|
氰戊菊酯
CAS号: 51630-58-1
英文名称: Phenvalerate
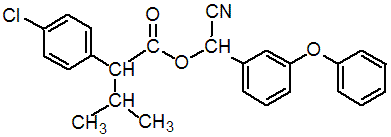
化学名称: 2,2-二甲基-3-(2,2-二氯乙烯基)环丙烷羧酸-α-氰基- (3-苯氧基)苄酯;cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl-4-chloro-alpha-(1-methylethyl)phenylacetate;
其它名称 :敌虫菊酯、速灭杀丁、中西杀灭菊酯
分子式: C25H22ClNO3
分子量: 419.9
理化性质: 原药为黄色油状液体。b.p.300℃(4.9×103Pa ,25℃),蒸气压3.703×10-5Pa,相对密度1.175(25℃),折射率n21.5D1.5655。能溶于甲醇、丙酮、乙二醇、氯仿、二甲苯等有机溶剂,20℃时溶解度均大于450g/L;微溶于己烷;难溶于水。分配系灵敏1.03×10-5(23℃)。热稳定性好,75℃放置100h无明显分解,对酸不稳定,pH>8不稳定,对光稳定。
毒性: 氰戊菊酯属中等毒性杀虫剂,原药大鼠急性经口LD50为451mg/kg,大鼠急性经皮LD50>5000mg/kg,大鼠急性吸入LC50>101mg/m3,,对兔皮肤有轻度刺激,对眼睛有中度刺激。没有致突变、致畸和致癌作用。对鱼和水生动物毒性很大,对鸟类毒性不大,对蜜蜂安全。 野鸭经口LD50:9932。鱼毒TLm(48h):虹鳟4.6ng/kg(小),7.3ng/kg(大)。大白菜、菜豆、番茄上的最大允许残留量为1.0mg/kg。ADI为0.06mg/kg。
作用特点及杀虫谱: 广谱、高效、快速拟除虫菊酯。以触杀和胃毒作用为主,无内吸作用,对螨类无效,对鳞翅目幼虫、直翅目、半翅目、双翅目害虫有效,但对螨无效。用于防治棉花蚜虫、叶蝉、蝽象、卷叶虫、菜青虫、大豆食心虫、小麦黏虫、红铃虫、棉铃虫、柑橘潜叶蛾幼虫,推荐用量用20%乳油对水2000倍液喷雾。注意不要在桑园、鱼塘、蜂场附近使用。已产生抗性的棉蚜、棉铃虫应停止使用。
用于防治棉花、蔬菜、果树、水稻、玉米、大豆、烟草等作物的害虫。
使用方法 : 1、棉花害虫的防治 棉铃虫于卵孵盛期、幼虫蛀蕾铃之前施药,每亩用20%乳油25-50ml水喷雾。 棉红铃虫在卵孵盛期也可用此浓度进行有效防治。同时可兼治红蜘蛛、小造桥虫、金钢钻、卷叶虫、蓟马、盲蝽等害虫。 棉蚜每亩用20%乳油10-25ml,对伏蚜则要增加用量。
2、果树害虫的防治 柑橘潜叶蛾在各季新梢放梢初期施药,用20%乳油5000-8000倍喷雾。同时兼治橘蚜、卷叶蛾、木虱等。 柑橘介壳虫于卵孵盛期用20%乳油2000-4000倍液喷雾。
3、蔬菜害虫的防治 菜青虫2-3龄幼虫发生期施药,每亩用20%乳油10-25ml。 小菜蛾在3龄前用20%乳油15-30ml/亩进行防治。
4、茶树害虫的防治 茶尺蠖、茶毛虫、丽绿刺蛾均于3龄幼虫期前施药,用20%乳油4000-8000倍喷雾。 茶丽绿刺蛾、黑刺粉虱于若虫高峰期,用20%乳油4000-8000倍喷雾。(现禁止用于茶叶)
5、大豆害虫的防治 防治食心虫于大豆开花盛期、卵孵高峰期施药,每亩用20%乳油20-40ml,能有效防治豆荚被害,同时可兼治蚜虫、地老虎。
6、小麦害虫的防治 防治麦蚜、粘虫、于麦蚜发生期、粘虫2-3龄幼虫发生期施药,用20%乳油3000-4000倍液喷雾。
剂型: 20%、30%乳油。
生产方法:方法一: 在相转移催化剂、液碱存在下,对氯氰苄与溴代丙烷回流反应数小时,甲苯为溶剂,生成对氯苯基回流反应数小时,生成对氯苯基异丁腈,然后加入65%硫酸溶剂,回流反应,生成2-对氯苯基-3-甲基丁酸(简称戊菊酸),加入规定量的氯化亚砜,反应数小时,得戊菊酰氯,最后以环己烷为溶剂,在相转移催化剂存在下,醚醛(间苯氧基苯甲醛)、氰化钠与戊菊酰氯反应数小时,经后处理,即得氰戊菊酯原油。
方法二(α-羟基磺酸钠法):以间苯氧基苯甲醛与亚硫酸氢钠加成后的产物,直接与氰化钠水溶液作用生成氰醇,同时迅速与2-(对氯苯基)-3-甲基丁酰氯作用,生成氰戊菊酯。
氰戊菊酯分子中有2个不对称碳原子,因此有S,S、S,R、R,S、R,R四种旋光异构体。其中S,S体药效最高,R,R体药效最低。提高S,S体主要方法如下。
使用手征性相转移催化剂合成 以(S)-(-)-α甲基苄胺为拆分剂,把外消旋体α-异丙基对氯苯乙酸拆分,得S体酸,再合成相应的S-酰氯。然后再与间苯氧基苯甲醛、氰化钠作用,使用手征性的N-苄基辛可尼定氯化铵(BCDC)为相转移催化剂,得非对映异构体S,S和S,R体,其中S,S体过量5%。此法操作简单,反应条件温和,收率高,是一种很有前途的不对称合成的方法。该法手征性相转移催化剂的选择和反应条件尚需探索。
化学拆分-差向异构体 先将α-异丙基对氯苯乙酸化学拆分制成S-酸,经酰氯化后,再与间苯氧基苯甲醛、氰化钠作用,制成氰戊菊酯S,S体和S,R体。再利用它们理化性质的不同,把它们分离开来。最后将S,R体差向异构体制成S,S体。S,S体即顺式氰戊菊酸。
此法已在日本工业化。优点是S,S体纯度高、质量好、收率高,缺点是R酸用途有待开拓,成本相对较高。
差向异构化法 利用体(S,R与R,S对映体)与β体(S,S与R,R对映体)理化性质的不同,将它们分离开来。再将体差向异构体为β体。此法投资少、操作简单、反应条件温和,是一种很有前途的工艺路线,已进行工业化试验。
生产情况:1973年在日本合成,日本住友化学公司(Sumitomo Chemical CO.)于1976年发展的品种,1981年已在世界60多个国家正式注册或受到推荐。国内生产企业:山东大成农药股份有限公司;南通市正达农化有限公司;南京荣诚化工有限公司;江苏瑞东农药有限公司;江苏耕耘化学有限公司;金唐化学工业集团公司;淄博农邦农药有限公司;青岛美德龙化工有限公司; 江苏皇马农化有限公司;灌云县光大农化有限公司;上海中西药业股份有限公司;山东京蓬生物药业股份有限公司
|
|
fenvalerate
Insecticide, acaricide, ixodicide
IRAC 3; pyrethroid
NOMENCLATURE
Common name fenvalerate (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ESA)
IUPAC name (RS)-a-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (RS)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-methylbutyrate
Chemical Abstracts name cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl 4-chloro-a-(1-methylethyl)benzeneacetate
CAS RN [51630-58-1] unstated stereochemistry Development codes S-5602 (Sumitomo); WL 43 775 (Shell) Official codes OMS 2000
