|
methiocarb
Molluscicide, insecticide, acaricide, bird repellent
IRAC 1A; carbamate
NOMENCLATURE
Common name methiocarb (BSI, Canada, New Zealand, Republic of South Africa, Turkey, ESA, E-ISO); methiocarbe ((m) F-ISO); mercaptodimethur (alternative name, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, France, Germany); no name (Eire, USA)
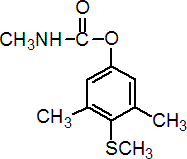
IUPAC name 4-methylthio-3,5-xylyl methylcarbamate
Chemical Abstracts name 3,5-dimethyl-4-(methylthio)phenyl methylcarbamate
CAS RN [2032-65-7] EEC no. 217-991-2 Development codes Bayer 37 344; H 321 (Bayer) Official codes OMS 93; ENT 25 726
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 225.3 M.f. C11H15NO2S Form Colourless crystals, with a phenol-like odour. M.p. 119 ºC V.p. 0.015 mPa (20 ºC); 0.036 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 3.08 (20 °C) Henry 1.2 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (20 °C) S.g./density 1.236 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 27 mg/l (20 ºC). In dichloromethane >200, isopropanol 53, toluene 33, hexane 1.3 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Unstable in highly alkaline media. Hydrolysis DT50 (22 ºC) >1 y (pH 4), <35 d (pH 7), 6 h (pH 9). Photodegradation contributes to the overall elimination of methiocarb from the environment; DT50 6-16 d.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by G. Unterstenhöfer (Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. (Engl. Ed.), 1962, 15,181). Introduced by Bayer AG in 1962. Patents FR 1275658; DE 1162352 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Molluscicide with neurotoxic action. Non-systemic insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. Uses Control of slugs and snails in a wide range of agricultural situations. Broad-range control of Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, Diptera, Thysanoptera and Homoptera (including soil insects), and spider mites in pome fruit, stone fruit, citrus fruit, strawberries, hops, potatoes, beet, maize, oilseed rape, vegetables, and ornamentals. Used as seed treatment for control of frit flies on maize, flea beetles on oilseed rape, and leaf miners on beet; and also acts as a bird repellent. Phytotoxicity May lead to fruit thinning on apple trees, if applied earlier than four weeks after petal fall. Formulation types DP; GB; RB; SC; WP; Seed treatment. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Draza' (Bayer CropScience); 'Mazda' (Barclay); 'Mesurol' (Bayer CropScience, Gowan); 'Poacher' (Barclay)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Decoy Wetex' (Bayer CropScience); 'Exit' (Bayer CropScience); 'Huron' (Bayer CropScience); 'Karan' (Bayer CropScience); 'Lupus' (Bayer CropScience); 'Rivet' (Bayer CropScience)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by rplc (CIPAC Handbook, 1988, D, 130; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 984.10). Residues determined by rplc (ibid., 985.23) or by glc (M. C. Bowman & M. Beroza, J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem.,1969, 52, 1054; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M2, M13). Methods for the determination of residues are available from Bayer CropScience. In drinking water, by rplc and fluorimetry of liberated methylamine (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 991.06).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 83, 85 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats c. 33, female rats c. 47, mice 52-58, guinea pigs c. 40, dogs 25 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male and female rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >0.3 mg/l air (aerosol); c. 0.5 mg/l (dust). NOEL In 2 feeding trials, NOEL for rats and mice 67, dogs 5 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.02 mg/kg b.w. [1998]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ib; EPA (formulation) I EC classification T; R25| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for male mallard ducks 7.1-9.4, Japanese quail 5-10 mg/kg. LC50 (7 d) for bobwhite quail: no signs of toxicity as birds were repelled by 'Mesurol'. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 0.754, rainbow trout 0.436-4.7, golden orfe 3.8 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.019 mg/l. Algae ErC50 for Scenedesmus subspicatus 1.15 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees (depending on mode of application). Worms LC50 for Eisenia foetida >200 mg/kg dry soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 64 (WHO, 1986; a review of carbamate insecticides in general). Animals In dogs and mice, following oral administration, methiocarb is rapidly absorbed and excreted, principally in the urine, with only a small proportion in the faeces. Metabolism involves hydrolysis, oxidation, and hydroxylation, followed by excretion in free or conjugated form. There is a continuous decrease of activity in all organs. Metabolism of carbamate insecticides is reviewed (M. Cool & C. K. Jankowski in "Insecticides"). Plants In plants, the methylthio group is oxidised to sulfoxide and sulfone, with hydrolysis to the corresponding thiophenol, methylsulfoxide-phenol, and methylsulfonyl-phenol (M. C. Bowman & M. Beroza, J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1969, 52, 1054-1063). Soil/Environment Degradation in soil is rapid. The important metabolites are methylsulfinylphenol and methylsulfonylphenol.
|