|
flufenacet
Herbicide
HRAC K3 WSSA 15; oxyacetamide
NOMENCLATURE
Common name flufenacet (BSI, pa ISO)
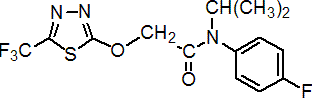
IUPAC name 4'-fluoro-N-isopropyl-2-(5-trifluoromethyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yloxy)acetanilide
Chemical Abstracts name N-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-(1-methylethyl)-2-[[5-(trifluoromethyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl]oxy]acetamide
Other names fluthiamide* (rejected BSI name) CAS RN [142459-58-3] Development codes BAY FOE 5043; FOE 5043 (Bayer)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 363.3 M.f. C14H13F4N3O2S Form White to tan solid. M.p. 76-79 °C V.p. 9 ´ 10-2 mPa (20 °C); flufenacet isomerises on heating; therefore the data refer to the N- isomer as the main component of the gaseous phase KOW logP = 3.2 (24 °C) Henry 9 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.); but see note on vapour pressure S.g./density 1.45 (20 °C) Solubility In water 56 (pH 4), 56 (pH 7), 54 (pH 9) mg/l (25 °C). In acetone, dichloromethane, dimethylformamide, toluene and dimethyl sulfoxide >200, isopropanol 170, n-hexane 8.7, n-octanol 88, polyethylene glycol 74 (all in g/l). Stability Stable to hydrolysis at pH 5-9. Stable to photolysis at pH 5.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by R. Deege et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1995, 1, 43). Developed by Bayer AG. Patents EP 00348737 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Its effect is an unclassified inhibition of cell division and cell growth. Primary target site may be in fatty acid metabolism. Tolerance is attributed to rapid detoxification by glutathione transferases. Mode of action Pre- and early post- emergence herbicide. It is systemic, with apoplastic transport and distribution and with meristematic activity. Uses Selective herbicide with broad spectrum grass control and control of some broad-leaved weeds; pre-plant-incorporated, pre-plant-surface, pre-emergence in maize and soya beans, pre-planting in tomatoes, pre-emergence in potatoes and sunflowers, and post-emergence in maize, wheat and rice. Application rates up to 0.9 kg a.s./ha. Formulation types EC; GR; SC; WG; WP. Selected products: 'Cadou' (Bayer CropScience); 'Drago' (Bayer CropScience); mixtures: 'Axiom' (+ metribuzin) (Bayer CropScience); 'Domain' (+ metribuzin) (Bayer CropScience); 'Epic' (+ isoxaflutole) (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Define' (Bayer CropScience); 'Tiara' (Bayer CropScience) mixtures: 'Artist' (+ metribuzin) (Bayer CropScience); 'Aspect' (+ atrazine) (Bayer CropScience); 'Axiom AT' (+ metribuzin+ atrazine) (Bayer CropScience); 'Bastille' (+ metribuzin) (Bayer CropScience); 'Cadou Star' (+ isoxaflutole) (Bayer CropScience); 'Crystal' (+ pendimethalin) (BASF); 'Diplôme' (+ metosulam) (Bayer CropScience); 'Draeda' (+ metribuzin) (Bayer CropScience); 'Drago 3.4' (+ 2,4-D) (Bayer CropScience); 'Fedor' (+ metribuzin) (Bayer CropScience); 'Herold' (+ diflufenican) (Bayer CropScience); 'Malibu Pack' (+ pendimethalin) (BASF); 'Plateen' (+ metribuzin) (Bayer CropScience); 'Terano' (+ metosulam) (Bayer CropScience)
ANALYSIS
Details of methods for product and residue analysis are available from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 1617, female rats 589 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Not an eye or skin irritant (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >3740 mg/m3 (aerosol). NOEL (2 y) for rats 25 mg/kg diet; (12 mo) for dogs 40 mg/kg diet; (20 mo) for mice 50 mg/kg diet. ADI 0.01 mg/kg b.w. (Bayer 1996). Other Non-mutagenic (Ames test); non-teratogenic (rabbit and rat). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R22, R48/22| R43| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 1608 mg/kg. LC50 (6 d) for bobwhite quail >5317, mallard ducks >4970 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 2.13, rainbow trout 5.84 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 30.9 mg/l. Algae EC50 (120 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 0.00452 mg/l, Anabaena flos-aquae 0.035 mg/l. In additional testing, recovery of affected algae populations has been demonstrated. Bees LD50 (oral) >329.5 µg/bee; (contact) >387.2 µg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida 219 mg/kg dry soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals After oral administration, flufenacet is rapidly excreted by animals (rat, goat, hen); hence accumulation in organs and tissues is not to be expected. Metabolism takes place via cleavage of the molecule, followed by conjugation of the fluorophenyl moiety with cysteine and formation of a thiadazolone and its various conjugates. Plants In maize, soya beans and cotton, flufenacet is rapidly and extensively metabolised; no parent compound was detected, even at early sampling dates. Although only three metabolites were of quantitative significance, a "total residue" approach was defined for plants, based on the total amount of N-fluorophenyl-N-isopropyl-derived residues. Soil/Environment Flufenacet is readily degraded in soil, ultimately forming CO2; DT50 10-54 d. Stable to photolysis in soil. Koc (sandy loam) 354 (range 233-613). Results from lysimeter studies demonstrate that, even under worst case conditions, contamination by the parent compound of soil layers below 1.2 m, or of groundwater, at concentrations >0.1 mg/l, are very unlikely.
|