|
imazosulfuron
Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; sulfonylurea
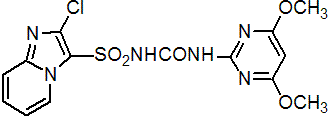
NOMENCLATURE
Common name imazosulfuron (BSI, pa E-ISO)
IUPAC name 1-(2-chloroimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-ylsulfonyl)-3-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)urea
Chemical Abstracts name 2-chloro-N-[[(4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)amino]carbonyl]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-sulfonamide
CAS RN [122548-33-8] Development codes TH-913
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 412.8 M.f. C14H13ClN6O5S Form Crystalline powder. M.p. 183-184 ºC (decomp.) V.p. 4.5 ´ 10-5 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 0.049 (pH 7, 25 ºC) S.g./density 1.574 g/ml (25.5 ºC) Solubility In water 6.75 (pH 5.1), 67 (pH 6.1), 308 (pH 7.0) (all in mg/l, 25 ºC). In acetonitrile 2500, ethyl acetate 2200, acetone 4800, dichloromethane 12 900, xylene 400 (all in mg/l, 25 °C). pKa 4.0
COMMERCIALISATION
History Development rights licensed to Takeda Chemical Industries Ltd (now Sumitomo Chemical Takeda Agro Company Ltd) by Urania Chemicals GmbH (now Spiess-Urania) in 1994. Manufacturers Sumitomo Chemical Takeda
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Acts by inhibiting biosynthesis of the essential amino acids valine and isoleucine, hence stopping cell division and plant growth. Selectivity derives from rapid metabolism in the crop. Metabolic basis of selectivity in sulfonylureas reviewed (M. K. Koeppe & H. M. Brown, Agro-Food-Industry, 6, 9-14 (1995)). Mode of action Absorbed by plants mainly through the roots and translocated throughout the plant. Inhibits shoot growth and retards root development. Uses Controls most annual (excluding Echinochloa oryzicola) and perennial broad-leaved weeds and sedges in paddy rice (75-95 g/ha) and turf (500-1000 g/ha). Formulation types GR; SC. Selected products: 'Sibatito' (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Takeoff' (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Kocis' (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda, Sipcam Inagra); 'Longet' (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda) mixtures: 'Award' (+ pyributicarb+ daimuron) (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Crush' (+ cafenstrole+ daimuron) (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Gosign' (+ daimuron+ esprocarb) (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Hayate' (+ pretilachlor+ daimuron+ dimethametryn) (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Batl' (+ mefenacet+ daimuron) (Nihon Bayer, Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Donichi' (+ daimuron+ fentrazamide) (Bayer CropScience, Sumitomo Chemical Takeda, SDS Biotech KK); 'Kikkubai' (+ daimuron+ etobenzanid) (Hodogaya, Sumitomo Chemical Takeda, SDS Biotech KK); 'Leading' (+ fentrazamide) (Nihon Bayer); 'Sheriff' (+ pretilachlor+ cyhalofop-butyl+ dimethametryn) (Otsuka, Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'The-One' (+ pentoxazone+ daimuron) (Kaken, Sumitomo Chemical Takeda)
ANALYSIS
Product and residue analysis by hplc. Methods for sulfonylurea residues in crops, soil and water reviewed (A. C. Barefoot et al., Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1995, 2, 707).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats and mice >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male and female rats >2000 mg/kg. Not irritant to eyes and skin (rabbits); not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >2.4 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for male rats 106.1, female rats 132.46 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for male and female dogs 75 mg/kg b.w. daily. Not oncogenic in rats and mice. Not teratogenic in rats and rabbits. Other No mutagenic effects in Ames, DNA-repair and chromosomal aberration tests.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks 2250 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for carp 250 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) >100 mg/l. Bees LD50 (48 h) (oral) 48.2 mg/bee; (contact) 66.5 mg/bee.
|