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. grade fenvalerate is 92.1% pure. Mol. wt. 419.9 M.f. C25H22ClNO3 Form Tech. fenvalerate is a viscous yellow or brown liquid, sometimes partly crystalline at room temperature. M.p. 39.5-53.7 °C (pure) B.p. Decomposes on distillation. V.p. 1.92 ´ 10-2 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 5.01 (23 ºC) S.g./density 1.175 (25 ºC) Solubility In water <10 mg/l (25 ºC). In n-hexane 53, xylene ³200, methanol 84 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Stable to heat and moisture. Relatively stable in acidic media, but rapidly hydrolysed in alkaline media. F.p. 230 °C
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by N. Ohno et al. (Agric. Biol. Chem., 1974, 38, 881) and results of field trials by M. D. Mowlam et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1977, 2, 649). Introduced by Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd and, in some countries, by Shell International Chemical Co. (who no longer manufacture or market it). Patents GB 1439615; US 4062968 both to Sumitomo Manufacturers Agrochem; Aimco; Ankur; Bharat; Dhanuka; Dow AgroSciences; Ficom; Gujarat; JIE; Krishi Rasayan; Parry; Rallis; RPG; SC Enviro Agro; Sharda; Sumitomo; United Phosphorus
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Acts on the nervous system of insects, disturbs the function of neurons by interaction with the sodium channel. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. Uses Control of a wide range of pests, including those resistant to organochlorine, organophosphorus, and carbamate insecticides. Uses include control of chewing, sucking, and boring insects (particularly Lepidoptera, Diptera, Orthoptera, Hemiptera, and Coleoptera) in fruit, vines, olives, hops, nuts, vegetables, cucurbits, cotton, oilseed rape, sunflowers, alfalfa, cereals, maize, sorghum, potatoes, beet, peanuts, soya beans, tobacco, sugar cane, ornamentals, forestry, and on non-crop land. Used for control of flying and crawling insects in public health situations and in animal houses. Also used as an animal ectoparasiticide. Formulation types EC; UL; SC; WP. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Sumicidin' (Sumitomo); 'Arfen' (Ramcides); 'Devifen' (Devidayal); 'Dufen' (Dhanuka); 'Fenkill' (United Phosphorus); 'Fenny' (Nagarjuna Agrichem); 'Fenval' (RPG); 'Kayvalerate' (Krishi Rasayan); 'Newfen' (Gharda); 'Sanvalerate' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Shasicidin' (Sanonda); 'Starfen' (Shaw Wallace); 'Sumitox' (Aimco); 'Valour' (Crop Health); 'Vapcocidin' (Vapco); 'Vifenva' (Vipesco)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Agrocidin' (Chemvet); 'Bhasma' (Biostadt); 'Fencur' (BEC); 'Fenero' (Sabero); 'Fenirate' (Agrochem); 'Fyrate' (public health) (Chemvet); 'Krifen' (Krishi Rasayan); 'Parryfen' (Parry); 'Shamiethrin' (Zhong-Xi); 'Stalker' (Indofil); 'Tribute' (Bayer CropScience); 'Triumphcard' (Dhanuka) mixtures: 'Vegehon' (+ dimethoate) (Sumitomo); 'Bifentox' (+ dimethoate) (Vipesco); 'Fenikill' (+ fenitrothion) (Vapco); 'Koranda' (+ acephate) (Rallis); 'Miejingthrin' (+ propargite) (Zhong-Xi); 'Pre Ling' (+ phoxim) (Zhong-Xi); 'Vifensu' (+ fenitrothion) (Vipesco) Discontinued products: 'Belmark' * (Cyanamid); 'Cekufenvalerato' * (Cequisa); 'Pydrin' * (DuPont)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis of pyrethroids reviewed by E. Papadopoulou-Mourkidou in Comp. Analyt. Profiles. By hplc (idem, ibid.; E. Papadopoulou-Mourkidou, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1988, 16, 31; 1984, 13, 121) or by glc (CIPAC Handbook, 1988, D, 100; ibid., 1995, G, 68-70). Residues determined by glc with ECD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 998.01; A. Ambrus et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1981, 64, 733; Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, 6, S19; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M11). Details available from Sumitomo Chemical Co.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 47 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). See also A. J. Gray & D. M. Soderlund, Chapt. 5 in "Insecticides". IARC ref. 53 class 3 Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 451 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits 1000-3200, rats >5000 mg/kg. Slightly irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 for rats >101 mg/m3. NOEL (2 y) for rats 250 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.02 mg/kg b.w. [1986]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for domestic fowl >1600, mallard ducks 9932 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 for quail >10 000, mallard ducks 5500 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.0036 mg/l. Bees Toxic to bees. Contact LD50 0.23 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 95 (WHO, 1990). EHC 95 cites rapid degradation and decomposition, reduced toxicity of its degradation products, and absence of leaching in soil. Although laboratory tests show high toxicity for fish and bees, these effects are markedly reduced under field conditions because of adsorption to sediments, and the compound's strong repellent effect. The report concludes that risks to the environment are unlikely when it is applied as recommended. Animals In mammals, following oral administration, fenvalerate is rapidly metabolised. Up to 96% is excreted in the faeces within 6-14 days. For a study of the metabolism of fenvalerate in the laying hen, see J. Agric. Food Chem., 1989, 37, 190. Plants In plants, fenvalerate is split into two parts by cleavage of the ether group, followed by further hydroxylation in the 2- and 4- positions of the phenoxy ring, and hydrolysis of the nitrile group to amide and carboxyl groups. The majority of the acids and phenols thus formed are converted into glucosides. Soil/Environment In aqueous media, the ester bond is hydrolysed. In light, decarboxylation occurs, with recombination of the cleaved moieties (R. L. Holmstead et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1977, 25, 56-58). DT50 in soil c. 75-80 d.
|