|
fomesafen
Herbicide
HRAC E WSSA 14; diphenyl ether
NOMENCLATURE
fomesafen
Common name fomesafen (BSI, draft E-ISO, ANSI); fomésafène ((m) draft F-ISO)
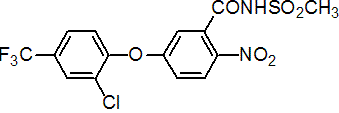
IUPAC name 5-(2-chloro-a,a,a-trifluoro-p-tolyloxy)-N-methylsulfonyl-2-nitrobenzamide
Chemical Abstracts name 5-[2-chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-N-(methylsulfonyl)-2-nitrobenzamide
CAS RN [72178-02-0] EEC no. 276-439-9 Development codes PP021 (ICI)
fomesafen-sodium
CAS RN [108731-70-0]
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
fomesafen
Mol. wt. 438.8 M.f. C15H10ClF3N2O6S Form White crystals. M.p. 219 °C V.p. <4 ´ 10-3 mPa (20 °C) KOW logP = 2.9 (pH 1), <2.2 (pH 4-10) Henry <2 ´ 10-7 Pa m3 mol-1 (pH 7, 20 °C) S.g./density 1.61 (20 °C) Solubility In pure water c. 50, <10 (pH 1-2), 10 000 (pH 9) (all in mg/l, 20 ºC). Stability Stable in storage for at least 6 months at 50 ºC. Decomposed by light. Stable at pH 3 and 11 (40 °C). Stable to aqueous photolysis for 32 d (pH 7, 25 °C). pKa 2.83 (20 ºC); forms water-soluble salts (e.g. fomesafen-sodium)
fomesafen-sodium
Mol. wt. 460.7 M.f. C15H9ClF3N2NaO6S
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by S. R. Colby et al. (Proc. Int. Congr. Plant Prot., 10th, 1983, 1, 295). Introduced by ICI Plant Protection Division (now Syngenta AG). Patents EP 3416 Manufacturers Sannong; Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitor. Mode of action Selective herbicide, absorbed by both leaves and roots, with very limited translocation in the phloem. Uses Early post-emergence control of broad-leaved weeds in soya beans. Applied at 200-400 g/ha. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic to soya beans and to other crops such as beans of the genus Phaseolus and the leguminous cover crops Pueraria and Calapogonium. Formulation types ME; SL.
fomesafen-sodium
Selected products: 'Flex' (Syngenta); 'Flexstar' (Syngenta); 'Reflex' (Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
fomesafen-sodium
Mixtures: 'Fusiflex' (+ fluazifop-P-butyl) (Syngenta); 'Reflex T' (+ terbutryn) (Syngenta); 'Tornado' (+ fluazifop-P-butyl) (Syngenta); 'Twister' (+ fenoxaprop-P-ethyl+ fluazifop-P-butyl) (Syngenta); 'Typhoon' (+ fluazifop-P-butyl) (Syngenta) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Faster' * (+ bentazone-sodium) (BASF)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc with u.v. detection. Residue analysis in soil by hplc; in crops by tlc, hplc or nmr. Details available from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
fomesafen
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 1250-2000, female rats 1600 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >1000 mg/kg. Mild skin irritant; mild to moderate eye irritant (rabbits). Extreme skin sensitiser (Magnusson & Kligman test), not a skin sensitiser (ear/flank Stevens test, guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for male rats 4.97 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for rats 5 mg/kg b.w. daily; (18 mo) for mice 1 mg/kg b.w. daily (liver tumours in mice due to peroxisome proliferation - not relevant to man); (6 mo) for dogs 1 mg/kg b.w. daily. NOEL developmental toxicity for rabbits 2.5 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.05 mg/kg. Other Genotoxicity negative. Not oncogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R22
fomesafen-sodium
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 1860, female rats 1500 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >780 mg/kg. Other Not oncogenic.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
fomesafen
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >5000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >20 000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 170, bluegill sunfish 1507 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 0.33 g/l. Algae EC50 170 mg/l. Bees Low oral and contact toxicity to bees. LD50 (oral) ³50 mg/bee; (contact) ³100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) >1000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Plants In soya beans, the diphenyl ether bond is rapidly cleaved to give inactive metabolites. Soil/Environment In soil, degrades slowly under aerobic conditions, DT50 >6 mo, but degrades more rapidly under anaerobic conditions, DT50 <1-2 mo. Koc 34-
|