|
flocoumafen
Rodenticide
coumarin anticoagulant
NOMENCLATURE
Common name flocoumafen (BSI, draft E-ISO); flocoumafène ((m) (draft F-ISO))
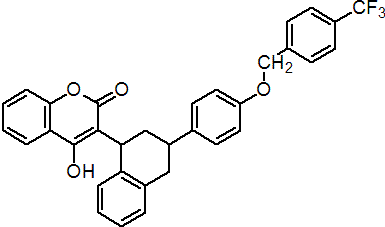
IUPAC name 4-hydroxy-3-[1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-3-[4-(4-trifluoromethylbenzyloxy)phenyl]-1-naphthyl]coumarin (mixture of cis- to trans- isomers in the ratio range 60:40 to 40:60)
Chemical Abstracts name 4-hydroxy-3-[1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-3-[4-[[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methoxy]phenyl]-1-naphthalenyl]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one
CAS RN [90035-08-8] unstated stereochemistry Development codes WL 108 366 (Shell), CL 183540, BAS 322 I
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition ³955 g/kg pure; 50-80% cis- isomer Mol. wt. 542.6 M.f. C33H25F3O4 Form Off-white solid. M.p. 166.1-168.3 °C V.p. <<1 mPa (20 °C, 25 ºC, 50 °C; OECD 104, vapour pressure balance method) KOW logP = 4.51 Solubility In water 0.114 mg/l (pH 7, 20°C). In n-heptane 0.3, acetonitrile 13.7, methanol 14.1, n-octanol 17.4, toluene 31.3, ethyl acetate 59.8, dichloromethane 146, acetone 350 (all in g/l, 20°C). Stability Stable to hydrolysis; at 50 ºC and pH 7-9, no detectable degradation occurred in 4 weeks. Thermally stable up to 250 ºC. pKa 4.5
COMMERCIALISATION
History Rodenticide reported by D. J. Bowler et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1984, 2, 397). Introduced by Shell International Chemical Co., Ltd (now BASF AG). Manufacturers BASF
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Second-generation indirect anticoagulant. Inhibits the metabolism of vitamin K1, and thus depletes vitamin K1-dependent clotting factors in plasma. Blocks formation of prothrombin. Uses Control of rodents including Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus, R. rattus, Arvicanthis niloticus, Bandicota spp., Praomys natalensis, R. argentiventer, R. rattus diardii, R. losea, R. tiomanicus and Sigmodon hispidus. Effective against rodents which have become resistant to other anticoagulant rodenticides. In addition to use around buildings, it is effective in controlling rodents in field and plantation crops including cocoa, cotton, oilpalm, rice and sugar cane. Formulation types BB; GB; RB. Selected products: 'Storm' (BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Stratagem' (BASF)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc, details available from BASF.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 0.25, dogs 0.075-0.25 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits 0.87 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 0.16-1.4 mg/l. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ia; EPA (formulation) I EC classification T+; R26/27/28| T; R48/23/24/25| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for chickens >100, Japanese quail >300, mallard ducks > 104 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail 62, mallard ducks 12 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.067, bluegill sunfish 0.112 mg/l. Ready to use formulations (50 mg/kg) are non-toxic to aquatic species. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 0.170 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. ErC50 (72 h) >18.2 mg/l.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 175 (WHO, 1995) Animals Major residues in rats are the stereoisomers of flocoumafen.
|