|
hexaflumuron
Insecticide
IRAC 15; benzoylurea
NOMENCLATURE
Common name hexaflumuron (BSI, ANSI, draft E-ISO)
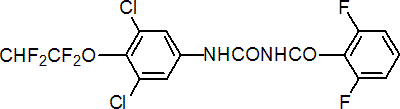
IUPAC name 1-[3,5-dichloro-4-(1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethoxy)phenyl]-3-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)urea
Chemical Abstracts name N-[[[3,5-dichloro-4-(1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethoxy)phenyl]amino]carbonyl]-2,6-difluorobenzamide
CAS RN [86479-06-3] Development codes XRD-473; DE-473 (both Dow)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 461.1 M.f. C16H8Cl2F6N2O3 Form White crystalline powder. M.p. 202-205 ºC B.p. >300 °C V.p. 0.059 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 5.68 Henry 1.01 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.68 (by pycnometer) Solubility In water 0.027 mg/l (18 ºC). In methanol 11.3, xylene 5.2 (both in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Undergoes 60% hydrolysis in 35 d (pH 9). Photolysis DT50 6.3 d (pH 5.0, 25 ºC).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by R. J. Sbragia et al. (Proc. Int. Congr. Plant Prot., 10th, 1983, 1, 417). Introduced for crop uses in Latin America in 1987 by Dow (now Dow AgroSciences). Introduced for subterranean termite control in 1995 by DowElanco (now Dow AgroSciences). Manufacturers Dow AgroSciences; SNPE
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Chitin synthesis inhibitor. Mode of action Ingested, systemic insecticide. Uses Used in agriculture for control of larvae of Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, Homoptera, and Diptera on top fruit, cotton, and potatoes. Major use now is in bait, for control of subterranean termites at 0.5% in a cellulose bait matrix. Application rates for fruit and vegetables 10-30 g/hl; for cotton 50-75 g/ha. Formulation types EC; SC. Selected products: 'Consult' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Recruit II' (termite bait) (Dow AgroSciences)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Centratec' (termite bait) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Hexafluron' (technical product) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Recruit' (termite bait) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Sentrichon' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Sentricon' (termite bait) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Trueno' (crop protection uses) (Dow AgroSciences) Discontinued products: 'Consol' * (DowElanco)
ANALYSIS
Product and residue analysis by glc or hplc. Details available from Dow AgroSciences.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits); no skin sensitisation (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >2.5 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for rats 75 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for dogs 2 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1.5 y) for mice 25 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.02 mg/kg b.w. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III (tech.), IV ('Recruit II')
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LC50 for bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg; acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >2000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 for bobwhite quail 4786, mallard ducks >5200 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout >500, bluegill sunfish >100 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.0001 mg/l. Significant hazard to Daphnia spp. only, in field conditions. Algae EC50 (96 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum >3.2 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral and contact) >0.1 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida >880 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. Low toxicity.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Soil/Environment Moderate rate of degradation in soil, moisture dependent; soil DT50 at 100% of 1/3 bar moisture 50-64 d; at 50% of 1/3 bar moisture 110-159 d (25 °C) . Soil Kd 147-1326, Kom 3096-41 170; strongly adsorbed on a wide range of soils.
|