|
fluthiacet-methyl
Herbicide
HRAC E WSSA 14; thiadiazole
NOMENCLATURE
Common name fluthiacet-methyl (BSI, pa ISO)
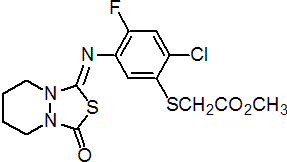
IUPAC name methyl [2-chloro-4-fluoro-5-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-3-oxo-1H,3H-[1,3,4]thiadiazolo[3,4-a]pyridazin-1-ylideneamino)phenylthio]acetate
Chemical Abstracts name methyl [[2-chloro-4-fluoro-5-[(tetrahydro-3-oxo-1H,3H-[1,3,4]thiadiazolo[3,4-a]pyridazin-1-ylidene)amino]phenyl]thio]acetate
CAS RN [117337-19-6]; [149253-65-6] for the acid Development codes KIH-9201 (Kumiai); CGA-248,757 (Ciba-Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 403.9 M.f. C15H15ClFN3O3S2 Form White powder. M.p. 105.0-106.5 °C (OECD 102) V.p. 4.41 ´ 10-4 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 3.77 (25 °C) Henry 2.1 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 0.43 (bulk, 20 °C) Solubility In water 0.85 (distilled), 0.78 (pH 5 & 7), 0.22 (pH 9) mg/l (25 ºC). In methanol 4.41, acetone 101, toluene 84, n-octanol 1.86, acetonitrile 68.7, ethyl acetate 73.5, dichloromethane 9 (all in g/l, 25 °C); in n-hexane 0.232 g/l (20 °C). Stability In water, DT50 484.8 d (pH 5), 17.7 d (pH 7), 0.2 d (pH 9). In light, DT50 4.92 d.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by Kumiai Chemical Industry Co., Ltd and Ciba-Geigy AG (now Syngenta AG) (T. Miyazawa et al., Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1993, 1, 23). Syngenta divested their interests to Kumiai in 2001. Patents US 4885023; US 4906279; EP-B-0273417 Manufacturers Ihara/Kumiai
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitor, causing accumulation of protoporphyrins, enhancing peroxidation of membrane lipids, and leading to irreversible damage to membrane structure and cellular function. Converted to the active substance in sensitive plants. Mode of action Selective, contact herbicide, requiring light for activity. Uses Post-emergence herbicide for control of broad-leaved weeds (e.g. Abutilon theophrasti, Chenopodium album, Amaranthus retroflexus and Xanthium strumarium) in maize and soya beans, at 4-15 g/ha. Formulation types WP. Selected products: 'Appeal' (Kumiai)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Action' (Kumiai)
ANALYSIS
Product and residue analysis by glc with NPD.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritant to skin and slightly irritant to eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h, nose exposure) for rats >5.048 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 2.1 mg/kg b.w. daily; (18 mo) for mice 0.1 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for male dogs 2000 ppm (58 mg/kg daily), female dogs 1000 ppm (30.3 mg/kg daily). ADI 0.014 mg/kg b.w. Other Non-mutagenic, non-teratogenic in rats and rabbits. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >2250 mg/kg. LC50 for blue quail >5620 ppm. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for trout 0.043, carp 0.60, bluegill sunfish 0.14, sheepshead minnow 0.16 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >2.3 mg/l. Algae EC50 for Selenastrum capricornutum 2.86 mg/l. NOEL (5 d) for Anabaena flos-aquae 18.4 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (96 h) for Eastern oyster 700, mysid shrimp 280 ppb. EC50 for Lemna gibba 2.2 ppb. Bees LD50 (contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 for earthworms >948 mg/kg dry soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In the rat, within 48 h, 80% is eliminated via the faeces, 14% via urine. Metabolism proceeds via hydrolysis of the methyl ester, isomerisation at the thiadiazole ring and hydroxylation of the tetrahydropyridazine moiety. Plants Field residues in beans are <0.01 ppm. In glasshouse studies, negligible residues are found at 10 ´ rate; organosoluble metabolites are similar to those in the rat. Soil/Environment DT50 (hydrolysis, pH 7) 18 d, (photolysis on soil) 21 d, (u.v. light) 2 h. In loam soil, DT50 1.2 d (25 °C, 75% of max. water capacity). Koc (adsorption) 448-1883; Koc (desorption) 1445-2782.
|