|
halosulfuron-methyl
Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; sulfonylurea
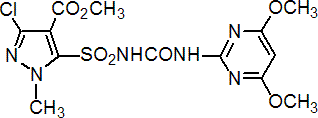
NOMENCLATURE
halosulfuron-methyl
Common name halosulfuron-methyl (BSI, pa E-ISO)
IUPAC name methyl 3-chloro-5-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-ylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)-1-methylpyrazole-4-carboxylate
Chemical Abstracts name methyl 3-chloro-5-[[[[(4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate
CAS RN [100784-20-1] Development codes A-841101; NC-319 (both Nissan); MON-12000 (Monsanto)
halosulfuron
Common name halosulfuron (BSI, pa E-ISO)
IUPAC name 3-chloro-5-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-ylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)-1-methylpyrazole-4-carboxylic acid
Chemical Abstracts name 3-chloro-5-[[[[(4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid
CAS RN [135397-30-7]
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
halosulfuron-methyl
Mol. wt. 434.8 M.f. C13H15ClN6O7S Form White powder. M.p. 175.5-177.2 ºC V.p. <0.01 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = -0.0186 (pH 7, 23? ºC) S.g./density 1.618 g/ml (25 ºC) Solubility In water 0.015 (pH 5), 1.65 (pH 7) g/l (20 ºC). In methanol 1.62 g/l (20 ºC). Stability Stable under normal storage conditions. pKa 3.44 (22 ºC)
halosulfuron
Mol. wt. 420.8 M.f. C12H13ClN6O7S
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by K. Suzuki et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1991, 1, 31). Discovered by Nissan Chemical Industries, Ltd and developed jointly by Monsanto Co. and Nissan. Registered in US in 1994. Manufacturers Nissan
APPLICATIONS
halosulfuron-methyl
Biochemistry Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Acts by inhibiting biosynthesis of the essential amino acids valine and isoleucine, hence stopping cell division and plant growth. Selectivity derives from rapid metabolism in the crop. Metabolic basis of selectivity in sulfonylureas reviewed (M. K. Koeppe & H. M. Brown, Agro-Food-Industry, 6, 9-14 (1995)). Mode of action Systemic herbicide, absorbed by the root system and/or leaf surface, and translocated to meristem tissues. Uses Halosulfuron-methyl has demonstrated activity for the control of annual broad-leaved weeds and nutsedge species, in maize, sugar cane, rice, sorghum, nuts and turf. Efficacy has been observed with post-emergence (18-35 g/ha) applications. Phytotoxicity Some hybrids or varieties of sweet corn and popcorn may be sensitive. Formulation types WG; WP. Selected products: 'Manage' (turf) (Nissan, Monsanto); 'Permit' (field maize and sorghum) (Nissan, Monsanto); 'Sandea' (Monsanto, Gowan); 'Sempra' (crop and turf use) (Nissan, Monsanto)
OTHER PRODUCTS
halosulfuron-methyl
'Inpool' (Nissan); 'Servian' (Nissan, Syngenta); 'Shawow' (Nissan) mixtures: 'Redstar' (+ cafenstrole+ cyhalofop-butyl+ daimuron) (Nissan); 'Yukon' (+ dicamba-sodium) (Nissan, Monsanto); 'Agrohitter' (+ indanofan+ quinoclamine) (Nihon Nohyaku, Agro-Kanesho) Discontinued products: 'Battalion' * (Monsanto)
ANALYSIS
Details from Nissan.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
halosulfuron-methyl
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 8866, mice 11 173 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Non-sensitising to skin (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >6.0 mg/l. NOEL (104 w) for male rats 108.3, female rats 56.3 mg/kg daily; (18 mo) for male mice 410, female mice 1215 mg/kg daily; (1 y) for male and female dogs 10 mg/kg daily. ADI (EPA) 0.1 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U (company classification); EPA (formulation) IV (75 WP)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
halosulfuron-methyl
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2250 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish >118, rainbow trout >131 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) >107 mg/l. Algae EC50 (5 d) for green algae (Selenastrum capricornutum) 0.0053, blue-green algae (Anabaena flos-aquae) 0.158 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (96 h, flow through) for oysters 116 ppm, mysid shrimp (Mysidopsis bahia) 106 mg/l. IC50 (14 d) for Lemna gibba 0.038 mg/l (pH 5). Bees LD50 (dermal) >100 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Rapidly eliminated from rats, in urine and faeces. The major metabolite is desmethyl halosulfuron-methyl. Further demethylation or hydroxylation of the pyrimidine ring yielded several minor mono- and di- hydroxylated metabolites. Plants The major metabolite in maize is 3-chloro-1-methyl-5-sulfamoylpyrazole-4-carboxylic acid (cleavage of urea bridge and ester hydrolysis). Soil/Environment Extensively metabolised in soil. In acidic soils, by hydrolytic cleavage of the sulfonylurea bridge to give aminopyrimidine and 3-chlorosulfonamide ester metabolites, which can undergo further hydrolysis to the acid. In alkaline soils, rearrangement and contraction of the sulfonylurea linkage, and opening of the pyrimidine ring are more important pathways. Under acidic and alkaline laboratory aerobic soil conditions, mineralisation to CO2 reached 9% and 62%, respy., after one year. DT50 <18 d. Although laboratory adsorption/desorption studies indicated the potential for moderate mobility of halosulfuron-methyl, field studies demonstrated that mobility is limited, probably because of rapid soil dissipation.
|