|
mesotrione
Herbicide
HRAC F2 WSSA 28; triketone
NOMENCLATURE
Common name mesotrione (BSI, pa ISO)
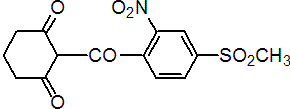
IUPAC name 2-(4-mesyl-2-nitrobenzoyl)cyclohexane-1,3-dione
Chemical Abstracts name 2-[4-(methylsulfonyl)-2-nitrobenzoyl]-1,3-cyclohexanedione
CAS RN [104206-82-8] Development codes ZA 1296 (Zeneca)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 339.3 M.f. C14H13NO7S M.p. 165 °C V.p. 5.69 ´ 10-3 mPa (20 °C). Henry <5.1 ´ 10-7 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) Solubility In water 2.2 (pH 4.8), 15 (pH 6.9), 22 (pH 9) (all in g/l, 20 °C). Stability Stable to hydrolysis (pH 4 - 9). pKa 3.12
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by R. A. Wichert et al., Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1999, 1, 105. See also J. Dyson et al., Proc. 9th IUPAC Int. Congr. Pestic. Chem., London, 1998, 2, 6A-021. Developed by Syngenta AG and first registered in 2001. Manufacturers Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry p-Hydroxyphenyl pyruvate dioxygenase inhibitor, which ultimately affects carotenoid biosynthesis. Selectivity in maize derives from differential metabolism (to the 4-hydroxy derivative) and also possibly from slower foliar uptake. Mode of action Uptake is foliar and via the root, with both acropetal and basipetal translocation. Symptoms are whitening of leaves, followed by necrosis of the meristematic tissue. Uses Under development for pre- (at 100-225 g/ha) and post- (at 70-150 g/ha) emergence control of broad-leaved weeds, such as Xanthium strumarium, Ambrosia trifida, Abutilon theophrasti, and Chenopodium, Amaranthus and Polygonum spp., and some grass weeds, in maize. Formulation types SC. Selected products: mixtures: 'Callisto' (+ atrazine) (Syngenta); 'Camix' (+ S-metolachlor+ benoxacor) (Syngenta); 'Lumax' (+ S-metolachlor+ benoxacor) (Syngenta)
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male and female rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male and female rats >2000 mg/kg. Practically non-irritant to skin, mild irritant to eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for male and female rats >5 mg/l. ADI 0.01 mg/kg b.w. (proposed)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2000, mallard ducks >5200 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish and rainbow trout >120 mg/l. Daphnia L(E)C50 (48 h, static) 900 mg/l. Algae L(E)C50 (72 h, static) for Selenastrum capricornutum 4.5 mg/l. Worms NOEL ³1000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Key metabolites in animals, plants and soil include MNBA [4-(methylsulfonyl)-2-nitrobenzoic acid] and AMBA [2-amino-4-(methylsulfonyl)benzoic acid] Soil/Environment Stable to hydrolysis under sterile conditions at pH 5-9, with <10% degradation after 30 d (25 °C). Aqueous photolysis DT50 (sterile) 84 d. Soil adsorption is significantly influenced by pH and % o.c; Koc 387 (soil pH 4.6) to 19 (pH 7.7); Kd is linear with % o.c and ranges from 1-5. Degradation is influenced by soil pH; DT50 31.5 d (pH 5.0, % o.c. 2.0) to 4.0 d (pH 7.7, % o.c. 0.9). Environmental fate may be determined by soil pH and half-life as the only important parameters. See R. A. Wichert et al., Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1999, 1, 105; and J. Dyson et al., Proc. 9th IUPAC Int. Congr. Pestic. Chem., London, 1998, 2, 6A-021.
|