|
metalaxyl-M
Fungicide
FRAC 4, A1; phenylamide: acylalanine
NOMENCLATURE
Common name metalaxyl-M (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO)
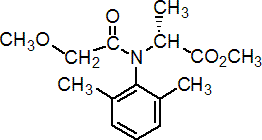
IUPAC name methyl N-(methoxyacetyl)-N-(2,6-xylyl)-D-alaninate; methyl (R)-2-{[(2,6-dimethylphenyl)methoxyacetyl]amino}propionate
Chemical Abstracts name methyl N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N-(methoxyacetyl)-D-alaninate
Other names R-metalaxyl; CGA 76539; mefenoxam (only in USA) CAS RN [70630-17-0] Development codes CGA 329351 (Ciba-Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition (R)- enantiomer of metalaxyl. Mol. wt. 279.3 M.f. C15H21NO4 Form Pale yellow to light brown, viscous liquid. M.p. -38.7 °C (glass transition temperature) B.p. Decomp. c. 270 °C V.p. 3.3 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 1.71 (25 °C) Henry 3.5 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.125 (20 °C) Solubility In water 26 g/l (25 °C). In n-hexane 59 g/l; miscible with acetone, ethyl acetate, methanol, dichloromethane, toluene, n-octanol. Stability Hydrolytically stable under acidic and neutral conditions (DT50 >200 d). Under alkaline conditions, DT50 116 d (pH 9, 25 °C). Specific rotation Negative F.p. 179 °C (EEC A10)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by C. Nuninger et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1996, 1, 41). Developed by Ciba-Geigy AG (now Syngenta AG) and introduced in the US in 1996. Patents PCT Patent appl. WO96/01559; ZA-P.95/5708 Manufacturers Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits protein synthesis in fungi, by interference with the synthesis of ribosomal RNA. The (R)- (metalaxyl-M) and (S)- isomers have the same mode of action, but differ considerably in effectiveness. Mode of action Systemic fungicide with protective and curative action, absorbed through the leaves, stems, and roots. Uses To control diseases caused by air- and soil-borne Peronosporales on a wide range of temperate, subtropical and tropical crops. Foliar sprays with mixtures of metalaxyl-M and protectant fungicides are recommended to control air-borne diseases caused by Pseudoperonospora humuli on hops, Phytophthora infestans on potatoes and tomatoes, Peronospora tabacina on tobacco, Plasmopara viticola on vines, downy mildews of vegetables, and Bremia lactucae on lettuce, at 100-140 g metalaxyl-M/ha. Soil applications of metalaxyl-M alone are used to control soil-borne pathogens causing root and lower stem rots on avocado and citrus, Phytophthora nicotianae on tobacco, Phytophthora spp. on peppers, and Pythium spp. on many different crops, including ornamentals, at 250-1000 g/ha. Seed treatments control systemic Peronosporaceae on maize, peas, sorghum and sunflowers, at 35 - 300 g/100 kg seed, as well as damping-off (Pythium spp.) of various crops, at 8.25-17.5 g/100 kg seed. Formulation types DS; EC; FS; GR; SC; WG; WP. Selected products: 'Apron XL' (Syngenta); 'Ridomil Gold' (Syngenta); mixtures: 'Maxim XL' (+ fludioxonil) (seed treatment) (Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Mefenoxam' (Syngenta); 'SL 567A' (Syngenta); 'Ultra Flourish' (Nufarm Americas) mixtures: 'Apron Maxx' (+ fludioxonil) (Syngenta); 'Bion MX' (+ acibenzolar-S-methyl) (Syngenta); 'Dividend XL' (+ difenoconazole) (Syngenta); 'Epok' (+ fluazinam) (Syngenta); 'Folio Gold' (+ chlorothalonil) (Syngenta); 'Fubol Gold' (+ mancozeb) (Syngenta); 'Helix' (+ thiamethoxam+ difenoconazole+ fludioxonil) (Syngenta); 'Mefenoxam MZ' (+ mancozeb) (Syngenta); 'Mefenoxam PC' (+ quintozene) (Syngenta); 'Ridomil Gold Combi' (+ folpet) (Syngenta); 'Ridomil Gold Copper' (+ copper hydroxide) (Syngenta); 'Ridomil Gold MZ' (+ mancozeb) (Syngenta); 'Ridomil Gold PC' (+ quintozene) (Syngenta); 'Ridomil Gold Plus' (+ copper oxychloride) (Syngenta); 'Wakil XL' (+ cymoxanil+ fludioxonil) (Syngenta); 'Flouronil' (+ chlorothalonil) (Nufarm Americas)
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 667 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Not a skin irritant (rabbits); risk of serious damage to eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >2290 mg/m3. NOEL for rats 2.5, mice 35.7, dogs 8.0 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.025 mg/kg b.w. Other Not oncogenic, not mutagenic, not teratogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II (company classification) EC classification Xn; R22| Xi; R41
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LD50 (14 d) for bobwhite quail 981-1419 mg/kg. LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail >5620 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout >100 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >100 mg/l. Algae ErC50 (72 h) for Scenedesmus subspicatus 103 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (96 h) for Eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) 9.7 mg/l. Bees LD50 (48 h, contact) 25 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida 830 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. EC formulation (480 g/l ) harmless to Poecilus cupreus and Orius insidiosus (IOBC).
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, following oral administration, rapidly absorbed and also rapidly and almost completely eliminated in urine and faeces. Metabolism proceeds via hydrolysis of the ester bond, oxidation of the 2-(6)-methyl group and of the phenyl ring and N-dealkylation. Residues in tissues were generally low and there was no evidence for accumulation or retention of metalaxyl-M or its metabolites. Plants Metabolised by more than 4 types of phase I reaction (oxidation of the phenyl ring, oxidation of the methyl group, cleavage of the methyl ester and N-dealkylation) to form eight metabolites; at phase II, most of the metabolites are sugar conjugated. Soil/Environment DT50 in soil 21 d (realistic range 5-30 d). Koc 45 ml/g (realistic range 30-300 ml/g). Stable to photolysis.
|