|
fentrazamide
Herbicide
HRAC K3 WSSA 15; tetrazolinone
NOMENCLATURE
Common name fentrazamide (BSI; pa ISO)
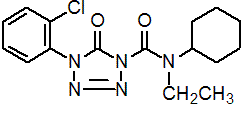
IUPAC name 4-(2-chlorophenyl)-N-cyclohexyl-N-ethyl-4,5-dihydro-5-oxo-1H-tetrazole-1-carboxamide
Chemical Abstracts name 4-(2-chlorophenyl)-N-cyclohexyl-N-ethyl-4,5-dihydro-5-oxo-1H-tetrazole-1-carboxamide
CAS RN [158237-07-1] Development codes YRC 2388; BAY YRC 2388 (Bayer); NBA 061
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 349.8 M.f. C16H20ClN5O2 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 79 °C V.p. 5 ´ 10-5 mPa (20 °C) KOW logP = 3.60 (20 °C) Henry 7 ´ 10-6 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.30 (20 °C) Solubility In water 2.3 mg/l (20 °C). In n-heptane 2.1, isopropanol 32, dichloromethane and xylene >250 (all in g/l, 20 °C). Stability DT50 (pH 5) >300 d, (pH 7) >500 d, (pH 9) c. 70 d (all 25 °C). In pure water, photolysis DT50 c. 20 d; in natural water, c. 10 d (both 25 °C).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Discovered by Nihon Bayer Agrochem K.K. in 1992 and reported by L. Yasui et al. (Proc. 1997 Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1, 67). Developed by Bayer AG. Manufacturers Bayer CropScience
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cell division inhibitor. Primary target site may be in fatty acid metabolism. Basis of selectivity is positional; fentrazamide is adsorbed to the surface soil layer and is not touched by the growing point of transplanted rice seedlings. Mode of action Inhibits cell division in root and meristem, causing cessation of growth and distortion of elongated tissue. Uses Control of barnyardgrass (Echinochloa spp.) and annual sedges, from weed pre-emergence up to 3-leaf stage, in rice. Can also be applied at transplanting stage. Formulation types GF; GR; SC; WG. Selected products: 'Lecs' (Bayer CropScience); mixtures: 'Innova GR 75' (+ bensulfuron-methyl) (Nihon Bayer); 'Lecspro' (+ propanil) (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Bai Tian Jing' (Bayer CropScience); 'Dongsimae' (Bayer CropScience) mixtures: 'Agalia' (+ cyclosulfamuron+ daimuron) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Bigsure' (+ cyclosulfamuron+ daimuron) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Donichi' (+ imazosulfuron+ daimuron) (Bayer CropScience, Sumitomo Chemical Takeda, SDS Biotech KK); 'Doublestar' (+ pyrazosulfuron-ethyl) (Bayer CropScience); 'Inebrite' (+ azimsulfuron+ bensulfuron-methyl) (Bayer CropScience); 'Innova GR 51' (+ bensulfuron-methyl+ daimuron) (Nihon Bayer); 'Innova L SC' (+ bensulfuron-methyl+ daimuron) (Nihon Bayer); 'Innova SC' (+ bensulfuron-methyl) (Nihon Bayer); 'Leading' (+ imazosulfuron) (Nihon Bayer); 'Naegamae' (+ cyclosulfamuron) (Misung); 'Smart' (+ benzobicyclon+ benzofenap) (SDS Biotech KK, Bayer CropScience)
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Not an eye or skin irritant (rabbits); not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 for rats >5000 mg/m3. NOEL For rats 10.3, mice 28.0, dogs 0.52 mg/kg b.w. ADI 0.005 mg/kg b.w. (Japan). Other Not mutagenic or teratogenic.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 (14 d) for Japanese quail and bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for carp 3.2, rainbow trout 3.4 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (24 h) >10 mg/l. Algae EpC50 (72 h) for green algae 6.04 mg/l; no long-term impact on algae, quick recovery. Other aquatic spp. LC50 (96 h) for freshwater shrimps 6.5, Corbicula mussels >100 mg/l. Bees LD50 (topical) for honeybees >150 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida >1000 mg/kg dry substrate. Other beneficial spp. NOEC for silkworms 100 ppm.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals The main pathway of biotransformation proceeded via hydrolytic cleavage of the parent compound. Plants Metabolism was investigated in rice plants under paddy conditions; no parent compound was detected in any plant fraction. Soil/Environment Under paddy soil conditions, fentrazamide was rapidly eliminated from the water phase and thoroughly degraded and mineralised in the submerged soils. In field and laboratory trials under paddy conditions, the calculated half-lives were in the range of a few days and several weeks, respy. Based on Koc values, fentrazamide can be classified as immobile.
|