|
fenoxycarb
Insecticide
IRAC 7B; juvenile hormone mimic
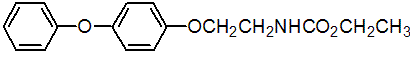
NOMENCLATURE
Common name fenoxycarb (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO, ANSI)
IUPAC name ethyl 2-(4-phenoxyphenoxy)ethylcarbamate
Chemical Abstracts name ethyl [2-(4-phenoxyphenoxy)ethyl]carbamate
CAS RN [72490-01-8]; formerly [79127-80-3] EEC no. 276-696-7 Development codes Ro 135223 (Dr Maag); NRK 121 (Nippon Kayaku); CGA 114597 (Ciba-Geigy) Official codes OMS 3010
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 301.3 M.f. C17H19NO4 Form Colourless to white crystals. M.p. 53-54 ºC (OECD 102) V.p. 8.67 ´ 10-4 mPa (25 ºC) (OECD 104) KOW logP = 4.07 (25 ºC) (OECD 107) Henry 3.3 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.23 (20 ºC) (OECD 109) Solubility In water 7.9 mg/l (pH 7.55-7.84, 25 ºC). In ethanol 510, acetone 770, toluene 630, n-hexane 5.3, n-octanol 130 (all in g/l). Stability Stable to light. Stable to hydrolysis in aqueous solutions at pH 3, 7, and 9 at 50 ºC. F.p. c. 224 ºC
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by S. Dorn et al. (Z. Pflanzenkr. Pflanzenschutz, 1981, 88, 269). Introduced by R. Maag Ltd (now Syngenta AG) and first marketed in 1985. Patents EP 4334; US 4215139 to Roche Manufacturers Sannong; Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibitor of juvenile hormone-specific esterases. Mode of action Non-neurotoxic insect growth regulator with contact and stomach action. Exhibits a strong juvenile hormone activity, inhibiting metamorphosis to the adult stage and interfering with the moulting of early instar larvae. Uses Control of Lepidoptera, scale insects, and suckers on fruit (including citrus), cotton, olives, vines and ornamentals; Coleoptera and Lepidoptera in stored products; and also cockroaches, fleas, mosquito larvae and fire ants in public health situations. Phytotoxicity Some varieties of pears, vines, citrus fruit and ornamentals may be injured. Formulation types EC; RB; WG; WP. Selected products: 'Insegar' (Syngenta); mixtures: 'Dicare' (+ diafenthiuron) (Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Comply' (Syngenta); 'Eclipse' (Syngenta); 'Logic' (Syngenta); 'Precision' (Syngenta); 'Torus' (Syngenta) mixtures: 'Lufox' (+ lufenuron) (Syngenta) Discontinued products: 'Pictyl' * (Dr Maag)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc. Residues determined by glc or preferably by hplc (R. Haenni & P. E. Muller, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1988, 16, 21).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >10 000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg (occlusive). Non-irritating and non-sensitising to skin (maximisation test); not an eye irritant. Inhalation LC50 for rats >4400 mg/m3 air. NOEL (18 mo) for mice 5.5 mg/kg b.w.; (2 y) for rats 8 mg/kg b.w. ADI 0.055 mg/kg b.w. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (company classification) EC classification N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail >7000 mg/kg. LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail >25 000 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for carp 10.3, rainbow trout 1.6 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.4 mg/l. Algae EC50 (96 h) for Scenedesmus subspicatus 1.10 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to bees; oral LC50 (24 h) >1000 ppm. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms 850 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. Under field conditions, fenoxycarb (formulated as 'Insegar 25 WP') is safe to predators such as Phytoseiidae, to endoparasitic Hymenoptera species, to certain predators such as predatory bugs, and it is semi-selective on certain predators such as coccinellids.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 64 (WHO, 1986; a review of carbamate insecticides in general). Animals In rats, the major metabolic path is ring hydroxylation to form ethyl [2-[p-(p-hydroxyphenoxy)phenoxy]ethyl]carbamate. Plants Rapidly degraded in plants. Soil/Environment Low mobility in soil, no bioaccumulation. Relatively fast degradation in soil and water: DT50 1.7-2.5 months (lab.), few to 31 days (field).
|