|
methamidophos
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 1B; organophosphate
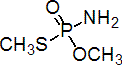
NOMENCLATURE
Common name methamidophos (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI)
IUPAC name O,S-dimethyl phosphoramidothioate
Chemical Abstracts name O,S-dimethyl phosphoramidothioate
Other names acephate-met CAS RN [10265-92-6] EEC no. 233-606-0 Development codes Ortho 9006 (Chevron); Bayer 71 628; SRA 5172 (Bayer) Official codes ENT 27 396
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 141.1 M.f. C2H8NO2PS Form Colourless crystals, with a mercaptan-like odour. M.p. 45 °C (purified a.i.) B.p. decomp. >160 °C V.p. 2.3 mPa (20 ºC); 4.7 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = -0.8 (20 °C) Henry <1.6 ´ 10-6 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc., 20 °C) S.g./density 1.27 (20 ºC) Solubility In water >200 g/l (20 ºC). In isopropanol >200, dichloromethane >200, hexane 0.1-1, toluene 2-5 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Stable at ambient temperature, but decomposes on heating without boiling. Stable at pH 3-8. Hydrolysed in acids and alkalis, DT50 (22 ºC) 1.8 y (pH 4), 110 h (pH 7), 72 h (pH 9). Photodegradation is of minor importance. F.p. c. 42 °C (EU A9/ASTN-D56)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by I. Hammann (Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. (Engl. Ed.), 1970, 23, 133). Introduced by Chevron Chemical Co. and by Bayer AG. Patents US 3309266; DE 1210835 to Bayer Manufacturers Bayer CropScience; CAC; Crystal; Jin Hung; Jingma; Pilarquim; Q.E.A.C.A.; Reposo; Sannong; Sanonda; Sinon; Sundat; Taiwan Tainan Giant; Tekchem; Westrade
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Systemic insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. Absorbed by the roots and leaves. Uses Control of chewing and sucking insects, and spider mites on ornamentals, potatoes, pome fruit, stone fruit, citrus fruit, vines, hops, brassicas, beet, cotton, maize, tobacco, and other crops. Applied at 0.3-1.2 kg/ha. Formulation types SL. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Cekumidofos' (Cequisa); 'Giant' (Sanonda); 'Lucamet' (Inquiport); 'Matón' (Ingeniería Industrial); 'Methaphos' (Efthymiadis); 'Monitor' (Bayer CropScience, Arvesta, Valent); 'MTD-600' (Westrade); 'Patrole' (Reposo); 'Pilaron' (Pilarquim); 'Rometa' (Rotam); 'Tamaron' (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Afitox T' (Siapa); 'Agromon' (AgroSan); 'Bullet' (CAS); 'Citrimet' (Plaaskem S.A.); 'Meta' (Agricultura Nacional); 'Metasint' (Westrade); 'Nitofol' (Bayer CropScience); 'Sherman' (Chemiplant); 'Tamanox' (Crystal); 'Themanitar' (Sanonda) mixtures: 'Ninja' (+ cypermethrin) (Reposo) Discontinued products: 'Jiaanlin' * (Shenzhen Jiangshan); 'Orthotox' * (Schering) mixtures: 'Taifun' * (+ imidacloprid) (Turkey) (Bayer)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by rplc (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 992.01; CIPAC Handbook, 1992, E, 139-144), by i.r. spectrometry or by glc (J. B. Leary, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1973, 7, 339). Residues determined by glc with FID (idem, ibid.; Manu. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, 6, S19; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M5; M. A. Luke et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1981, 64, 1187; A. Ambrus et al., ibid., p. 733). Details available from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 59, 61 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 15.6, female rats 13.0 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male rabbits 122, female rabbits 69 mg/kg. Not irritating to skin; slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for male and female rats (nose only) 213 mg/m3. NOEL (1 y) for dogs 0.06 mg/kg b.w. daily; (2 y) for rats 0.1 mg/kg b.w. daily; (2 y) for mice 0.7-0.8 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.004 mg/kg b.w. [1990]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ib; EPA (formulation) I EC classification T+; R28| T; R24| Xi; R36| N; R50 PIC SL formulations of the substance which exceed 600 g a.i./l are included
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 10 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite 42, Japanese quail 92, mallard ducks 1302 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h, static) for rainbow trout 25, bluegill sunfish (static) 34, sheepshead minnow 5.6 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 0.27 mg/l. Algae ErC50 (96 h, static) for Scenedesmus subspicatus >178 mg/l. Bees Toxic to bees. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida 44 mg/kg dry soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals In rats and farm animals, radiolabelled methamidophos was absorbed rapidly and distributed uniformly among all organs and tissues. More than half of the radioactivity was rapidly eliminated from the body, mainly via urine and respiratory air. Radioactivity remaining in the animal was incorporated into endogenous compounds (carbon-1 pool) and eliminated with the natural turnover of these compounds. Metabolism in the rat was by deamination and demethylation. Plants After treatment with methamidophos via the roots, the a.i. was taken up rapidly and translocated into the leaves with the transpiration flow. However, a more prolonged uptake via the roots cannot be expected because of rapid degradation in soil. After foliar treatment, methamidophos was taken up rapidly; however, there was little translocation into untreated parts of the plant. Soil/Environment Rapidly degraded in soil; field DT50 c. <2 d. In water, DT50 5-27 d (pH 7); photolysis may contribute to degradation. Rapidly degraded in air, DT50 0.578 d.
|