|
malathion
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 1B; organophosphate
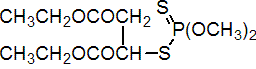
NOMENCLATURE
Common name malathion (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ESA, BAN); maldison (Australia, New Zealand); malathon (JMAF); mercaptothion (South Africa); carbofos (USSR); no name (Germany); mercaptotion (Argentina)
IUPAC name diethyl (dimethoxythiophosphorylthio)succinate; S-1,2-bis(ethoxycarbonyl)ethyl O,O-dimethyl phosphorodithioate
Chemical Abstracts name diethyl [(dimethoxyphosphinothioyl)thio]butanedioate
CAS RN [121-75-5] EEC no. 204-497-7 Development codes EI 4049 (Cyanamid) Official codes OMS 1; ENT 17 034
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. grade is c. 95% pure. Mol. wt. 330.4 M.f. C10H19O6PS2 Form Tech. is a clear, amber liquid. M.p. 2.85 ºC B.p. 156-157 ºC/0.7 mmHg. V.p. 5.3 mPa (30 ºC) KOW logP = 2.75 Henry 1.21 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.23 (25 ºC) Solubility In water 145 mg/l (25 ºC). Miscible with most organic solvents, e.g. alcohols, esters, ketones, ethers, aromatic hydrocarbons. Slightly soluble in petroleum ether and some types of mineral oil. Stability Relatively stable in neutral, aqueous media. Decomposed by strong acids and by alkali; hydrolysis DT50 107 d (pH 5), 6 d (pH 7), 0.5 d (pH 9) (all 25 °C); F.p. 163 °C (Pensky-Martens closed cup)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by G. A. Johnson et al. (J. Econ. Entomol., 1952, 45, 279). Introduced by American Cyanamid Co.; rights transferred to Cheminova in 1991. Patents US 2578652 Manufacturers Agrochem; Aimco; Cheminova; Ficom; Hindustan; Lucava; Sharda; Sinochem Ningbo; Tekchem
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor; proinsecticide, activated by metabolic oxidative desulfuration to the corresponding oxon. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide and acaricide with contact, stomach, and respiratory action. Uses Used to control Coleoptera, Diptera, Hemiptera, Hymenoptera and Lepidoptera in a wide range of crops, including cotton, pome, soft and stone fruit, potatoes, rice and vegetables. Used extensively to control major arthropod disease vectors (Culicidae) in public health programmes, ectoparasites (Diptera, Acari, Mallophaga) of cattle, poultry, dogs and cats, human head and body lice (Anoplura), household insects (Diptera, Orthoptera), and for the protection of stored grain. Typical application rates for agricultural uses 0.5-1.25 kg/ha. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic in general, if used as recommended, but glasshouse cucurbits and beans, certain ornamentals, and some varieties of apple, pear, and grape may be injured. Formulation types DP; EC; EW; UL; WP. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials (residual toxicity may be decreased). Selected products: 'Fyfanon' (Cheminova, Helena); 'Cekumal' (Cequisa); 'Devimalt' (Devidayal); 'Dustrin' (Vapco); 'Hilmala' (Hindustan); 'Hilthion' (Hindustan); 'Kemavert' (Kemio); 'Lucathion' (Lucava); 'Malathane' (Agriphar); 'Malatox' (Pesticides India, Caffaro); 'Maltox' (Aimco); 'MLT' (Sumitomo); 'Mythion' (Crop Health); 'White Star' (Sanonda)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Cythion' (BASF, Helena); 'Malathon' (BASF); 'Admal' (public health) (Chemvet); 'Agrothion' (Agrochem); 'Atrapa' (Griffin); 'Avepol' (Agricultura Nacional); 'Dipamal' (Papaeconomou); 'Krishi Mathion' (Krishi Rasayan); 'Lupara' (Chemiplant); 'Malac' (Chemia); 'Malixol' (Bayer CropScience); 'Ramathion' (Krishi Rasayan); 'Sunbugger' (Sungro); 'Vap-Malathion' (Vapco) mixtures: 'B.W.A.C.T.' (+ grandlure) (Plato); 'TMP' (+ grandlure) (Plato) Discontinued products: 'Malagran' * (Cyanamid); 'Malatol' * (Cyanamid); 'Celthion' * (Excel)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc (CIPAC Handbook, 1983, 1B, 1849; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 979.05). Residues determined by glc, with TID or FPD, by tlc, by paper chromatography, or by single sweep oscillographic polarography (ibid., 957.15*, 968.24*, 970.52, 970.53*; Pestic. Anal. Man., 1979, I, 201-A, 201-G, 201-H, 201-I; Analyst (London), 1973, 98, 19; 1977, 102, 858; 1980, 105, 515; 1985, 110, 765; Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, 3,5, 6, S8, S10, S13, S17, S19; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M2, M5, M10).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 80, 82 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). IARC ref. 30 class 3 Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 1375-5500 mg/kg (pure), mice 775-3320 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 (24 h) for rabbits 4100-8800, rats >2000 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.2 mg/l. NOEL In 2 y trials on rats, the only effects seen at 500 ppm (29 mg/kg b.w. daily) was inhibition of cholinesterase in plasma and red blood cells. ADI (JMPR) 0.3 mg/kg b.w. [1997]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III (Fyfanon tech. and 5 EC) EC classification Xn; R22
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail 3500, ring-necked pheasants 4320 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 0.1, largemouth bass 0.28 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 1.0 mg/l. Algae EC50 (72 h) 13 mg/l. Bees Toxic to bees. LD50 (topical) 0.71 mg/bee. Worms LC50 613 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals In mammals, following oral administration, the major part of the dose is excreted in the urine and faeces within 24 hours. Degradation is by oxidative desulfuration by liver microsomal enzymes, leading to the formation of malaoxon; malathion and malaoxon are hydrolysed and thus detoxified by carboxylesterases. In insects, metabolism involves hydrolysis of the carboxylate and phosphorodithioate esters, and oxidation to malaoxon. Plants De-esterified to its mono- and di- carboxylic acids, which are cleaved to yield succinic acid, which is subsequently incorporated into plant constituents. Soil/Environment Under normal conditions, it is 99% degraded by hydrolysis within 7 d.
|