|
linuron
Herbicide
HRAC C2 WSSA 7; urea
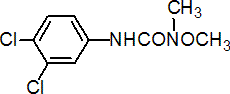
NOMENCLATURE
Common name linuron (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, WSSA, JMAF)
IUPAC name 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1-methoxy-1-methylurea
Chemical Abstracts name N'-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-N-methoxy-N-methylurea
CAS RN [330-55-2] EEC no. 206-356-5 Development codes DPX-Z326 (DuPont); AE F002810 (AgrEvo); Hoe 02 810 (Hoechst)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is ³94% pure. Mol. wt. 249.1 M.f. C9H10Cl2N2O2 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 93-95 ºC V.p. 0.051 mPa (20 ºC); 7.1 mPa (50 ºC) (EC method) KOW logP = 3.00 Henry 2.0 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (20 °C) S.g./density 1.49 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 63.8 mg/l (20 ºC, pH 7). In acetone 500, benzene, ethanol 150, xylene 130 (all in g/kg, 25 ºC). Readily soluble in dimethylformamide, chloroform, and diethyl ether. Moderately soluble in aromatic hydrocarbons. Sparingly soluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons. Stability Stable at m.p. and in aqueous solution at pH 5, 7 & 9; DT50 945 d at all three pH values.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by K. Härtel (Meded. Landbouwhogesch. Opzoekingsstn. Staat Gent, 1962, 27, 1275). Introduced by E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co. (who no longer manufacture or market it) and by Hoechst AG (now Bayer CropScience). Rights acquired by Makhteshim-Agan in 2003. Patents DE 1028986; GB 852422 both to Hoechst Manufacturers Drexel; Griffin; Makhteshim-Agan
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site. Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed principally by the roots but also by the foliage, with translocation primarily acropetally in the xylem. Uses Pre- and post-emergence control of annual grass and broad-leaved weeds, and some seedling perennial weeds, in asparagus, artichokes, carrots, parsley, fennel, parsnips, herbs and spices, celery, celeriac, onions, leeks, garlic, potatoes, peas, field beans, soya beans, cereals, maize, sorghum, cotton, flax, sunflowers, sugar cane, ornamentals, established vines, bananas, cassava, coffee, tea, rice, peanuts, ornamental trees and shrubs, and other crops. Formulation types EC; SC; WP. Selected products: 'Afalon' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Linex' (Griffin); 'Lorox' (Griffin); 'Linurex' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Siolcid' (Siapa)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Agro Kimolin' (AgroSan); 'Lincon 50' (DAPT); 'Teliron' (Chemiplant) mixtures: 'Blois' (+ trifluralin) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Linpro' (+ prometryn) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Seppic lin' (+ lenacil) (DuPont); 'Valinate' (+ chlorsulfuron) (DuPont); 'Afalon S' (+ monolinuron) (Makhteshim-Agan, Bayer CropScience); 'Alistell' (+ MCPA+ 2,4-DB) (Syngenta); 'Centaure' (+ trifluralin+ clomazone) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Chandor' (+ trifluralin) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Crescendo' (+ trifluralin+ isoxaben) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Elset Mix' (+ trifluralin+ isoxaben) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Gadisan' (+ trifluralin) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Linnet' (+ trifluralin) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Sciandor' (+ trifluralin) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Trinulan' (+ trifluralin) (Dow AgroSciences) Discontinued products: 'Linorox' * (DuPont) mixtures: 'Gemini' * (+ chlorimuron-ethyl) (DuPont); 'Lorox Plus' * (+ chlorimuron-ethyl) (DuPont); 'New Lorox Plus' * (+ chlorimuron-ethyl) (DuPont); 'Bronox' * (+ trietazine) (Schering); 'Dualin' * (+ metolachlor) (Novartis); 'Linamex' * (+ butralin) (Nufarm SA, Zeneca); 'Mudekan' * (+ trifluralin) (Dow); 'Neminfest' * (+ trifluralin) (Isagro); 'Profalon' * (+ chlorpropham) (Hortichem); 'Trifluron' * (+ trifluralin) (United Phosphorus)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc (Anal Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1982, 12). Impurities by tlc (CIPAC Handbook, 1994, F, 336). Residues determined by hplc or glc (H. L. Pease et al., Anal. Methods Pestic., Plant Growth Regul. Food Addit., 1967, 5, 433; Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1972, 6, 659; Man. Pestic. Anal. Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, 1987, 1, 241). In water, by lc with u.v. detection (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 992.14). Details available from Makhteshim-Agan.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 1500-4000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Mild skin irritant (rabbits); not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >6.15 mg/l air. NOEL (1 y) for dogs 25 ppm (0.9 mg/kg b.w.). Tumour promoter in rats. ADI 0.008 mg/kg b.w. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III EC classification R40| Xn; R22, R48/22| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 940 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducklings 3083 ppm, >5000 mg/kg (values from separate studies), ring-necked pheasants 3438 ppm, Japanese quail >5000 ppm diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 3.15, sheepshead minnow 0.89 mg/l; NOEC 0.49 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.75 mg/l, 0.12 mg/l (separate studies). Other aquatic spp. LC50 (96 h) for mysid shrimp (Mysidopsis bahia) 3.4 mg/l; NOEC 2.1 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral) >1600 mg/g bee b.w. Worms LC50 for Eisenia foetida >1000 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. Harmless to other beneficial arthropods.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals The major metabolites arise from demethylation and demethoxylation. Plants In plants, metabolism involves demethylation and demethoxylation. Soil/Environment Microbial degradation is the primary factor in disappearance from soil. Half-life under field conditions is c. 2-5 mo (F. Kempson-Jones & R. J. Hance, Pestic. Sci., 1979, 10, 449). In soil, DT50 38-67 d. Soil adsorption Koc 500-600.
|