|
methoprene
Insecticide
IRAC 7A; juvenile hormone mimic
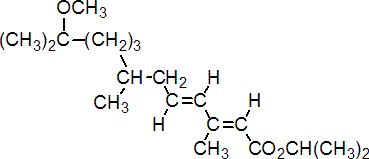
NOMENCLATURE
Common name methoprene (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, ESA)
IUPAC name isopropyl (E,E)-(RS)-11-methoxy-3,7,11-trimethyldodeca-2,4-dienoate
Chemical Abstracts name (E,E)-(?-1-methylethyl 11-methoxy-3,7,11-trimethyl-2,4-dodecadienoate; isopropyl (2E,4E,7S)-11-methoxy-3,7,11-trimethyl-2,4-dodecadienoate (for (S)-isomer)
Other names (S)-methoprene (refers to the resolved (S)- enantiomer) CAS RN [40596-69-8] (E,E)- isomers; [41205-06-5] (E,E)-(?- isomers; [65733-16-6] (E,E)-(S)- isomer; [65733-17-7] (E,E)-(R)- isomer Development codes ZR 515 (Sandoz); SAN 800 (Sandoz); SAN 810 (Sandoz) for (S)-methoprene Official codes OMS 1697
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Except where indicated otherwise, all data refer to the (RS)- (E,E)- isomer pair. Mol. wt. 310.5 M.f. C19H34O3 Form Tech. is a pale yellow liquid, with a fruity odour. B.p. 256 °C; 100 ºC/0.05 mmHg; ((S)-methoprene >262 °C) V.p. 0.79 mPa (25 °C, gas saturation method); a separate determination gave 3.15 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP >6 Henry 4.76 ´ 10-1 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 0.924 (20 °C), 0.921 (25 ºC) Solubility In water 0.76 mg/l (20 °C); ((S)-methoprene) 6.85 mg/l (20 °C). Miscible with all common organic solvents. Stability Stable in water, organic solvents, and in the presence of aqueous acids and alkalis. Sensitive to u.v. light. Specific rotation [a]20D = +5.64 ((S)-methoprene) F.p. 136 ºC (closed cup)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insect growth regulator reported by C. A. Henrick et al. (J. Agric. Food Chem., 1973, 21, 354). Introduced by Zoecon Corp., acquired by Sandoz AG (later Novartis Crop Protection AG), and transferred to Novartis Animal Health and Wellmark International. Patents US 3904662; US 3912815 Manufacturers Bábolna; Wellmark
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Acts as an insect juvenile hormone analogue that inhibits insect maturation processes. Mode of action Insect growth regulator (juvenile hormone analogue), preventing metamorphosis to viable adults when applied to egg and larval stages. Uses Control of many insect pests (especially Diptera and Pharaoh's ants, but also Coleoptera, Homoptera and Siphonaptera) in public health, stored commodities (including tobacco), food handling, processing and storage establishments, mushroom houses, on animals, and on plants (including glasshouse plants). Particular uses include control of mosquito larvae; sciarid flies in mushroom houses; cigarette beetles and tobacco moths in stored tobacco; Pharaoh's ants; leaf miners on glasshouse chrysanthemums; stored product pests in food and tobacco processing plants and warehouses; etc. Formulation types AE; AL; AP; CS; EC; GR; RB; SL. Selected products: 'Altosid' (Wellmark); 'Biopren-BM' (name also used for (S)- isomer.) (Bábolna); 'Ovitrol' (Wellmark)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Apex' (Wellmark, Novartis A H); 'Biosid' ((S)- isomer) (Zanus); 'Diacon' (Wellmark); 'Dianex' (Wellmark); 'Extinguish' (Wellmark); 'Fleatrol' (Wellmark); 'Kabat' (Wellmark); 'Pánik-B' (Bábolna); 'Pharorid' (Wellmark); 'Precor' (Wellmark); 'Siphotrol' (Wellmark); 'Ticktox-BT' (Bábolna)
ANALYSIS
Product and residue analysis by gc-ms.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 92, 94 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). CODEX (1984). EPA FR 59:11570 (11 Mar 94). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >5000 mg/kg, ((S)- isomer >5050 mg/kg). Non-irritating to eyes, moderately irritating ((S)- isomer slightly irritating) to skin (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 for rats >4.94 mg/l, ((S)- isomer >2.38 mg/l). NOEL In 2 y feeding trials, rats receiving 5000 mg/kg diet and mice receiving 2500 mg/kg diet showed no ill-effects. No teratogenic effects on rats at 1000 mg/kg and on rabbits at 500 mg/kg. No mutagenic effects on rats at 2000 mg/kg. No reproductive adverse effects in 3-generation reproduction studies on rats at 500 ppm diet. ADI (JMPR) (racemate) 0.09 mg/kg b.w.; (S-methoprene) 0.05 mg/kg b.w. [2001]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Dietary LC50 (8 d) for chickens >4640 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for trout >0.37 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 89 mg/l. Algae EC50 (48-96 h) for Scenedesmus subspicatus 1.33 mg/ml. Other aquatic spp. Toxic to aquatic Diptera. Bees Non-toxic to adult bees; LD50 (oral and topical) >1000 mg/bee. Bee larvae are sensitive at 0.2 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, the secondary metabolite cholesterol has been identified. Plants In plants, degradation principally involves ester hydrolysis, O-demethylation, and oxidative cleavage of the double bond at the 4-position. In alfalfa and rice, the principal metabolite is 7-methoxycitronellal. Soil/Environment In soil, rapidly degraded, under aerobic and anaerobic conditions, DT50 c. 10 d; CO2 is the major product.
|