|
imazapic
Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; imidazolinone
NOMENCLATURE
Common name imazapic (BSI, pa ISO)
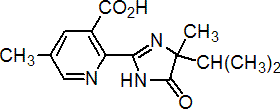
IUPAC name (RS)-2-(4-isopropyl-4-methyl-5-oxo-2-imidazolin-2-yl)-5-methylnicotinic acid
Chemical Abstracts name (?-2-[4,5-dihydro-4-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)-5-oxo-1H-imidazol-2-yl]-5-methyl-3-pyridinecarboxylic acid
Other names imazameth* (rejected BSI name proposal) CAS RN [104098-48-8] acid, unstated stereochemistry (formerly [81334-60-3]); [104098-49-9] ammonium salt, unstated stereochemistry Development codes AC 263 222; CL 263 222 (both Cyanamid)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 275.3 M.f. C14H17N3O3 Form Off-white to tan powder. M.p. 204-206 ºC V.p. <1 ´ 10-2 mPa (60 ºC) KOW logP = 0.393 (pH 4, 5, 6 buffer, 25 ºC) Solubility In deionised water 2150 ppm (25 ºC). In acetone 18.9 mg/ml (25 °C). pKa pKa1 2.0, pKa2 3.6, pKa3 11.1
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by M. Wixson et al. (Proc. South. Weed Sci. Soc., 45, 341 (1992)). Introduced by American Cyanamid Co. (now BASF AG) in 1996. Manufacturers BASF
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Selectivity in peanuts is attributed to rapid detoxification via hydroxylation and glycosylation (B. Tecle et al., Proc. 1997 Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 2, 605); lack of selectivity in soya beans explained (idem, ibid.). Mode of action Systemic, contact and residual herbicide. Weeds stop growing within 8 h of application, and begin to turn yellow 1-3 d later. Uses For post- and pre- emergence residual control of a wide range of annual and perennial weeds in pasture, rangeland and noncropland areas, at rates up to 0.188 lb/a. Formulation types WG; SL. Selected products: 'Cadre' (BASF); 'Plateau' (BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Flame' (BASF); 'Oraban' (BASF) mixtures: 'Midas' (+ imazapyr+ MCPA-2-ethylhexyl) (BASF); 'Oasis' (+ 2,4-D-2-ethylhexyl) (BASF); 'OnDuty' (+ imazapyr) (BASF)
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Moderately irritating to eyes; slightly irritating to skin (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 for rats 4.83 mg/l air. NOEL (90 d) for rats 20 000 ppm (1625 mg/kg daily). Dermal NOEL (21 d) for rabbits 1000 mg/kg. Teratogenicity NOEL (maternal) for rats 1000, rabbits 350 mg/kg daily; (foetal) for rats 1000, rabbits 500 mg/kg daily. ADI 0.50 mg/kg. Other Non-mutagenic, non-genotoxic, non-carcinogenic, non-teratogenic. Toxicity class EPA (formulation) III (70 WG); IV (2 SL)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Oral LD50 for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >2150 mg/kg. LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >5000 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for channel catfish, rainbow trout and bluegill sunfish >100 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >100 mg/l. Algae EC50 (120 h) for Selenastrum >51.7 mg/l, for Anabaena >49.9 mg/l, for Skeletonema >44.1 mg/l, for Navicula >46.4 mg/l. Bees LD50 (contact) >100 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Does not bioaccumulate in animals; if ingested then rapidly excreted through urine and faeces. Soil/Environment The primary route of degradation in soil is via microbial activity; DT50 31-410 d, depending upon soil and climatic conditions. Aqueous DT50 <8 h; imazapic is degraded by aqueous photolysis in the presence of sunlight.
|