|
flurochloridone
Herbicide
HRAC F1 WSSA 12
NOMENCLATURE
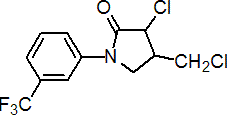
Common name flurochloridone (BSI, draft E-ISO, draft F-ISO); fluorochloridone (WSSA)
IUPAC name (3RS,4RS;3RS,4SR)-3-chloro-4-chloromethyl-1-(a,a,a-trifluoro-m-tolyl)-2-pyrrolidinone (in ratio 3:1)
Chemical Abstracts name 3-chloro-4-(chloromethyl)-1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-pyrrolidinone
CAS RN [61213-25-0] unstated stereochemistry EEC no. 262-661-3 Development codes R-40244 (Stauffer)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition A mixture of cis- and trans- isomers in the ratio 1:3. Mol. wt. 312.1 M.f. C12H10Cl2F3NO Form Brown-beige, waxy solid. M.p. 40.9 °C (eutectic); 69.5 °C (trans- isomer) B.p. 212.5 °C/10 mmHg V.p. 0.44 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 3.36 Henry 3.9 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.19 (20 °C) Solubility In water 35.1 (distilled), 20.4 (pH 9) (both in mg/l, 25 °C). In ethanol 100, kerosene <5 (both in g/l, 20 ºC). Readily soluble in acetone, chlorobenzene, and xylene. Stability Stable to hydrolysis at pH 5, 7 and 9 (25 °C); in acidic media and at elevated temperatures, decomposition occurs; DT50 138 d (100 ºC), 15 d (120 ºC). DT50 (60 ºC) 7 d (pH 4), 18 d (pH 7). Aqueous photolysis DT50 4.3 d (cis-/trans-), 2.4 d (cis-), 4.4 d (trans-) (all pH 7, 25 °C).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by F. Pereiro et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1982, 1, 225). Introduced by Stauffer Chemical Co. (now Syngenta AG) in 1985. Rights acquired by Agan Chemical Manufacturers Ltd in 2002. Patents DE 2612731 Manufacturers Agan
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits synthesis of carotenoids (which prevent chlorophyll from undergoing photo-oxidation) by inhibition of phytoene desaturase. Mode of action Selective herbicide, absorbed by the roots, stems, and coleoptiles. Uses Applied at 250-750 g/ha pre-emergence to control a wide range of weeds in sunflowers, carrots and other umbelliferous crops; Stellaria media, Veronica hederifolia and Viola arvensis in winter wheat and winter rye; Galium aparine, Solanum nigrum and Veronica persica in potatoes. Formulation types CS; EC. Selected products: 'Racer' (Agan)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Rainbow' (Agan) mixtures: 'Racer Duo' (+ acetochlor) (Agan); 'Twin Pack Gold' (+ S-metolachlor) (Agan); 'Twin Pack Premix' (+ acetochlor) (Agan)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by gc. Residues in crops or soils determined by gc. Details of analytical methods available from Agan.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 4000, female rats 3650 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >5000 mg/kg; practically non-irritating to skin, not irritant to eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >0.121 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for male rats 100 mg/kg diet (3.9 mg/kg b.w. daily), female rats 400 mg/kg diet (19.3 mg/kg b.w. daily). Other Genotoxicity negative. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >5000 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 3.0, bluegill sunfish 6.7 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 5.1 mg/l. Algae EbC50 (96 h) for Chlorella vulgaris 0.0064 mg/l. Bees Not hazardous to bees. LD50 (contact and oral) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 691 mg/kg. Other beneficial spp. Harmless to carabid beetles, Lycosid spider, Aphidius and Typhlodromus.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Flurochloridone is extensively metabolised and rapidly excreted in rats; >95% of orally applied dose was excreted in 90 h. Metabolism by oxidation, hydrolysis and glutathione conjugation yielded numerous metabolites in urine and faeces. Plants Flurochloridone is rapidly metabolised in plants. Numerous minor metabolites are formed through oxidation and conjugation. Residue levels of flurochloridone in crops are generally <0.05 mg/kg. Soil/Environment In the lab., flurochloridone is readily degraded in soil, mostly forming CO2 and a bound residue; DT50 (3 soil types, aerobic, 28 °C) 4, 5 and 27 d; two metabolites were formed, which were readily degraded further. In aerobic sediment, flurochloridone degraded with DT50 3-18 d (2 soils). In the field, DT50 9-70 d. Koc 680-1300, Kd 8-19, indicating low potential mobility on the McCall classification scale; flurochloridone does not leach because it is adsorbed and readily degraded in soil. For water, see Stability.
|