|
imazapyr
Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; imidazolinone
NOMENCLATURE
imazapyr
Common name imazapyr (BSI, ANSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO)
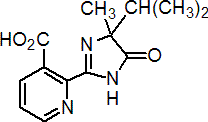
IUPAC name 2-(4-isopropyl-4-methyl-5-oxo-2-imidazolin-2-yl)nicotinic acid
Chemical Abstracts name (?-2-[4,5-dihydro-4-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)-5-oxo-1H-imidazol-2-yl]-3-pyridinecarboxylic acid
CAS RN [81334-34-1] unstated stereochemistry; [94795-74-1], [108224-78-8] former numbers Development codes AC 252 925; CL 252 925 (both Cyanamid)
imazapyr-isopropylammonium
CAS RN [81510-83-0] unstated stereochemistry
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
imazapyr
Mol. wt. 261.3 M.f. C13H15N3O3 Form White to tan powder, with a slight odour of acetic acid. M.p. 169-173 ºC V.p. <0.013 mPa (60 ºC) KOW logP = 0.11 (22 ºC, unstated pH) Solubility In water 9.74 g/l (15 ºC), 11.3 g/l (25 ºC). In acetone 3.39, dimethyl sulfoxide 47.1, hexane 0.00095, methanol 10.5, dichloromethane 8.72, toluene 0.180 (all in g/100 ml). Stability Stable for at least 2 years at 25 ºC, 1 year at 37 ºC, and 3 months at 45 ºC. Stable in aqueous media at pH 5 to pH 9 in the dark; avoid storage >45 ºC. In solution, the acid is decomposed in simulated sunlight; DT50 6 d at pH 5 to pH 9. pKa pKa1 1.9, pKa2 3.6, pKa3 11
imazapyr-isopropylammonium
Mol. wt. 320.4 M.f. C16H24N4O3 Form Colourless solid. M.p. 128-130 ºC.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by P. L. Orwick et al. (Proc. South. Weed Sci. Soc. Annu. Mtg., 36th, 1983, p. 291). Introduced by American Cyanamid Co. (now BASF AG); first marketed in 1985. Manufacturers BASF
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Thus causes disruption of protein synthesis, which leads to interference in DNA synthesis and cell growth. This results in chlorosis and tissue necrosis of new leaves. Mode of action Systemic, contact and residual herbicide, absorbed by the foliage and roots, with rapid translocation in the xylem and phloem to the meristematic regions, where it accumulates. Uses Imazapyr-isopropylammonium is used for pre- and post-emergence control of annual and perennial grasses, sedges and broad-leaved weeds, as well as many brush and deciduous tree species. Used in non-crop areas, such as industrial sites, railways, roads, drainage channels, etc., at 0.25-1.7 kg/ha; in forestry management, at 0.25-1.7 kg/ha; and in plantations of rubber trees and oil palms, at 0.125-1.0 kg/ha. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic to conifers. Rubber trees and oil palms show good tolerance, though application onto foliage is not selective, and care should be taken to avoid contact of the spray with the foliage of oil palms and the leaves and young bark of rubber trees. Formulation types EC; GR; SL.
imazapyr-isopropylammonium
Selected products: 'Arsenal' (BASF); 'Chopper' (BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
imazapyr
Mixtures: 'Lightning' (+ imazethapyr) (BASF); 'Midas' (+ MCPA-2-ethylhexyl+ imazapic) (BASF); 'OnDuty' (+ imazapic) (BASF); 'Sahara' (+ diuron) (BASF); 'Topsite' (+ diuron) (BASF)
imazapyr-isopropylammonium
'Calemba' (BASF); 'Stalker' (BASF); 'Parade' (Nomix-Chipman) mixtures: 'Onestep' (+ glyphosate-isopropylammonium) (BASF) Discontinued products: 'Assault' * (Cyanamid); 'Contain' * (Cyanamid)
ANALYSIS
Product by glc. Residues (1) in raspberries and bilberries, by glc; (2) in pine branches, leaves and on forest floors, by hplc. Details from BASF. (3) In soil, by hplc after extraction with ammonium bicarbonate and clean up (C. S. Helling & M. A. Doherty, Pestic. Sci., 45, 21-26 (1995)).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
imazapyr
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male and female rats >5000, female mice >2000, male and female rabbits 4800 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male and female rabbits >2000, male and female rats >2000 mg/kg. Eye irritant; mild skin irritant (rabbits). No skin sensitisation (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 for male and female rats >5.1 mg/l air. NOEL (13 w) for rats 10 000 mg/kg b.w. (highest dose tested). No teratogenic or foetotoxic effects were observed at 1000 mg/kg b.w. in rats or 400 mg/kg b.w. in rabbits (highest doses tested). Other Acute i.p. LD50 for male rats 2500, female rats 2500-3200 mg/kg. Non-mutagenic, non-carcinogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV EC classification Xi; R36| R52, R53
imazapyr-isopropylammonium
Oral Acute oral LD50 >1130 mg/kg a.e. (as 226 g/kg formulation with surfactant). Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for mice >2000 mg tech./kg.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
imazapyr
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >2150 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout, bluegill sunfish, and channel catfish >100 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >100 mg/l. Algae EC50 (120 h) for Selenastrum 71 mg/l, for Anabaena 11.7 mg/l, for Skeletonema 85.5 mg/l, for Navicula >59 mg/l. Bees Dermal LD50 for honeybees >100 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, following oral administration, c. 87% of the dose was excreted in the urine and faeces within 24 hours. In muscle and fat tissues and blood, residual levels were <0.01 mg/kg at both 24 and 192 hours. Plants Following foliar application, residues in plants decline rapidly in the first 24 hours and are exuded from the roots into the soil. The major residue in plants is the parent compound. Soil/Environment Soil residual activity 6 months to 2 years in temperate climates, 3 to 6 months in tropical climates; the major residue is the parent compound; degradation is primarily due to soil microbial activity. In water DT50 7 days; degradation is due to photolysis. Bioaccumulation in the environment is highly unlikely.
|