|
fenpiclonil
Fungicide
FRAC 12, E2; phenylpyrrole
NOMENCLATURE
Common name fenpiclonil (BSI, draft E-ISO)
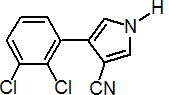
IUPAC name 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)pyrrole-3-carbonitrile
Chemical Abstracts name 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile
CAS RN [74738-17-3] Development codes CGA 142 705 (Ciba-Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 237.1 M.f. C11H6Cl2N2 Form White crystals. M.p. 144.9-151.1 ºC V.p. 1.1 ´ 10-2 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 3.86 (25 ºC) Henry 5.4 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.53 (20 °C) Solubility In water 4.8 mg/l (25 ºC). In ethanol 73, acetone 360, toluene 7.2, n-hexane 0.026, n-octanol 41 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Not hydrolysed after 6 h at 100 ºC between pH 3 and 9. Stable up to 250 ºC.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by D. Nevill et al. (Proc. 1988 Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1, 65). Introduced in Switzerland (1988) by Ciba-Geigy AG (now Syngenta AG). Patents EP 236272
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits MAP kinase, in osmotic signal transduction. Mode of action Slightly systemic, contact fungicide with long-lasting activity. Uses Effective against seed-borne pathogens of cereals, especially Fusarium nivale and Tilletia caries. On non-cereal crops, controls a wide range of seed- and soil-borne fungi (Alternaria, Ascochyta, Aspergillus, Fusarium, Helminthosporium, Rhizoctonia and Penicillium spp.). Having a different mode of action, fenpiclonil gives good control of all isolates of F. nivale, including those resistant to carbendazim and related fungicides. On cereals and peas, used at 20 g/100 kg seed; on potatoes, at 20-50 g/t (depending on target pathogens). Formulation types DS; FS; WS. Selected products: 'Beret' (Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Discontinued products: 'Electer' * (Novartis); 'Galbas' * (Novartis); 'Gambit' * (Novartis) mixtures: 'Larin' * (+ imazalil+ tebuconazole) (seed treatment, Germany) (Syngenta); 'Arena' * (+ tebuconazole) (seed treatment, Germany) (Bayer)
ANALYSIS
Residue determination by hplc. Details available from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats, mice, and rabbits >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to eyes and skin (rabbits); non-sensitising (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >1.5 mg/l air. NOEL for rats 1.25, mice 20, dogs 100 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.0125 mg/kg b.w. Other Non-teratogenic and non-mutagenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2510 mg/kg. LC50 for mallard ducks >5620, bobwhite quail 3976 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.8, carp 1.2, bluegill sunfish 0.76, catfish 1.3 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 1.3 mg/l. Algae LC50 (5 d) for Scenedesmus subspicatus 0.22 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to honeybees; LD50 (oral and contact) >5 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida 67 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. Harmless to carabid beetles.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract into the general circulation; rapidly excreted and almost completely eliminated, mostly in the faeces. The dominant metabolic pathway is oxidation of the pyrrole ring at the 2-position. A minor pathway is hydroxylation of the phenyl ring. All metabolites are excreted as conjugates, mainly as glucuronides. Plants Degradation proceeds via oxidation of the pyrrole ring followed by hydrolysis of the nitrile group. Opening of the pyrrole ring and hydroxylation of the phenyl ring are further degradation steps. The parent is, however, the relevant residue; between 13-15 minor metabolites were also observed. Soil/Environment Relatively persistent in soil; formation of bound residues represents the major route for dissipation. In leaching and adsorption/desorption experiments, the compound proved to be immobile in soil, RMF 0.3. Photolytic DT50 in water 70 min.
|