|
monocrotophos
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 1B; organophosphate
NOMENCLATURE
Common name monocrotophos (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ESA, JMAF)
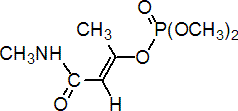
IUPAC name dimethyl (E)-1-methyl-2-(methylcarbamoyl)vinyl phosphate; 3-dimethoxyphosphinoyloxy-N-methylisocrotonamide
Chemical Abstracts name (E)-dimethyl 1-methyl-3-(methylamino)-3-oxo-1-propenyl phosphate
CAS RN [6923-22-4] (formerly [919-44-8]) monocrotophos; [919-44-8] (Z)- analogue; [2157-98-4] (E)- + (Z)- compounds EEC no. 230-042-7 Development codes C 1414 (Ciba); SD 9129 (Shell) Official codes OMS 834; ENT 27 129
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 223.2 M.f. C7H14NO5P Form Colourless, hygroscopic crystals; (tech., ³74%: dark brown semi-solid). M.p. 54-55 ºC B.p. 125 ºC/0.0005 mmHg V.p. 2.9 ´ 10-1 mPa (20 ºC); 9.8 ´ 10-1 mPa (separate studies) KOW logP = -0.22 (calc.) S.g./density 1.22 kg/l (20 ºC). Solubility In water 100% (20 ºC). In methanol 100%, acetone 70%, n-octanol 25%, toluene 6% (all 20 ºC). Sparingly soluble in kerosene and diesel oil. Stability Decomposes >38 ºC, thermal run-away reactions can occur >55 ºC; on hydrolysis (20 ºC), DT50 (calc.) 96 d (pH 5), 66 d (pH 7), 17 d (pH 9); unstable in short-chain alcohols. Decomposes on some inert materials (care should be taken when carrying out chromatography).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Introduced by Ciba AG (became Novartis Crop Protection AG, who ceased to manufacture or market it) and by Shell Chemical Co. (now BASF AG). Patents BE 552284; GB 829576 both to Ciba-Geigy Manufacturers Aimco; BASF; CAC; Cheminova; Comlets; Crystal; DE-NOCIL; Hindustan; Hui Kwang; India Pesticides; Makhteshim-Agan; Nagarjuna Agrichem; Parry; Q.E.A.C.A.; Rallis; Sabero; Sharda; Sinon; Sudarshan; Taiwan Tainan Giant; United Phosphorus
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Systemic insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. Penetrates plant tissue rapidly. Uses Control of a broad spectrum of pests, including sucking, chewing, and boring insects, and spider mites on cotton, citrus, olives, rice, maize, sorghum, sugar cane, sugar beet, peanuts, potatoes, soya beans, vegetables, ornamentals, and tobacco. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic when used as directed, although slight injury may be caused to some varieties of apple, pear, cherry, peach, and sorghum. Formulation types SL; UL. Compatibility Incompatible with pesticides which are alkaline in reaction. Selected products: 'Azodrin' (BASF); 'Agrodrin' (Inquiport); 'Balwan' (Rallis); 'Croton' (RPG); 'Devimono' (Devidayal); 'Efacron' (Efthymiadis); 'Hilcron' (Hindustan); 'Lucadrin' (Lucava); 'Macabre' (Sanonda); 'Monitor' (Crop Health); 'Monocron' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Monocrown' (Nagarjuna Agrichem); 'Monodhan' (Dhanuka); 'Monodrin' (Hui Kwang); 'Monostar' (Shaw Wallace); 'Monovol' (Ralchem); 'Pilardrin' (Pilarquim)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Aimocron' (Aimco); 'Apadrin' (Bayer CropScience); 'Atom' (Indofil); 'Canon' (CAS); 'Crisodrin' (Crystal); 'Cropaphos' (Papaeconomou); 'Crotos' (Isagro); 'Dominator' (Sanonda); 'Kadett' (Pesticides India); 'Monacron' (AgroSan); 'Mosum' (Sabero); 'Parryfos' (Parry); 'R C Pos' (Ramcides); 'Rasayan Fos' (Krishi Rasayan); 'Susvin' (Q.E.A.C.A.) Discontinued products: 'Nuvacron' * (Novartis); 'Agrophos' * (Agrochem); 'Cekumonocrotofos' * (Cequisa); 'Phoskill' * (United Phosphorus)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by rp hplc with u.v. detection (CIPAC Handbook, 1992, E, 145-150), or by glc; details available from BASF or Syngenta. Residues determined by glc using phosphorus-sensitive detectors (Pestic. Anal. Man., 1979, I, 201-H, 201-I; ibid, 1979, II; A. Ambrus et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1981, 64, 733; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 985.22; Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, S19; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M2, M5; Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1972, 6, 287).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 68, 70, 74, 76 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 18, female rats 20 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits 130-250, male rats 126, female rats 112 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats c. 0.08 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) estimated by WHO (JMPR,1972) as: for rats 0.5 mg/kg diet (0.025 mg/kg daily); for dogs 0.5 mg/kg diet (0.0125 mg/kg daily). ADI (JMPR) 0.0006 mg/kg b.w. [1995]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ib; EPA (formulation) I EC classification R68| T+; R26/28| T; R24| N; R50, R53 PIC SL formulations of the substance which exceed 600 g a.i./l are included.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 (14 d) for mallard ducklings 4.8, male Japanese quail 3.7, male bobwhite quail 0.94, chickens 6.7, young pheasants 2.8, partridges 6.5, pigeons 2.8, house sparrows 1.5 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (48 h) for rainbow trout 7 mg/l; (24 h) for rainbow trout 12, bluegill sunfish 23 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (24 h) 0.24 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. LC50 (96 h) for Gammarus fasciatus 0.3, Macrobrachium lamerrii 1.9, Crassostrea virginica >1 mg/l. Bees Highly toxic to bees. LD50 (oral) 0.028-0.033 mg/bee; (topical) 0.025-0.35 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Metabolism and breakdown in plants, animals and soil has been reviewed (K. I. Beynon et al., Residue Rev., 1973, 47,55). Animals In mammals, following oral administration, 60-65% is excreted within 24 hours, predominantly in the urine. Soil/Environment Rapidly degraded in soil; DT50 (lab.) 1-5 d.
|