|
imibenconazole
Fungicide
FRAC 3, G1; DMI: triazole
NOMENCLATURE
Common name imibenconazole (BSI, draft E-ISO)
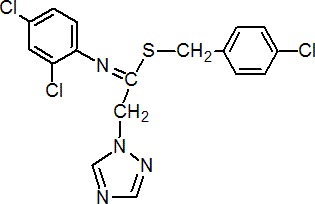
IUPAC name S-(4-chlorobenzyl) N-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)acetimidothioate
Chemical Abstracts name (4-chlorophenyl)methyl N-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-1-ethanimidothioate
CAS RN [86598-92-7] unstated stereochemistry Development codes HF-6305 (tech.); HF-8505 (formulation)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 411.7 M.f. C17H13Cl3N4S Form Pale yellowish crystals. M.p. 89.5-90 ºC V.p. 8.5 ´ 10-5 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 4.94 Solubility In water 1.7 mg/l (20 ºC). In acetone 1063, benzene 580, xylene 250, methanol 120 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable in weak alkali; unstable in acid and in strong alkali; DT50 <1 d (pH 1), 6 d (pH 5), 88 d (pH 7), 92 d (pH 9), <1 d (pH 13) (25 °C).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by H. Ohyama et al. (Abstr. 9th Annu. Meeting Pestic. Sci. Soc. Jpn., 1984, p. 120; Proc. 1988 Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 2, 519). Introduced by Hokko Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. and first marketed in 1994. Patents JP 85026391; US 4512989; GB 2109371 Manufacturers Hokko
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Ergosterol biosynthesis inhibition (steroid demethylation inhibitor); at higher doses (³10 ppm), it is physically incorporated into the cell membrane and causes direct physical destruction of the cell (Y. Ogawa, Agchem. Japan,67, 20 (1995)). Mode of action Curative and preventative systemic foliar fungicide. Inhibits growth of both the germ tube and mycelium. Uses Effective against a broad range of diseases affecting fruit, turf, vegetables and ornamentals. Controls Venturia inaequalis, Podosphaera leucotricha, Alternaria mali, Gymnosporangium yamadae (rust), Gloeodes pomigena (sooty blotch) and Zygophiala spp. (fly speck) in apples, at 100-150 g/ha; Venturia nashicola and Gymnosporangium asiaticum in pears, at 75-100 g/ha; Cladosporium carpophilum and Monilinia fructicola in peaches; M. fructicola in apricots; C. carpophilum in Japanese apricots; Elsino?ampelina (anthracnose), Pestalotia spp. and Uncinula necator in grapes (100-150 g/ha); Elsino?fawcettii in citrus. Other uses are in turf, at 67-100 g/ha, against Sclerotinia homoeocarpa, Cochliobolus spp., Curvularia geniculata and Puccinia zoisiae; in tea, at 150 g/ha, against Colletotrichum theae-sinensis, Exobasidium vexans and Pseudocercospora theae; in melon and water melon, against Sphaerotheca fuliginea; in peanut, against Mycosphaerella arachidis; in roses, at 100-200 g/ha, against Diplocarpon rosae, Sphaerotheca pannosa; in chrysanthemums against Puccinia horiana. Formulation types EC; WG; WP. Compatibility Incompatible with pesticides which are strongly acidic. Selected products: 'Manage' (Hokko)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Hwaksiran' (Dong Bang)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis is by hplc. Residue analysis is by glc with NPD.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 2800, female rats 3000, male and female mice >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male and female rats >2000 mg/kg. Slight irritant to eyes; non-irritant to skin (rabbits). Slight skin sensitisation (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >1020 mg/m3. NOEL (2 y) for rats 100 mg/kg diet. ADI 0.0085 mg/kg. Other Non-mutagenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >2250 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 1.0, rainbow trout 0.67, carp 0.84 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (6 h) >100 mg/l. Algae EC50 for algae >1000 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral) >125 mg/bee; (contact) >200 mg/bee. Worms LC50 for earthworms >1000 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Imibenconazole orally administered to rats is rapidly metabolised and eliminated. The major metabolite is 2',4'-dichloro-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)acetanilide. Plants Imibenconazole applied to grapes and apples is degraded or metabolised rapidly. The main metabolite is 2',4'-dichloro-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)acetanilide. Soil/Environment Rapidly degrades in soil: DT50 (lab.) 4-20 d, (field) 1-28 d. Koc 2813-23 391.
|