|
iprodione
Fungicide
FRAC 2, F1; dicarboximide
NOMENCLATURE
Common name iprodione (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI)
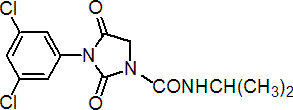
IUPAC name 3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-N-isopropyl-2,4-dioxoimidazolidine-1-carboxamide
Chemical Abstracts name 3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-N-(1-methylethyl)-2,4-dioxo-1-imidazolidinecarboxamide
Other names glycophene* (rejected common name proposal) CAS RN [36734-19-7] EEC no. 253-178-9 Development codes 26 019 RP (Rhône-Poulenc)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is ³96% pure. Mol. wt. 330.2 M.f. C13H13Cl2N3O3 Form White, odourless, non-hygroscopic crystals or powder. M.p. 134 ºC; (tech., 128-128.5 ºC) V.p. 5 ´ 10-4 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 3.0 (pH 3 and 5) S.g./density 1.00 (20 ºC); (tech., 1.434-1.435) Solubility In water 13 mg/l (20 ºC). In n-octanol 10, acetonitrile 168, toluene 150, ethyl acetate 225, acetone 342, dichloromethane 450, hexane 0.59 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Relatively stable in acid media, but decomposed in alkaline media. DT50 1-7 d (pH 7), <1 h (pH 9). Aqueous solutions are degraded by u.v. light, but are relatively stable in simulated sunlight.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by L. Lacroix et al. (Phytiatr. Phytopharm., 1974, 23, 165). Introduced by Rhône-Poulenc Agrochimie (now Bayer CropScience). Some rights, primarily in Europe, acquired by BASF AG in 2003. Patents GB 1312536; US 3755350; FR 2120222 Manufacturers BASF; Sannong; Sharda; Sinon; Sundat
APPLICATIONS
Mode of action Contact fungicide with protective and curative action. Inhibits germination of spores and growth of fungal mycelium. Uses Control of Botrytis, Monilia, Sclerotinia, Alternaria, Corticium, Fusarium, Helminthosporium, Phoma, Rhizoctonia, Typhula spp., etc. Used mainly on sunflowers, cereals, fruit trees, berry fruit, oilseed rape, rice, cotton, vegetables, and vines as a foliar spray, at 0.5-1.0 kg/ha, and on turf, at 3-12 kg/ha. Can also be used as a post-harvest dip, as a seed treatment, or as a dip or spray at planting. Formulation types DP; EC; FS; SC; SU; WG; WP. Selected products: 'Amazzones' (Rocca); 'Botrix' (Agrimix); 'Kidan' (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Rover' (Vapco); 'Rovral' (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Verisan' (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Viroval' (Vipesco)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Dirac' (Bayer CropScience, BASF) mixtures: 'Compass' (+ thiophanate-methyl) (BASF); 'Snooker' (+ thiophanate-methyl) (BASF); 'But' (+ bromuconazole) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Calidan' (+ carbendazim) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Diva' (+ chlorothalonil) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Pacha' (+ carbendazim) (Philagro); 'Premis Or' (+ triticonazole+ anthraquinone) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Vitesse' (+ carbendazim) (Bayer CropScience, BASF) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Chipco' * (+ fosetyl-aluminium) (Aventis)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by rplc or glc (CIPAC Handbook, 1995, G, 98-104; L. Lacroix et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1980, 11, 247). Residues determined by glc with ECD (idem, ibid.; Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, 6, S8, S19; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M1, M12).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 74, 76 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats and mice >2000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats and rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.16 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 150 mg/kg diet; (1 y) for dogs 18 mg/kg b.w. ADI (JMPR) 0.06 mg/kg b.w. [1995]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV EC classification R40| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2000, mallard ducks >10 400 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 4.1, bluegill sunfish 3.7 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.25 mg/l. Algae EC50 (120 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 1.9 mg/l. Bees Contact LD50 >0.4 mg/bee. Worms LC50 for earthworms >1000 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. Harmless.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, ruminants and birds, iprodione is rapidly eliminated. It also undergoes extensive metabolism, by hydrolysis and rearrangement reactions. Plants Metabolism studies in cereals, fruit, leafy and oily crops showed that iprodione is the dominant component of the total residue resulting from foliar application. Soil/Environment Rapidly metabolised in soil, with formation of CO2. DT50 (lab.) 20-80 d; (field) 20-160 d. Koc 373 to 1551. Rate of degradation increases with successive treatments, hence accumulation does not occur.
|