|
flumetralin
Plant growth regulator
NOMENCLATURE
Common name flumetralin (BSI, draft E-ISO); flumétraline ((f) draft F-ISO)
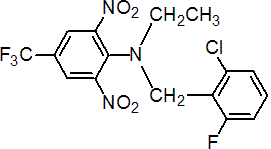
IUPAC name N-(2-chloro-6-fluorobenzyl)-N-ethyl-a,a,a-trifluoro-2,6-dinitro-p-toluidine
Chemical Abstracts name 2-chloro-N-[2,6-dinitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-N-ethyl-6-fluorobenzenemethanamine
CAS RN [62924-70-3] Development codes CGA 41 065 (Ciba-Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 421.7 M.f. C16H12ClF4N3O4 Form Yellow to orange, odourless crystals. M.p. 101.0-103.0 ºC; (tech., 92.4-103.8 ºC) V.p. 3.2 ´ 10-2 mPa (25 ºC) (OECD 104) KOW logP = 5.45 (25 ºC) Henry 0.19 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.54 Solubility In water 0.07 mg/l (25 ºC). In acetone 560, toluene 400, ethanol 18, n-hexane 14, n-octanol 6.8 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Decomposes exothermically above 250 ºC. Hydrolytically stable between pH 5 and pH 9.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Plant growth regulator reported by M. Wilcox et al. (Proc. Plant Growth Regul. Working Group, 1977, 4, 194). Introduced by Ciba-Geigy AG (now Syngenta AG) and first marketed in 1983. Patents BE 891327; GB 1531260 Manufacturers Milenia; Syngenta; Zhejiang
APPLICATIONS
Mode of action Plant growth regulator, which has a local systemic effect. Uses Control of sucker growth in tobacco, applied at 10-15 ml of 1-35% solution per plant. Phytotoxicity May cause some injury to immature plants. Formulation types EC. Selected products: 'Prime' (Syngenta); 'Prime+' (Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Podos' (Milenia); 'Yiyaming' (Zhejiang) Discontinued products: 'Premier' * (Ciba)
ANALYSIS
Residues determined by glc using ECD or FID. Details available from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. EC formulation (150 g/l) is a moderate skin irritant and an extreme eye irritant. Inhalation LC50 for rats >2130 mg/m3. NOEL (2 y) for rats and mice 300 ppm. ADI 0.17 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U EC classification Xi; R36/38| R43| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducklings >2000 mg/kg. LC50 for mallard ducklings and bobwhite quail >5000 ppm. Fish Toxic to fish; LC50 for bluegill sunfish 18, trout 25 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >66 mg/l. Algae EC50 for Selenastrum >0.85 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EdC50 for Lemna gibba 0.15 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic. Worms LC50 for earthworms >1000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Metabolic reactions include reduction of the nitro groups, acetylation of the amino groups and hydroxylation of the phenyl ring. Plants Metabolism in tobacco is rapid and extensive; reduction or complete removal of substituents occurs. Soil/Environment Strongly adsorbed and therefore immobile in soil; degradation is by photolysis. Stable to hydrolysis at pH 5, 7 and 9.
|