|
mepanipyrim
Fungicide
FRAC 9, D1; anilinopyrimidine
NOMENCLATURE
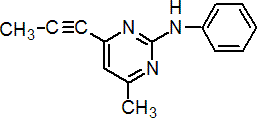
Common name mepanipyrim (BSI, draft E-ISO)
IUPAC name N-(4-methyl-6-prop-1-ynylpyrimidin-2-yl)aniline
Chemical Abstracts name 4-methyl-N-phenyl-6-(1-propynyl)-2-pyrimidinamine
CAS RN [110235-47-7] Development codes KUF-6201; KIF-3535 (Kumiai)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is >94%. Mol. wt. 223.3 M.f. C14H13N3 Form White crystals/powder. M.p. 132.8 °C V.p. 2.32 ´ 10-2 mPa (20 °C) KOW logP = 3.28 (20 °C) Henry 1.67 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.2025 Solubility In water 3.10 mg/l (20 °C). In acetone 139, methanol 15.4, n-hexane 2.06 (all in g/l, 20 °C). Stability Stable in water (DT50 >1 y at pH 4-9). Stable to heat (no change over 14 d at 55 °C). Stable to light in water (DT50 12.9 d).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide discovered in 1985 and reported by Kumiai Chemical Industry Co., Ltd (S. Maeno et al.,Proc. 1990 Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 2, 415). Introduced by Kumiai and Ihara Chemical Industry Ltd in 1995. Patents US 4814338; EP 224339; JP 63208581 Manufacturers Ihara/Kumiai
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Proposed inhibitor of methionine biosynthesis, leading to inhibition of secretion of pathogen proteins such as the cell-wall degrading enzyme pectinase. Also inhibits uptake by the pathogen of amino acids, glucose, etc. Mode of action Non-systemic fungicide with preventative action. Inhibits penetration of pathogen into host plant, germ tube elongation and formation of appressorium. No inhibition of spore germination, spore formation and hyphal growth. Uses Control of grey mould on vines, strawberries, tomatoes and cucumbers; scab on apples and pears; and brown rot on peaches, at 0.2-0.75 kg/ha. Control of powdery mildew on strawberries, cucumbers, aubergines, persimmons, and roses, at 0.14 - 0.6 kg/ha. Formulation types SC; WP. Selected products: 'Cockpit' (Kumiai); 'Frupica' (Kumiai); 'Japica' (Kumiai)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Discontinued products: 'Fulpica' * (Kumiai)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc. Residue analysis by glc with NPD. Details from Kumiai.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats and mice >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Non-sensitising to skin (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h, whole body) for rats >0.59 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for male rats 2.45, female rats 3.07, male mice 56, female mice 68 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.024 mg/kg. Other Non-mutagenic, non-teratogenic (rats, rabbits). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >2250 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 3.8, rainbow trout 3.1 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (24 h) for D. carinata 5.0 mg/l. Algae EC50 (96 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 1.3 mg/l. Bees LC50 (oral) >1000 mg/l diet; (contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida >1000 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, 96-100% of the dose was excreted via faeces and urine within 96 h. Mepanipyrim was degraded into several metabolites. Plants Major metabolites were 2-hydroxypropyl-, 2,3-dihydroxypropyl- and 4-hydroxyphenyl- derivatives of mepanipyrim.
|