|
indoxacarb
Insecticide
IRAC 22; oxadiazine
NOMENCLATURE
Common name indoxacarb (BSI, pa ISO, ANSI)
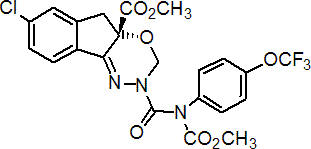
IUPAC name methyl (S)-N-[7-chloro-2,3,4a,5-tetrahydro-4a-(methoxycarbonyl)indeno[1,2-e][1,3,4]oxadiazin-2-ylcarbonyl]-4'-(trifluoromethoxy)carbanilate
Chemical Abstracts name methyl (S)-7-chloro-2,5-dihydro-2-[[(methoxycarbonyl)[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]amino]carbonyl]-indeno[1,2-e][1,3,4]oxadiazine-4a(3H)-carboxylate
CAS RN [144171-61-9] DPX-JW062; [173584-44-6] DPX-KN128 Development codes DPX-JW062; DPX-MP062; DPX-KN128; DPX-KN127 (all DuPont) (see Composition)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition DPX-JW062 is a 1:1 mixture of the (active) (S)- and (inactive) (R)- isomers; DPX-MP062 is a 3:1 mixture of these isomers. The pure (S)- isomer is referred to as DPX-KN128, the (R)- isomer as DPX-KN127. Unless otherwise stated, data refer to DPX-KN128. Mol. wt. 527.8 M.f. C22H17ClF3N3O7 Form White powder. M.p. 88.1 °C V.p. 2.5 ´ 10-5 mPa (25°C) KOW logP = 4.65 Henry 6.0 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.44 (20°C) Solubility (DPX-KN128) In water 0.20 mg/l (25 °C). In n-octanol 14.5 g/l, methanol 103 g/l, acetonitrile 139 g/l, acetone >250 g/kg (25 °C). Stability Aqueous hydrolysis DT50 >30 d (pH 5), 38 d (pH 7), 1 d (pH 9).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by H. H. Harder et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1996, 2, 449). Developed by DuPont Agricultural Products and first registered in USA and marketed in 2000. Patents WO 9211249 (1992) Manufacturers DuPont
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry DPX-KN128, the active component, blocks sodium channels in nerve cells. Mode of action Insecticide active by contact and ingestion. Affected insects cease feeding, with poor co-ordination, paralysis and ultimately death. Uses DPX-MP062 is used for broad-spectrum control of Lepidoptera in cotton, vegetables and fruit, at 12.5-125 g/ha. Formulation types SC; WG. Selected products: 'Avaunt' (DuPont); 'Steward' (DuPont)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Avatar' (DuPont); 'Rumo' (DuPont); 'Tornado' (DuPont)
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral DPX-MP062: Acute oral LD50 for male rats 1732, female rats 268 mg/kg. Skin and eye DPX-MP062: Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >5000 mg/kg. No eye or skin irritation (rabbits). Dermal sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation DPX-KN128: LC50 for rats >2 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for male rats 60, female rats 40 ppm; (18 mo) for male and female mice 20 ppm; (1 y) for male and female dogs 40 ppm. Other Negative in the Ames test.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds DPX-MP062: Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 98 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for mallard ducks >5620, bobwhite quail 808 ppm. Fish DPX-MP062: LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 0.9, rainbow trout 0.65 mg/l. Daphnia DPX-MP062: LC50 (48 h) 0.60 mg/l. Bees DPX-MP062: LD50 (oral) 23.33 mg/bee; (contact) 1.34 mg/bee. Worms DPX-MP062: LC50 (14 d) >1250 mg/kg. Other beneficial spp. DPX-KN128 had little or no adverse effects on 4 species at 30-50 g/ha; more extended studies on Episyrphus balteatus and Typhlodromus pyri described (M. Mead-Briggs et al., Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1996, 1, 307).
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Metabolism in rats after oral dosing was studied using both DPX-JW062 and DPX-MP062. Most of the dose was excreted within 96 h. Extensive metabolism to numerous minor metabolites occurs. In urine, metabolites were cleaved products (indane or trifluoromethoxyphenyl ring products), whilst in faeces, major metabolites retained both these moieties. Major metabolic reactions included hydroxylation of the indane ring, hydrolysis of the carboxymethyl group from the amino nitrogen, and opening of the oxadiazine ring, which gave rise to cleaved products. Soil/Environment DT50 17 d in tama silt loam soil. Indoxacarb is considered to be moderately persistent; aerobic DT50 3-23 d, anaerobic DT50 186 d. It is considered to be immobile; Koc 3300-9600 ml/g. DT50 for aquatic photolysis 3.0 d (pH 5.0).
|