|
methidathion
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 1B; organophosphate
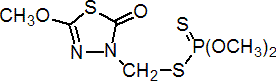
NOMENCLATURE
Common name methidathion (BSI, E-ISO, F-ISO, ANSI, ESA); DMTP (JMAF)
IUPAC name S-2,3-dihydro-5-methoxy-2-oxo-1,3,4-thiadiazol-3-ylmethyl O,O-dimethyl phosphorodithioate; 3-dimethoxyphosphinothioylthiomethyl-5-methoxy-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3H)-one
Chemical Abstracts name S-[(5-methoxy-2-oxo-1,3,4-thiadiazol-3(2H)-yl)methyl] O,O-dimethyl phosphorodithioate
CAS RN [950-37-8] EEC no. 213-449-4 Development codes GS 13 005 (Geigy) Official codes OMS 844; ENT 27 193
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 302.3 M.f. C6H11N2O4PS3 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 39-40 ºC V.p. 2.5 ´ 10-1 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 2.2 (OECD 107) Henry 3.3 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.51 (20 ºC) (OECD 109) Solubility In water 200 mg/l (25 ºC). In ethanol 150, acetone 670, toluene 720, hexane 11, n-octanol 14 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Rapidly hydrolysed in alkaline and strongly acidic media; DT50 (25 ºC) 30 min at pH 13. Relatively stable to hydrolysis in neutral and slightly acidic media.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by H. Grob et al. (Proc. Br. Insectic. Fungic. Conf., 3rd, 1965, p. 451). Introduced by J. R. Geigy S.A. (now Syngenta AG). Patents BE 623246; GB 1008451 Manufacturers Makhteshim-Agan; Sannong; Sharda; Sundat; Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. Uses Control of a wide range of sucking and chewing insects (especially scale insects) and spider mites in many crops, e.g. pome fruit, stone fruit, citrus fruit, vines, olives, hops, cotton, potatoes, beet, alfalfa, oilseed rape, maize, sunflowers, safflowers, tobacco, hazels, and some vegetables, at 30-60 g/hl (0.3-1.8 kg/ha). Formulation types EC; UL; WP. Compatibility Mixing with alkaline materials may reduce effectiveness. Selected products: 'Supracide' (Syngenta, Gowan); 'Ultracide' (Syngenta); 'Suprathion' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Ultracidin' (Vapco)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Oleo Supracide' (Syngenta); 'Oleo Ultracide' (Syngenta); 'Ultracid' (Syngenta); 'Advathion' (Chemvet); 'Mediatex' (Aragro); 'Siacide' (Siapa) mixtures: 'Maktion' (+ dimethoate) (Makhteshim-Agan)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc. Residues determined by glc (A. Ambrus et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1981, 64, 773; Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, 6, S8, S13, S19; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M2, M5, M12; D. O. Eberle & R. Suter, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1976, 8, 141).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 80, 82 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 25-54, mice 25-70, rabbits 63-80, guinea pigs 25 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits 200, rats 297-1663 mg/kg. Non-irritating to eyes and skin (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (Buehler test). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 140 mg/m3 air. NOEL Human volunteers tolerated daily oral doses of up to 0.11 mg/kg for at least 42 d without reaction. In 2 y feeding trials, NOEL for rats 4 mg/kg diet (0.2 mg/kg daily), for dogs 0.25 mg/kg daily. ADI 0.001 mg/kg b.w. [1997]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ib; EPA (formulation) I EC classification T+; R28| Xn; R21| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks 23.6-28 mg/kg. LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail 224 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.01, bluegill sunfish 0.002 mg/l. Algae EC50 (72 h) for Scenedesmus subspicatus 22 mg/l. Bees Slightly toxic to bees. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms 5.6 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. To be rated as detrimental to most beneficial arthropods in the short term. It has a limited surface residual effect which allows a re-immigration of beneficials from untreated parts.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals In mammals, methidathion is rapidly metabolised and excreted. Plants In plants, rapid metabolism occurs. The overall metabolic pattern indicates hydrolysis of the ester bond, cleavage of the heterocyclic moieties into fragments which are further oxidised to CO2. Soil/Environment Methidathion and its metabolites have a low mobility in soils. The compound is rapidly degraded in soil and water by chemical, photolytic and biological processes. DT50 3-18 d (laboratory and field results).
|