|
fludioxonil
Fungicide
FRAC 12, E2; phenylpyrrole
NOMENCLATURE
Common name fludioxonil (BSI, pa E-ISO)
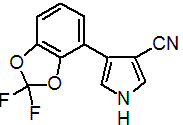
IUPAC name 4-(2,2-difluoro-1,3-benzodioxol-4-yl)pyrrole-3-carbonitrile
Chemical Abstracts name 4-(2,2-difluoro-1,3-benzodioxol-4-yl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile
CAS RN [131341-86-1] Development codes CGA 173506 (Ciba-Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 248.2 M.f. C12H6F2N2O2 Form Yellowish crystals. M.p. 199.8 ºC V.p. 3.9 ´ 10-4 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 4.12 (25 ºC) Henry 5.4 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.54 (20 °C) Solubility In water 1.8 mg/l (25 ºC). In acetone 190, ethanol 44, toluene 2.7, n-octanol 20, hexane 0.01 g/l (25 ºC). Stability Practically no hydrolysis at 70 ºC between pH 5 and 9. pKa pKa1 <0; pKa2 c. 14.1
COMMERCIALISATION
History Announced by Ciba-Geigy AG (now Syngenta AG) as a novel fungicide for seed treatment (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1990, 2, 825-830) and foliar use (ibid., pp. 399-406). First sales in 1993 as a cereal seed dressing and in 1995 as a foliar fungicide, both in France. Patents EP-206999; US 4705800 Manufacturers Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Mode of action is believed to be the same as for fenpiclonil. Inhibits MAP kinase, in osmotic signal transduction. Mode of action Non-systemic product with long residual activity. Uptake into the plant tissues and curative properties are generally limited. Inhibits mainly the germination of conidia and, to a lesser extent, the germ tube and mycelial growth. Uses As a seed treatment, for control of Fusarium spp., Microdochium, Rhizoctonia, Tilletia, Pyrenophora and Septoria in both cereal and non-cereal crops, at 2.5-10 g/100 kg. As a foliar fungicide, for control of Botrytis, Monilinia, Sclerotinia, and Alternaria in grapes, stone fruit, berry crops, vegetables, and ornamentals, at 250-500 g/ha; also on turf, against Fusarium, Helminthosporium, Rhizoctonia, Sclerotinia and Typhula, at 400-800 g/ha. Also as a post-harvest treatment on stonefruit at 30-60 g/hl against Botrytis, Monilinia and Penicillium. Formulation types DS; FS; SC; WG; WP. Selected products: 'Celest' (seed treatment) (Syngenta); 'Géoxe' (foliar) (Syngenta); mixtures: 'Maxim XL' (+ metalaxyl-M) (seed treatment) (Syngenta); 'Maxim' (+ metalaxyl) (seed treatment) (Syngenta); 'Switch' (+ cyprodinil) (foliar) (Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Atlas' (seed treatment) (Syngenta); 'Medallion' (Syngenta); 'Saphire' (foliar) (Syngenta); 'Savior' (foliar) (Syngenta); 'Scholar' (post-harvest) (Syngenta) mixtures: 'Apron Maxx' (+ metalaxyl-M) (Syngenta); 'Austral Plus' (+ tefluthrin+ anthraquinone) (Syngenta); 'Botryl' (+ cyprodinil) (ornamentals) (Syngenta); 'Celeste Orge' (+ tebuconazole+ anthraquinone+ cyprodinil) (seed treatment, France) (Syngenta); 'Helix' (+ metalaxyl-M+ thiamethoxam+ difenoconazole) (Syngenta); 'Landor CT' (+ tebuconazole+ difenoconazole) (seed treatment, Germany) (Syngenta); 'Maxim Apron' (+ metalaxyl) (Syngenta); 'Maxim MZ' (+ mancozeb) (Syngenta); 'Maxim Star' (+ cyproconazole) (Syngenta); 'Solitär' (+ tebuconazole+ cyprodinil) (seed treatment) (Syngenta); 'Wakil XL' (+ metalaxyl-M+ cymoxanil) (Syngenta); 'Arena C' (+ tebuconazole) (seed treatment, Germany) (Bayer CropScience); 'Justeet' (+ fenhexamid) (Japan) (Bayer CropScience) Discontinued products: 'Elyxor' * (Novartis); 'Wispect' * (Novartis) mixtures: 'Elyxor Star' * (+ tefluthrin+ anthraquinone) (Novartis)
ANALYSIS
Product by glc. Residues by hplc with u.v. detection. Details from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats and mice >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to eyes and skin (rabbits). Non-sensitising to skin (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >2.6 mg/m3 air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 40 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1.5 y) for mice 112 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for dogs 3.3 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.033 mg/kg b.w. Other Not teratogenic, not mutagenic, not oncogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U (company classification)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg. LC50 for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >5200 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 0.31, catfish 0.63, common carp 1.5, rainbow trout 0.5 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 1.1 mg/l. Algae EC50 (72 h) for Scenedesmus subspicatus 0.93 mg/l; (120 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 0.092 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic; LD50 (48 h, oral) >329 mg/bee; LC50 (48 h, contact) >101 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida >1000 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. No long-term substantial reduction in major groups of zooplankton, bentic macro-invertebrates, emergent insects, peryphyton or phytoplankton; no negative effects on Aleochara, Poecilus, Coccinella, Orius, Aphidius and Typhlodromus.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract into the general circulation and rapidly and almost completely excreted, via the faeces. The dominant metabolic pathway is oxidation of the pyrrole ring at the 2-position. A minor pathway is hydroxylation of the phenyl ring. All metabolites are excreted as conjugates, mainly as glucuronides. Plants Metabolism proceeds via the oxidation of the pyrrole ring, opening of the pyrrole ring and pyrrolidine carboxylic acid metabolite. In general, the compound is extensively metabolised to more than 10-15 minor metabolites. Soil/Environment Formation of bound residues is the major route for dissipation in soil; DT50 (lab.) 140-350 d, (field) 10-25 d. In leaching and adsorption/desorption experiments, the compound proved to be immobile in soil. Photolytic DT50 in water 9-10 d (natural sunlight).
|