-N,N-dimethyl-3-pyridinecarboxamide
CAS RN [111991-09-4] Development codes SL-950; MU-495 (both Ishihara Sangyo); DPX-V9360 (DuPont)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 410.4 M.f. C15H18N6O6S Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 169-172 °C V.p. <8 ´ 10-7 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = -0.36 (pH 5), -1.8 (pH 7), -2 (pH 9) Henry <4.68 ´ 10-9 Pa m3 mol-1 (25 °C) S.g./density 0.313 (bulk) Solubility In water 0.07 g/l. In acetone 18, ethanol 4.5, chloroform, dimethylformamide 64, acetonitrile 23, toluene 0.370, hexane <0.02, dichloromethane 160 (all in g/kg, 25 ºC). Stability Hydrolysis DT50 15 d (pH 5); stable at pH 7 & 9. pKa 4.6 (25 ºC) F.p. >200 °C (Cleveland open cup)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide developed by Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha, Ltd and by E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co. First registered in USA in June 1990 by E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co. and launched in France in 1992 by Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha, Ltd. Patents US 4789393 Manufacturers DuPont; IPESA; Ishihara Sangyo; Sannong; Sharda; Sundat
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Acts by inhibiting biosynthesis of the essential amino acids valine and isoleucine, hence stopping cell division and plant growth. Maize selectivity derives from selective metabolism (P450-mediated pyrimidine-5-hydroxylation, followed by conjugation with glucose). Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the foliage and roots, with rapid translocation in xylem and phloem to the meristematic tissues. Uses Selective post-emergence control in maize of annual grass weeds including Setaria, Echinochloa, Digitaria, Panicum, Lolium, and Avena spp., broad-leaved weeds including Amaranthus spp. and Cruciferae, and perennials such as Sorghum halepense and Agropyron repens. Applied at 35-70 g/ha. Formulation types SC; WG. Selected products: 'Accent' (DuPont); 'Dasul' (Ishihara Sangyo, Syngenta); 'Milagro' (France) (Ishihara Sangyo, Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Akizon' (Calliope); 'Elite' (Spain) (Ishihara Sangyo); 'Ghibli' (Italy) (ISK Biosciences); 'Lama' (France) (Ishihara Sangyo, Bayer CropScience); 'Mistral' (Ishihara Sangyo, Syngenta); 'Motivel' (Ishihara Sangyo, BASF); 'Nisshin' (Argentina) (Ishihara Sangyo); 'Onehope' (Japan) (Ishihara Sangyo); 'Samson' (Ishihara Sangyo); 'Sanson' (Ishihara Sangyo); 'Yu Nong Le' (Ishihara Sangyo) mixtures: 'Accent Gold' (+ rimsulfuron+ clopyralid+ flumetsulam) (DuPont); 'Basis Gold' (+ rimsulfuron+ atrazine) (DuPont); 'Steadfast' (+ rimsulfuron) (DuPont); 'Ultim' (+ rimsulfuron) (DuPont); 'Celebrity Plus' (+ dicamba-sodium+ diflufenzopyr) (diflufenzopyr also as sodium salt) (BASF); 'Celebrity' (+ dicamba-sodium) (BASF)
ANALYSIS
Product by hplc. Methods for sulfonylurea residues in crops, soil and water reviewed (A. C. Barefoot et al., Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1995, 2, 707). Details from Ishihara Sangyo.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male and female rats and mice >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male and female rats >2000 mg/kg. Moderate eye irritant; not a skin irritant (rabbits); not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). The 75% formulation is not an eye irritant. Inhalation LC50 for rats (4 h) 5.47 mg/l. NOEL In 28 d feeding trials on rats and mice, no adverse effect up to 30 g/kg diet. Other Non-mutagenic in the Ames test. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Dietary oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2250 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >5620 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish and rainbow trout >1000 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >1000 mg/l. Algae NOEC (96 h) for green algae 100 mg/l. Bees LD50 (contact) >20 mg/bee; dietary LC50 (48 h) >1000 ppm. NOEC 500 ppm. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms >1000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In goats, following a dose of 60 ppm, <0.1 ppm was found in tissues and milk; therefore nicosulfuron and its metabolites do not bioaccumulate. Hydrolysis of the sulfonylurea bridge and hydroxylation were the main metabolic pathways. Plants Degraded rapidly in maize, DT50 1.5-4.5 d. Residues <0.02 ppm in all crops. Hydrolysis of the sulfonylurea bridge to form the pyridine sulfonamide and pyrimidine amine, and hydroxylation on the pyrimidine ring, were the main metabolic pathways. Soil/Environment Soil DT50 (aerobic) 26 d (pH 6.1, 5.1% o.m., 25 °C). In four sandy loams, Kd (25 °C) 0.16 (pH 6.6, 1.1% o.m.) to 1.73 (pH 5.4, 4.3% o.m.). Photolysis DT50 (soil) 60-67 d; (water) 14-19 d (pH 5), 200-250 d (pH 7), 180-200 d (pH 9). Values from separate studies were: Soil DT50 24-43 d (20 °C); DT90 80-143 d (20 °C). Kd 0.05-0.7. In water, DT50 15 d (pH 5, 20 °C).
|