|
isoprothiolane
Fungicide, plant growth regulator
FRAC 6, F2; dithiolane
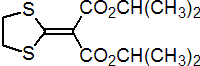
NOMENCLATURE
Common name isoprothiolane (BSI, JMAF, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO)
IUPAC name di-isopropyl 1,3-dithiolan-2-ylidenemalonate
Chemical Abstracts name bis(1-methylethyl)-1,3-dithiolan-2-ylidenepropanedioate
Other names IPT CAS RN [50512-35-1] Development codes SS 11 946; NNF-109 (both Nihon Nohyaku)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is ³96%. Mol. wt. 290.4 M.f. C12H18O4S2 Form Colourless, odourless crystals; (tech., yellow solid, with irritating smell). M.p. 54-54.5 ºC; (tech., 50-51 °C) B.p. 167-169 ºC/0.5 mmHg V.p. 18.8 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 3.3 (25 °C) Henry 0.1 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.044 Solubility In water 54 mg/l (25 ºC). In methanol 1510, ethanol 760, acetone 4060, chloroform 4130, benzene 2770, n-hexane 10 (all in g/l, 25 °C). Stability Stable to acid, alkali, light and heat.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by F. Araki et al. (Proc. Insectic. Fungic. Conf., 8th, 1975, 2, 715). Introduced by Nihon Nohyaku Co., Ltd in 1975. Manufacturers Nihon Nohyaku
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits penetration and elongation of infection hyphae, by inhibiting formation of infection peg or cellulase secretion. Mode of action Systemic fungicide with protective and curative action, absorbed by the leaves and roots, with translocation acropetally and basipetally. The mobility in rice plants of various analogues reported (M. Uchida,Pestic. Biochem. Physiol.,1980, 14, 249). Uses Controls the following pathogens and insect pests, at 400-600 g/ha (foliar spray), 3.0-6.0 g/nursery box (spreading treatment), 3.6-6.0 kg/ha (submerged treatment), 360-600 g/tree (soil incorporation): Pyricularia oryzae, Helminthosporium sigmoideum, Fusarium nivale on rice; Rosellinia necatrix on pome fruit, stone fruit and grapes; Delphacidae (planthoppers) on rice. Also used on rice to accelerate rooting, promote root elongation and control non-parasitic damping-off. Phytotoxicity Phytotoxic only to cucurbitaceae. Formulation types DP; EC; GR; WP; Driftless dust. Selected products: 'Fuji-one' (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Vifusi' (Vipesco)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Fudiolan' (Nihon Nohyaku) mixtures: 'Fuji-One Applaud Limber' (+ buprofezin+ furametpyr) (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Fuji-one Prince' (+ fipronil) (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Pika Pika' (+ pyroquilon+ fipronil) (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Vifuki' (+ iprobenfos) (Vipesco) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Fuji-One Kayaphos Oncol' * (+ propaphos+ benfuracarb) (Nihon Nohyaku)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (CIPAC Handbook, 1992, E, 105-9; T. Hattori & M. Kanauchi, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1978, 10, 229). Residues determined by glc with ECD (idem, ibid.).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 1190, female rats 1340, male mice 1340 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male and female rats >10 000 mg/kg. Slight eye irritant; not a skin irritant. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >2.7 mg/l. Other Non-mutagenic in the Ames test. In reproduction and teratogenicity studies on rats, no adverse effects were observed. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for male Japanese quail 4710, female Japanese quail 4180 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (48 h) for rainbow trout 6.8, carp 6.7 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (3 h) 62 ppm.
|