|
napropamide
Herbicide
HRAC K3 WSSA 15; alkanamide (acetamide)
NOMENCLATURE
Common name napropamide (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, WSSA, JMAF)
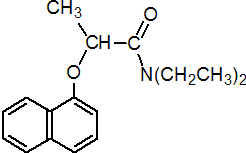
IUPAC name (RS)-N,N-diethyl-2-(1-naphthyloxy)propionamide
Chemical Abstracts name N,N-diethyl-2-(1-naphthalenyloxy)propanamide
CAS RN [15299-99-7] unstated stereochemistry; [41643-35-0] (R)-(-)- isomer; [41643-36-1] (S)-(+)- isomer Development codes R-7465 (Stauffer)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. grade is 92-96% pure. Mol. wt. 271.4 M.f. C17H21NO2 Form Colourless crystals; (tech., brown solid). M.p. 74.8-75.5 ºC; (tech., 68-70 ºC) V.p. 0.53 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 3.3 (25 ºC) Henry 1.94 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density Bulk density 0.584 g/ml Solubility In water 7.4 mg/l (25 ºC). In acetone, ethanol >1000, xylene 505, kerosene 62, hexane 15 (all in g/l, 20 ºC); miscible with acetone, ethanol, methyl isobutyl ketone. Stability No decomposition occurs over 16 h at 100 ºC. Decomposed by sunlight; DT50 25.7 min. Stable to hydrolysis between pH 4 and 10 at 40 ºC. F.p. >104 ºC
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by B. J. van den Brink et al. (Symp. New Herbic., 3rd, 1969, p. 35). Introduced by Stauffer Chemical Co. (now Syngenta AG). Divested to United Phosphorus Ltd. in 1997. Patents US 3480671; US 3718455 Manufacturers Gharda; United Phosphorus Ltd
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cell division inhibitor. Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the roots, with translocation acropetally. Inhibits root development and growth. Uses Pre-emergence control of annual grasses and broad-leaved weeds in asparagus, rhubarb, cucurbits, brassicas, oilseed rape, tomatoes, capsicums, potatoes, peas, nuts, fruit trees and bushes (including citrus), vines, strawberries, sunflowers, safflowers, ornamentals, tobacco, olives, figs, mint, turf, and other crops, at 2-6 kg/ha. The (R)-(-)- isomer is 8 times as toxic to 3 weed species as the (S)-(+)- isomer (J. H. Chan et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1975, 23,1008). Phytotoxicity Phytotoxic to wheat and barley. Formulation types EC; GR; SC; WP. Selected products: 'Devrinol' (Syngenta, United Phosphorus, Bayer CropScience); 'AC 650' (United Phosphorus Ltd); 'Naproguard' (Gharda)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Kusaless' (Nihon Nohyaku)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc. Residues in crops and soil determined by glc (G. G. Patchett et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1976, 8, 347). In drinking water, by glc with NPD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 991.07). Details of analytical methods available from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats >5000 mg tech./kg, female rats 4680 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >4640, guinea pigs >2000 mg/kg. Moderate eye irritant; not a skin irritant (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for rats 30 mg/kg b.w. daily; (90 d) for dogs 40 mg/kg b.w. daily. Developmental toxicity NOEL for rats and rabbits 1000 mg/kg b.w. daily; multigeneration study (rats) 30 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.11 mg/kg. Other Negative genotoxicity. Not oncogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds In 7-d feeding trials, no-effect level for bobwhite quail >5620 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 13-15, rainbow trout 9.4, goldfish >10 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 24 mg/l. Algae EC50 (96 h) for Chlorella vulgaris 4.5 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EbC50 (14 d) for Lemna minor 0.237 mg/l. Bees LD50 >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 >799 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, following oral administration, napropamide is rapidly and extensively metabolised. The majority of the dose is excreted via urine and faeces. Similar effects have been observed in poultry. Plants Rapidly metabolised via ring hydroxylation and N-dealkylation, followed by conjugation with sugars to produce water-soluble metabolites. Soil/Environment Koc 600 (range 470-1200). In aerobic laboratory soil, degradation is slow, DT50 446 d (30 °C); however, in the field, typical DT50 is 25 d (range 9-131 d in N. America/Germany). Photodegradation is an important mechanism for loss from soil. Degradates identified in soil are 1-naphthoxypropionic acid, 2-(a-naphthoxy)-N-ethyl-N-hydroxyethylpropionamide, 2-(a-naphthoxy)-N-ethylpropionamide, 2-(a-naphthoxy)propionic acid, 2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, 1,4-naphthoquinone and o-phthalic acid.
|