|
fluquinconazole
Fungicide
FRAC 3, G1; DMI: triazole
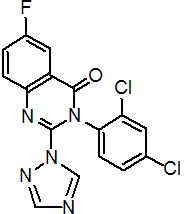
NOMENCLATURE
Common name fluquinconazole (BSI, draft ISO)
IUPAC name 3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-6-fluoro-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one
Chemical Abstracts name 3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-6-fluoro-2-((1H)-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-4(3H)-quinazolinone
CAS RN [136426-54-5] Development codes SN 597265 (Schering)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is 95.5% pure. Mol. wt. 376.2 M.f. C16H8Cl2FN5O Form Cream/pale brown, crystalline solid. M.p. 191.9-193 ºC; (tech., 184-192 °C) V.p. 6.4 ´ 10-6 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 3.24 (pH 5.6) Henry 2.09 ´ 10-6 Pa m3 mol-1 S.g./density 1.58 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 1 mg/l (pH 6.6, 20 ºC). In acetone 50, xylene 10, ethanol 3, dimethyl sulfoxide 200 (all in g/l). Stability In water, DT50 (25 ºC) 21.8 d (pH 7). Stable to light. Other properties Surface tension 70.91 mN m-1 (20 °C)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by P. E. Russell et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1992, 1, 411). Discovered and developed by AgrEvo GmbH (now Bayer CropScience). Some rights, primarily in Europe, acquired by BASF AG in 2003. Manufacturers Bayer CropScience
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Steroid demethylation (ergosterol biosynthesis) inhibitor. Mode of action Fungicide with protectant, eradicant and systemic properties. Is transported by the xylem, and there is also translaminar flow. Uses Control of a wide range of Ascomycetes, Deuteromycetes and Basidiomycetes, by foliar application, on broad-leaved and cereal crops, e.g. Venturia inaequalis and Podosphaera leucotricha in apples, Uncinula necator in vines, Puccinia and Septoria spp. in wheat, Cercospora, Erysiphe and others in sugar beet, and other economically important diseases in crops such as oilseed rape, stone fruit and other crops. Application rates vary from c. 4-8 g/ha on fruit and vines to 125-190 g/ha on field crops. Formulation types SC; SE; WG; WP; FS. Selected products: 'Palisade' (Bayer CropScience, BASF); mixtures: 'Galmano Plus' (+ prochloraz+ cuprous chloride) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Jockey' (+ prochloraz) (Bayer CropScience, BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Castellan' (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Galmano' (Bayer CropScience, BASF) mixtures: 'Castellan s' (+ sulfur) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Clarinet' (+ pyrimethanil) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Flamenco Plus' (+ prochloraz) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Jockey Plus' (+ prochloraz+ cuprous chloride) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Vision' (+ pyrimethanil) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Vista C' (+ carbendazim) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Vista CT' (+ chlorothalonil) (Bayer CropScience, BASF)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by reverse-phase hplc. Crop residues analysis by solvent extraction followed by gc with ECD. Methods for the determination of residues are available upon request from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male and female rats 112, male mice 325, female mice 180 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male rats 2679, female rats 625 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits), and not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 0.754 mg/l. NOEL (1 y) for rats 0.31, mice 1.1, dogs 0.5 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.005 mg/kg (proposed) Other Negative in the Ames and other mutagenicity tests. EC classification T; R23/25, R48/25| Xn; R21| Xi; R38| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >2000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 1.34, rainbow trout 1.90 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >5.0 mg/l. Algae For Selenastrum capricornutum,ErC50 46, EbC50 14 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. NOEC for Lemna minor 0.625 mg/l. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida >1000 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. Harmless to a range of representative species in the field.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Elimination of orally applied fluquinconazole was predominantly via faeces in rats, mice and dogs. In all three species unchanged fluquinconazole was the major compound along with smaller amounts of the dione and other minor metabolites. Plants Stable on plant surfaces; some hydrolysis to the dione is observed. Little absorption of fluquinconazole and the dione into the fruit and no evidence for translocation of residues on leaves to adjacent fruit. In wheat only a small amount is cleaved and further metabolised. Soil/Environment Degraded in soil under aerobic and anaerobic conditions; dissipation is mainly a hydrolytic process, but further degradation and mineralisation involves microbial action; the metabolites are finally transformed to soil-bound residues and CO2. Degradation rates depend on temperature, soil moisture, soil pH and organic matter content; typical field DT50 50-300 d. Strongly adsorbed to soils, Koc >738; soil column leaching studies and leaching models demonstrated that fluquinconazole will not leach to deeper soil layers and contaminate groundwater.
|