|
lufenuron
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 15; benzoylurea
NOMENCLATURE
Common name lufenuron (BSI, pa E-ISO, INN)
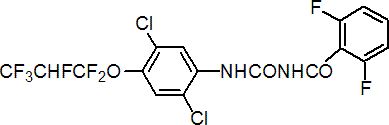
IUPAC name (RS)-1-[2,5-dichloro-4-(1,1,2,3,3,3-hexafluoropropoxy)phenyl]-3-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)urea
Chemical Abstracts name N-[[[2,5-dichloro-4-(1,1,2,3,3,3-hexafluoropropoxy)phenyl]amino]carbonyl]-2,6-difluorobenzamide
CAS RN [103055-07-8] Development codes CGA 184699 (Ciba-Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is ³98%. Mol. wt. 511.2 M.f. C17H8Cl2F8N2O3 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 168.7-169.4 °C (OECD 102) V.p. <4 ´ 10-3 mPa (25 ºC) (OECD 104) KOW logP = 5.12 (25 ºC) (OECD 117) Henry <3.41 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.66 at 20 ºC (OECD 109) Solubility In water <0.06 mg/l (25 ºC). In ethanol 41, acetone 460, toluene 72, n-hexane 0.13, n-octanol 8.9 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable in air and light. In water, DT50 32 d (pH 9), 70 d (pH 7), 160 d (pH 5). pKa >8.0
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported in poster session at RSC/SCI conference "Chemistry of Insecticides", Oxford, July 1989. Introduced by Ciba-Geigy (now Syngenta AG) in 1990. Manufacturers Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits chitin synthesis. Mode of action Acts mostly by ingestion; larvae are unable to moult, and also cease feeding. Uses Insect growth regulator for control of Lepidoptera and Coleoptera larvae on cotton, maize and vegetables; and citrus whitefly and rust mites on citrus fruit, at 10-50 g/ha. Also for the prevention and control of flea infestations on pets. Formulation types EC. Compatibility Not compatible with pesticides with alkaline reaction (lime sulfur, copper). Selected products: 'Match' (Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Axor' (Syngenta); 'Program' (Syngenta) mixtures: 'Lufox' (+ fenoxycarb) (Syngenta) Discontinued products: 'Instar' * (Ciba-Geigy)
ANALYSIS
Residue analysis by hplc. Details available from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to eyes and skin (rabbits). Non-sensitising to skin (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h, 20 ºC) for rats >2.35 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 2.0 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.01 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (company classification) EC classification R43| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >2000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5200 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout >73, carp >63, bluegill sunfish >29, catfish >45 mg/l. Daphnia Toxic to Daphnia. Algae Slightly toxic to algae. Bees LC50 (oral) >197 mg/bee. LD50 (topical) >200 mg/bee. Worms No adverse effects on earthworms.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Major route of elimination was via faeces, with very little degradation. Plants No metabolites occurred in significant amounts in the investigated target crops (cotton, tomatoes). Soil/Environment Lufenuron was rapidly degraded in biologically active soils under aerobic conditions. DT50 13-20 d. Lufenuron showed a very strong adsorption onto soil particles: Koc (mean value) 38 mg/g o.c.
|