|
hexazinone
Herbicide
HRAC C1 WSSA 5; 1,2,4-triazinone
NOMENCLATURE
Common name hexazinone (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, WSSA)
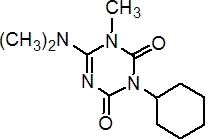
IUPAC name 3-cyclohexyl-6-dimethylamino-1-methyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-(1H,3H)-dione
Chemical Abstracts name 3-cyclohexyl-6-(dimethylamino)-1-methyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-(1H,3H)-dione
CAS RN [51235-04-2] EEC no. 257-074-4 Development codes DPX A3674 (DuPont)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 252.3 M.f. C12H20N4O2 Form Colourless, odourless crystals. M.p. 113.5 °C (purity >98%) B.p. Decomposes on distillation. V.p. 0.03 mPa (extrapolated) (25 ºC); 8.5 mPa (86 ºC) KOW logP = 1.2 (pH 7) S.g./density 1.25 Solubility In water 33 g/kg (25 ºC). In chloroform 3880, methanol 2650, benzene 940, dimethylformamide 836, acetone 792, toluene 386, hexane 3 (all in g/kg, 25 ºC). Stability Stable in aqueous media between pH 5 and pH 9 and below 37 ºC. Decomposed by strong acids and strong alkalis. Stable to light. pKa 2.2 (25 °C)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by T. J. Hernandez et al. (Proc. North Cent. Weed Control Conf., 1974, p. 138). Introduced by E. I. du Pont de Nemours Co.; first registered in USA in 1975. Patents US 3902887 Manufacturers DuPont; Milenia
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site. Mode of action Non-selective, primarily contact herbicide, absorbed by the leaves and roots, with translocation acropetally. Uses A post-emergence contact herbicide effective against many annual and biennial weeds and, except for Sorghum halepense, most perennial weeds, at 6-12 kg/ha. Used for selective control in alfalfa, pineapples, sugar cane and in plantations of certain coniferous species; also on non-crop areas, but not on sites adjacent to deciduous trees or other desirable plants. Phytotoxicity Should not be used for weed control in larch (Larix spp.) or in areas planted with deciduous species. Formulation types GR; SL; SP. Selected products: 'Velpar' (DuPont)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Pronone' (Pro-Serve) mixtures: 'Oustar' (+ sulfometuron-methyl) (DuPont); 'Hexaron' (+ diuron) (Milenia)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc or by glc with FID (C. L. McIntosh et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1984, 13, 267). Residues determined by glc (idem, ibid.; R. F. Holt, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1981, 29, 165). In drinking water, by glc with NPD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 991.07).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 1690, guinea pigs 860 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >5278 mg/kg. Reversible irritant to eyes (rabbits); non-irritating to skin (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (1 h) for rats >7.48 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for rats 200, mice 200 ppm; (1 y) for dogs 200 ppm. ADI 0.05 mg/kg b.w. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) II EC classification Xn; R22| Xi; R36| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 2258 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducklings >10 000 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout >320, bluegill sunfish >370 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 442 mg/l. Algae EC50 (120 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 0.007, for Anabaena flos-aquae 0.210 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (14 d) for Lemna gibba 0.034 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees; LD50 >60 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Major urinary metabolites in rats are 3-(4-hydroxycyclohexyl)-6-(dimethylamino)-1-methyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-(1H,3H)-dione, 3-cyclohexyl-6-(methylamino)-1-methyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-(1H,3H)-dione, and 3-(4-hydroxycyclohexyl)-6-(methylamino)-1-methyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-(1H,3H)-dione. Soil/Environment Microbial degradation occurs in soil and natural waters. The triazine ring is broken, with the liberation of CO2. DT50 in soil c. 1-6 mo, depending on climate and soil type.
|