|
flufenoxuron
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 15; benzoylurea
NOMENCLATURE
Common name flufenoxuron (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO)
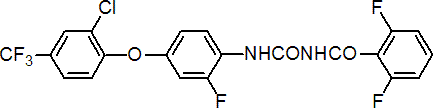
IUPAC name 1-[4-(2-chloro-a,a,a-trifluoro-p-tolyloxy)-2-fluorophenyl]-3-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)urea
Chemical Abstracts name N-[[[4-[2-chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-2-fluorophenyl]amino]carbonyl]-2,6-difluorobenzamide
CAS RN [101463-69-8] Development codes WL 115 110 (Shell); SKI-8503; AC 182621; AC 811 678 (both Cyanamid); BAS 307I (BASF)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition ³950 g/kg pure. Mol. wt. 488.8 M.f. C21H11ClF6N2O3 Form Tech. is a white, crystalline solid. M.p. 169-172 ºC (decomp.) V.p. 6.52 ´ 10-9 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 4.0 (pH 7) Henry 7.46 ´ 10-6 Pa m3 mol-1 S.g./density 0.62 Solubility In water 0.0186 (pH 4), 0.00152 (pH 7), 0.00373 (pH 9) (mg/l, 25 ºC). In acetone 82, xylene 6, dichloromethane 24, n-hexane 0.11, cyclohexane 95, dichloromethane 18.8, methanol 3.5, acetone 73.8 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable £190 ºC; to natural sunlight; thin film on glass stable >100 h in simulated sunlight. DT50 11 d (ambient in water). On hydrolysis (25 ºC), DT50 112 d (pH 5), 104 d (pH 7), 36.7 d (pH 9), 2.7 d (pH 12). pKa 10.1 (calc.) F.p. Not autoflammable; no explosive properties
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by M. Anderson et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1986, 1, 89). Evaluated by Shell Research Ltd. Product later marketed by American Cyanamid Co. (now BASF AG). Patents EP 161019 Manufacturers BASF
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Chitin synthesis inhibitor. Mode of action Insect and acarid growth regulator with contact and stomach action. Treated larvae die at the next moult or during the ensuing instar. Treated adults lay non-viable eggs. Uses Control of immature stages of many phytophagous mites (Aculus, Brevipalpus, Panonychus, Phyllocoptruta, Tetranychus spp.) and insect pests on pome fruit, vines, citrus fruit, tea, cotton, maize, soya beans, vegetables and ornamentals. Applied at 25-200 g/ha, depending on the crop and pests. Phytotoxicity None recorded. Formulation types EC; DC; WG. Selected products: 'Cascade' (BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Motto' (BASF); 'Pampass' (BASF) mixtures: 'Tenopa' (+ alpha-cypermethrin) (BASF, Sorex)
ANALYSIS
Product by lc. Residues by hplc. Details from BASF.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >3000 mg tech./kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats and mice >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to eyes and skin (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs, M&K). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.1 mg/l air. NOEL (1 y) for dogs 100 mg/kg diet (3.6 mg/kg b.w. daily); (2 y) for rats 50 mg/kg diet (2.5 mg/kg b.w. daily); (2 y) for mice 1000 mg/kg diet (170 mg/kg b.w. daily) ADI 0.025 mg/kg b.w. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout >4.9 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.04 mg/l. Algae EC50 (96 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum >4 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral) >109.1 mg/bee, (contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms >1000 mg/kg Other beneficial spp. Low hazard to predatory mites and other predatory and parasitic arthropods.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Soil/Environment Strongly adsorbed in soil, DT50 42 d (clay loam). Use in orchards over 3 years at a dose of 97.5 g/ha gave rise to low residues in soil which did not significantly affect soil organisms, including earthworms (J. M. Gilbert et al., Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1992, 2, 805-810).
|