|
myclobutanil
Fungicide
FRAC 3, G1; DMI: triazole
NOMENCLATURE
Common name myclobutanil (BSI, ANSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO)
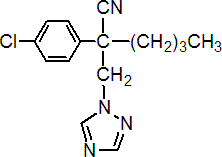
IUPAC name 2-p-chlorophenyl-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)hexanenitrile; 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)hexanenitrile
Chemical Abstracts name a-butyl-a-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-1-propanenitrile
CAS RN [88671-89-0] Development codes RH-3866 (Rohm & Haas)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 288.8 M.f. C15H17ClN4 Form Pale yellow solid. M.p. 63-68 ºC (tech.) B.p. 202-208 ºC/1 mmHg V.p. 0.213 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 2.94 (pH 7-8, 25 ºC) Henry 4.33 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) Solubility In water 142 mg/l (25 ºC). Soluble in common organic solvents, e.g. ketones, esters, alcohols and aromatic hydrocarbons, all 50-100 g/l. Insoluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons. Stability Stable under normal storage conditions. Aqueous solutions decompose on exposure to light, DT50 222 d (sterile water), 0.8 d (sensitised sterile water), 25 d (pond water); no hydrolysis (28 ºC) in 28 d (pH 5, 7, and 9).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Systemic fungicide reported by C. Orpin et al. (Proc. 1986 Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1b, 55) and developed by Rohm & Haas Co. (now Dow AgroSciences). First marketed in 1989. Patents US 4920139 Manufacturers Dow AgroSciences; Sharda; Shenyang
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits ergosterol biosynthesis (steroid demethylation inhibitor). Mode of action Systemic fungicide with protective and curative action. Translocated upwards in the plant. Uses Control of Ascomycetes, Fungi Imperfecti, and Basidiomycetes on a wide variety of crops. The primary use is for powdery mildew (Uncinula necator) control in vines and for combined leaf scab and powdery mildew control in apples. Application rates typically 30-60 g/ha. Also registered for control of Ascomycetes or Basidiomycetes diseases on a broad variety of crops including other pome fruit, stone fruit, cucurbits, strawberries, almonds, tomatoes, vegetables, hops, cotton, cereal seed treatments, turf and ornamentals. It is used as a foliar treatment for control of powdery mildew, shot-hole, blossom blight, anthracnose and rust in stone fruit and nuts; powdery mildew in cucurbits; powdery mildew and rusts on ornamentals; rusts on perennial grasses grown for seed; and as a seed treatment for control of seed- and soil-borne diseases in barley, maize, cotton, rice and wheat; and as a post-harvest treatment in crops such as banana. Formulation types EC; EW; WP; Seed treatment. Selected products: 'Eagle' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Nova' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Rally' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Systhane' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Pudong' (Rocca)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Laredo' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Nu-Flow M' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Mycloss' (Bayer CropScience, Philagro) mixtures: 'Sabithane' (+ dinocap) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Manhandle' (+ mancozeb) (Lesco) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Ravyl' * (+ ampropylfos+ anthraquinone) (Bayer)
ANALYSIS
Product and residues by gc with FID. Details from Dow AgroSciences.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 65, 67 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 1870, female rats 2090 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >5000 mg/kg. Not a skin irritant; can cause substantial irritation to the eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 for rats 5.1 mg/l. NOEL Dietary NOEL (90 d) for dogs 3.1 mg/kg b.w. daily. Reproductive NOEL for rats 14.7 mg/kg b.w. daily. NOAEL, based on chronic feeding, oncogenicity and reproductive studies 2.5 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.03 mg/kg b.w. [1992]. Other Non-teratogenic in rats and rabbits, and various mutagenicity tests proved negative. Not mutagenic in the Ames assay. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III EC classification R63| Xn; R22| Xi; R36| N; R51, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 510, grey partridges 1635 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks > 5000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 2.4, rainbow trout 2.0 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 11 mg/l. Algae EC50 (96 h) for Scenedesmus subspicatus 2.4 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to bees. LD50 (oral) 171 mg/bee; (contact) 200 mg/bee. Worms Acute LC50 for Eisenia foetida 99 mg/kg; reproduction NOEC for Eisenia foetida >10.3 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In animals, undergoes oxidation at the butyl group to a ketone and an alcohol, with partial conjugation to a glucoside. Following oral administration, rapidly excreted in the faeces and urine. Plants In plants, metabolism is the same as in animals. Soil/Environment In soil, DT50 66 d (silt loam). Decomposition is through highly polar triazole compounds, with further degradation by ring splitting. No degradation under anaerobic conditions. Stable to hydrolysis, but decomposes in aqueous solutions upon exposure to light; DT50 in pond water typically 15-25 days. Low mobility in soil; Koc 224-937 ml/g.
|