|
metolachlor
Herbicide
HRAC K3 WSSA 15; chloroacetamide
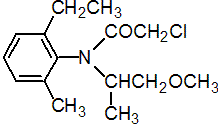
NOMENCLATURE
Common name metolachlor (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI, WSSA); métolachlore ((m) F-ISO)
IUPAC name 2-chloro-6'-ethyl-N-(2-methoxy-1-methylethyl)aceto-o-toluidide
Chemical Abstracts name 2-chloro-N-(2-ethyl-6-methylphenyl)-N-(2-methoxy-1-methylethyl)acetamide
CAS RN [51218-45-2] EEC no. 257-060-8 Development codes CGA 24 705 (Ciba-Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Racemic mixture of (1S)- and (1R)- isomers. Mol. wt. 283.8 M.f. C15H22ClNO2 Form Colourless to light tan liquid. M.p. -62.1 °C B.p. 100 ºC/0.001 mmHg V.p. 4.2 mPa (25 ºC) (OECD 104) KOW logP = 2.9 (25 ºC) Henry 2.4 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.12 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 488 mg/l (25 ºC) (OECD 105). Miscible with benzene, toluene, ethanol, acetone, xylene, hexane, dimethylformamide, dichloroethane, cyclohexanone, methanol, octanol, and dichloromethane. Insoluble in ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, and petroleum ether. Stability Stable up toc. 275 ºC. Hydrolysed by strong alkalis and strong mineral acids. On hydrolysis in buffer (20 ºC), DT50 (calc.) >200 d (2£pH £10). F.p. 190 °C (1013 mbar)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by H. R. Gerber et al. (Proc. Br. Weed Control Conf., 12th, 1974, 2, 787). Introduced by Ciba-Geigy AG (now Syngenta AG) and first marketed in 1976. Patents BE 800471; GB 1438311; GB 1438312 Manufacturers Drexel; Sannong; Sharda; Sundat; Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cell division inhibitor; more recent research suggests chloroacetamides may inhibit synthesis of very long chain fatty acids (J. Schmalfuss et al., Abstr. Meeting WSSA, Toronto, 40, 117-118, 2000; P. Böger, Abstr. III Int. Weed Control Congr., Brazil 2000). Maize tolerance of chloroacetamides is attributed to rapid detoxification by glutathione transferases. Mode of action Selective herbicide, absorbed predominantly by the hypocotyls and shoots. Inhibits germination. Uses Control of annual grasses and some broad-leaved weeds in maize, sorghum, cotton, sugar beet, fodder beet, sugar cane, potatoes, peanuts, soya beans, safflowers, sunflowers, various vegetables, fruit and nut trees, and woody ornamentals. Applied pre-emergence, pre-plant incorporated or early post-emergence at, 1.0-2.5 kg/ha. Often used in combination with broad-leaved herbicides, to extend the spectrum of activity. Phytotoxicity Well tolerated by most broad-leaved crops, maize, sorghum (safened with fluxofenim or oxabetrinil). Formulation types EC; FW; GR; SC.
OTHER PRODUCTS
Mixtures: 'Indiana' (+ pendimethalin) (BASF); 'Pyracur' (+ chloridazon) (BASF); 'Zeazin Mix Extra' (+ prometryn+ atrazine) (Istrochem) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Bicep II' * (+ atrazine+ benoxacor) (Syngenta); 'Bicep' * (+ atrazine) (USA) (Syngenta); 'Broadstrike Dual' * (+ flumetsulam) (Syngenta); 'Dual II' * (+ benoxacor) (USA) (Syngenta); 'Dual S' * (+ benoxacor) (Syngenta); 'Dual' * (+ benoxacor+ carbendazim) (Novartis); 'Dualin' * (+ linuron) (Novartis); 'Duelor + Safeneur' * (+ benoxacor) (France) (Syngenta); 'Gardoprim Plus' * (+ terbuthylazine) (Syngenta); 'Primagram' * (+ atrazine) (Novartis); 'Primextra Safeneur' * (+ atrazine+ benoxacor) (Syngenta); 'Primextra' * (+ atrazine+ benoxacor) (Europe) (Novartis); 'Zintan' * (+ pyridate+ terbuthylazine) (Syngenta); 'Turbo' * (+ metribuzin) (Bayer)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 985.06; CIPAC Handbook, 1988, D, 134). Residues determined by glc with TID or MCD. In drinking water, by glc with NPD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 991.07). Detailsavailable from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 2780 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >3170 mg/kg. Mild skin and eye irritant (rabbits). May cause skin sensitisation (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >1.75 mg/l air. NOEL (90 d) for rats 300 mg/kg diet (c. 15 mg/kg daily), for mice 100 mg/kg diet (c. 100 mg/kg daily), for dogs 300 mg/kg diet (c. 9.7 mg/kg daily). ADI 0.1 mg/kg b.w. Water GV 10 mg/l (TDI 3.5 mg/kg b.w.). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC classification (R43)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >2150 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >10 000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 3.9, carp 4.9, bluegill sunfish 10 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 25 mg/l. Algae EC50 for Scenedesmus subspicatus 0.1 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral and contact) >110 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms 140 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Rapidly oxidised by rat liver microsomal oxygenases via dechlorination, O-demethylation and side-chain oxidation (J. Agric. Food Chem., 1989, 37, 1088). Plants In plants, metabolism involves natural product conjugation of the chloroacetyl group, and hydrolysis and sugar conjugation at the ether group. Final metabolites are polar, water-soluble, and non-volatile. Soil/Environment Major aerobic metabolites are derivatives of oxanilic and sulfonic acids. DT50 in soil c. 20 d (field). Koc 121-309.
|