|
forchlorfenuron
Plant growth regulator
phenylurea
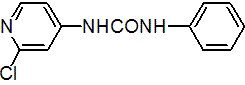
NOMENCLATURE
Common name forchlorfenuron (BSI, draft E-ISO, ANSI)
IUPAC name 1-(2-chloro-4-pyridyl)-3-phenylurea
Chemical Abstracts name N-(2-chloro-4-pyridinyl)-N'-phenylurea
Other names CPPU CAS RN [68157-60-8] Development codes KT-30; CN-11-3183; 4PU-30; SKW 20010; V-3183
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 247.7 M.f. C12H10ClN3O Form White to off-white crystalline powder. M.p. 165-170 ºC V.p. 4.6 ´ 10-5 mPa (25 ºC, gas saturation) KOW logP = 3.2 (20 ºC) S.g./density 1.3839 (25 °C) Solubility In water 39 mg/l (pH 6.4, 21 ºC). In methanol 119, ethanol 149, acetone 127, chloroform 2.7 (all in g/l) Stability Stable to heat, light and water.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Plant growth regulator reported by T. Okamoto et al., (Chem. Pharm. Bull., 26 (10), 3250 (1978); Phytochemistry, 17 (8), 1201 (1978)), and introduced by Kyowa Hakko Kogyo Co. Ltd. Evaluated initially by Sandoz Crop Protection Corp., and later by SKW Trostberg AG, who are seeking EU registration. EPA has granted an EUP to KIM-C1, LLC/Valent BioSciences, in California, USA. Patents Japan Kokai JP 1979/81275;DE OS 2843722; US 4193788. Manufacturers Kyowa
APPLICATIONS
Mode of action Absorbed by leaves, stem, cotyledon and germinated seeds. It promotes cell division, differentiation and development; induces budding of callus, and controls apical dominance; breaks dormancy of lateral buds and promotes germination; delays ageing process and maintains chlorophyll in excised leaves; regulates the transport of nutrients; promotes fruit formation, etc. Uses Used to increase the size of kiwifruit, table grapes and peaches; promote fruit set in melons, pumpkins and cucumbers; promote branching in apples; increase yield in potatoes, rice and wheat. Applied at 1-1000 ppm, depending on crop. Phytotoxicity Herbicidal activity at higher concentrations. Selected products: 'Fulmet' (Kyowa); 'Sitofex' (Degussa, BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Caplit' (Kyowa)
ANALYSIS
By hplc with u.v. detection; method validated at the 0.01 ppm level (unpublished).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 2787, female rats 1568, male mice 2218, female mice 2783 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats: no mortality in saturated atmosphere. NOEL 7.5 mg/kg b.w. daily.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2250 ng/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail >5600 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 9.2 mg/l; (48 h) for carp 8.6 mg/l, for goldfish 10-40 ppm. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 8.0 mg/l. Algae EC50 (3 h) 11 mg/l.
|